
The addition of hydrogen halides to unsymmetrical alkenes takes place according to
(A) markovnikov's rule
(B) kharasch effect
(C) peroxide effect
(D) none of these
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: The addition of hydrogen halides is called hydrohalogenation. It can occur in both symmetrical and asymmetrical alkenes and results in bond breakage of alkenes. A carbocation is formed during the process which can rearrange itself to become more stable.
Complete step by step solution:
-Alkenes are more reactive than alkynes except for the case of conjugated alkenes and/or alkynes. They undergo electrophilic addition reactions. Electrophiles attack the carbon and remove the double bond from it.
-The electrophiles always break the bond and attach to the carbon chain at the end. The bond breakage results in 1 more vacancy and this leads to the formation of a carbocation. The carbocation then attacks the nucleophile and forms compounds which do not have any degree of saturation.
-When halogen halides react with alkenes, the carbon attacks the hydrogen of the halogen halide due to its more electronegativity and hydrogen attaches to the carbon chain forming a carbocation. This carbocation then attacks the halide and in this way the product is formed.
-In case of unsymmetrical alkenes, markovnikov's rule is applied. According to this rule, the positive part of the reagent attaches to that carbon which has more number of hydrogen atoms in it. The negative part of the reagent attaches to that carbon which has less number of hydrogen atoms in it. It can be shown as

-So the addition of hydrogen halide is according to markovnikov's rule. Hydrogen attaches to the carbon with more number of hydrogen atoms first and carbocation is formed. It rearranges itself to gain stability and then the halide attaches itself to the carbocation. This way the reaction gets complete.
-Rate of the reaction is directly proportional to the stability of the carbocation formed during the reaction. An example of the above reaction by markovnikov's rule can be shown as
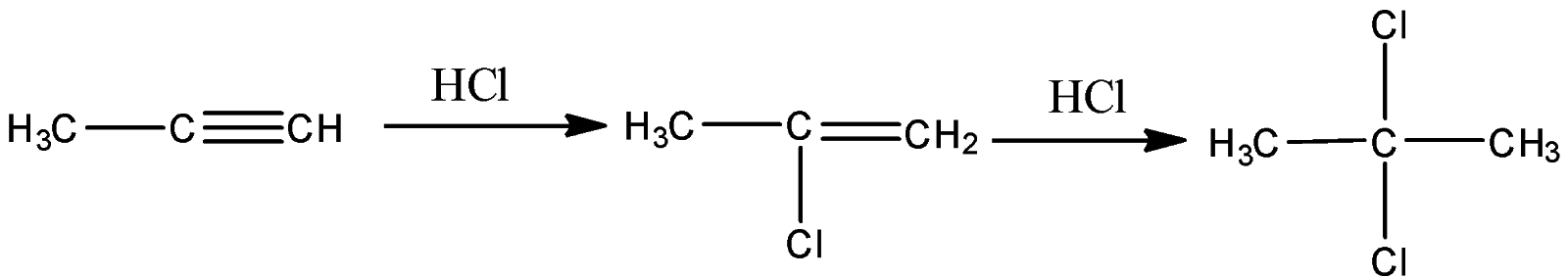
Thus the correct option is (A).
Note: Halogenation is different from hydrohalogenation. In the former, the halogen gas is added to the compound and in the form of its molecule with the formula ${{X}_{2}}$ where X represents the halogens. In the latter, HX gas is added to the compound after the completion of the reaction where X is the single atom of halogen.
Complete step by step solution:
-Alkenes are more reactive than alkynes except for the case of conjugated alkenes and/or alkynes. They undergo electrophilic addition reactions. Electrophiles attack the carbon and remove the double bond from it.
-The electrophiles always break the bond and attach to the carbon chain at the end. The bond breakage results in 1 more vacancy and this leads to the formation of a carbocation. The carbocation then attacks the nucleophile and forms compounds which do not have any degree of saturation.
-When halogen halides react with alkenes, the carbon attacks the hydrogen of the halogen halide due to its more electronegativity and hydrogen attaches to the carbon chain forming a carbocation. This carbocation then attacks the halide and in this way the product is formed.
-In case of unsymmetrical alkenes, markovnikov's rule is applied. According to this rule, the positive part of the reagent attaches to that carbon which has more number of hydrogen atoms in it. The negative part of the reagent attaches to that carbon which has less number of hydrogen atoms in it. It can be shown as

-So the addition of hydrogen halide is according to markovnikov's rule. Hydrogen attaches to the carbon with more number of hydrogen atoms first and carbocation is formed. It rearranges itself to gain stability and then the halide attaches itself to the carbocation. This way the reaction gets complete.
-Rate of the reaction is directly proportional to the stability of the carbocation formed during the reaction. An example of the above reaction by markovnikov's rule can be shown as

Thus the correct option is (A).
Note: Halogenation is different from hydrohalogenation. In the former, the halogen gas is added to the compound and in the form of its molecule with the formula ${{X}_{2}}$ where X represents the halogens. In the latter, HX gas is added to the compound after the completion of the reaction where X is the single atom of halogen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




