
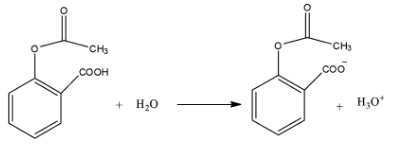
The active ingredient in aspirin is acetyl salicylic acid with\[{{K}_{a}}=\text{ }4.0\times {{10}^{-9}}\] . The pH of the solution obtained by dissolving two aspirin tablets (contain 0.36 g of acetyl salicylic acid in each tablet) in 250 ml of water is (log 2=0.3).

Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint: There is a formula to calculate the pH of the solution by using concentration of the solution.
\[pH=-\log ({{H}^{+}})\]
In the above formula the concentration of the hydrogen ion can be calculated as follows.
\[{{H}^{+}}=\alpha C\]
Here $\alpha $ = degree of dissociation
C = concentration of the solution
The degree of the dissociation can be calculated as follows.
\[\alpha =\sqrt{\dfrac{{{K}_{a}}}{C}}\]
Here ${{K}_{a}}$ = acid dissociation constant
Complete step-by-step answer:- In the question it is asked to find the pH of the solution by using the given data in the question.
- Initially we have to calculate the concentration of the acetyl salicylic acid by using the given data.
- The concentration of the acetyl salicylic acid is 0.36 g and the given volume is 0.52 L.
- The number of moles of the acetyl salicylic acid is = $\dfrac{0.36}{180}=0.002$
Here 180 = molecular weight of the acetyl salicylic acid.
- Now we can calculate the concentration of the acetyl salicylic acid from the number of moles.
- Concentration of the acid = $\dfrac{0.002}{0.25}=0.008$
- Now we can calculate the degree of dissociation of acetyl salicylic acid by using the below formula.
\[\alpha =\sqrt{\dfrac{{{K}_{a}}}{C}}\]
Here ${{K}_{a}}=\text{ }4.0\times {{10}^{-9}}$.
\[
\alpha =\sqrt{\dfrac{{{K}_{a}}}{C}} \\
\Rightarrow \alpha =\sqrt{\dfrac{4\times {{10}^{-9}}}{0.008}}=7.07\times {{10}^{-4}} \\
\]
- Now from the degree of dissociation constant we can calculate the hydrogen ion concentration and it is as follows.
\[
{{H}^{+}}=\alpha C \\
\Rightarrow {{H}^{+}}=0.008\times 7.07\times {{10}^{-4}} \\
\Rightarrow {{H}^{+}}=5.65\times {{10}^{-6}} \\
\]
- By substituting the hydrogen ion concentration in the formula to get the pH of the solution.
\[
pH=-\log ({{H}^{+}}) \\
\Rightarrow pH=-\log (5.65\times {{10}^{-6}}) \\
\Rightarrow pH=-0.7525+6 \\
\Rightarrow pH=5.25 \\
\]
- Therefore the pH of the solution is 5.25.
Note:We are supposed to go step by step. First we have to calculate the number of moles of the acid, next we have to calculate the concentration of the acid, next we have to calculate the degree of dissociation, next we have to calculate the hydrogen ion concentration and at last we are supposed to calculate the pH of the solution.
\[pH=-\log ({{H}^{+}})\]
In the above formula the concentration of the hydrogen ion can be calculated as follows.
\[{{H}^{+}}=\alpha C\]
Here $\alpha $ = degree of dissociation
C = concentration of the solution
The degree of the dissociation can be calculated as follows.
\[\alpha =\sqrt{\dfrac{{{K}_{a}}}{C}}\]
Here ${{K}_{a}}$ = acid dissociation constant
Complete step-by-step answer:- In the question it is asked to find the pH of the solution by using the given data in the question.
- Initially we have to calculate the concentration of the acetyl salicylic acid by using the given data.
- The concentration of the acetyl salicylic acid is 0.36 g and the given volume is 0.52 L.
- The number of moles of the acetyl salicylic acid is = $\dfrac{0.36}{180}=0.002$
Here 180 = molecular weight of the acetyl salicylic acid.
- Now we can calculate the concentration of the acetyl salicylic acid from the number of moles.
- Concentration of the acid = $\dfrac{0.002}{0.25}=0.008$
- Now we can calculate the degree of dissociation of acetyl salicylic acid by using the below formula.
\[\alpha =\sqrt{\dfrac{{{K}_{a}}}{C}}\]
Here ${{K}_{a}}=\text{ }4.0\times {{10}^{-9}}$.
\[
\alpha =\sqrt{\dfrac{{{K}_{a}}}{C}} \\
\Rightarrow \alpha =\sqrt{\dfrac{4\times {{10}^{-9}}}{0.008}}=7.07\times {{10}^{-4}} \\
\]
- Now from the degree of dissociation constant we can calculate the hydrogen ion concentration and it is as follows.
\[
{{H}^{+}}=\alpha C \\
\Rightarrow {{H}^{+}}=0.008\times 7.07\times {{10}^{-4}} \\
\Rightarrow {{H}^{+}}=5.65\times {{10}^{-6}} \\
\]
- By substituting the hydrogen ion concentration in the formula to get the pH of the solution.
\[
pH=-\log ({{H}^{+}}) \\
\Rightarrow pH=-\log (5.65\times {{10}^{-6}}) \\
\Rightarrow pH=-0.7525+6 \\
\Rightarrow pH=5.25 \\
\]
- Therefore the pH of the solution is 5.25.
Note:We are supposed to go step by step. First we have to calculate the number of moles of the acid, next we have to calculate the concentration of the acid, next we have to calculate the degree of dissociation, next we have to calculate the hydrogen ion concentration and at last we are supposed to calculate the pH of the solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




