
The absolute configuration of the given compound is:
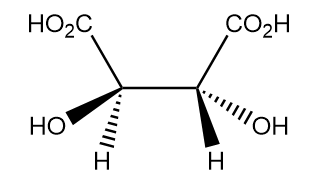
a. R, S
b. S, R
c. S, S
d. R, R

Answer
512.1k+ views
Hint : The spatial arrangement of atoms of a chiral molecule describing its stereochemical properties i.e., Rectus (R) or sinister (S) is known as absolute configuration of an organic compound. The compounds which differ in the absolute configuration of carbon atoms are referred to as enantiomers.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The RS absolute configuration is an important nomenclature for denoting enantiomers and is determined by CIP priority rules which states that the groups attached with the chiral centre must be given priority according to increasing atomic number i.e., the group which consist of an atom with greater atomic number will be given first priority.
After assigning priorities, on moving from first towards second via fourth group if the arrow is heading in clockwise direction then the configuration is R while if the arrow is heading in anticlockwise direction, then the configuration is S.
Let us check the allocation of priorities and absolute configuration of each chiral centre separately for the given compound.
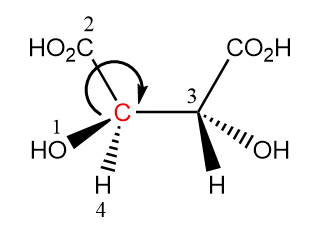
As the arrow moves in the clockwise direction on moving from the first priority group towards second. So, the configuration is R for considered chiral carbon.
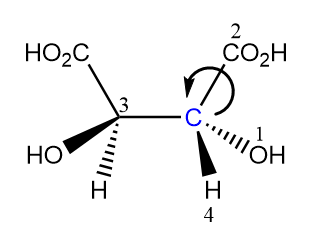
The arrow moves in the anticlockwise direction on moving from first priority group towards second that means the configuration must be S but the group with fourth priority is present above the plane. So, the configuration will be inverted and will be R for considered chiral carbon.
Hence, the absolute configuration of the given compound is R, R. Thus, option (D) is the correct answer.
Note :
While finding the absolute configuration of a chiral molecule, make sure that the least priority group must always present below the plane. If it is not present below the plane, then the rotation of the molecule takes place due to which the configuration of the molecule also gets inverted. Always remember that if there are odd numbers of rotations, then only inversion of configuration will be observed.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The RS absolute configuration is an important nomenclature for denoting enantiomers and is determined by CIP priority rules which states that the groups attached with the chiral centre must be given priority according to increasing atomic number i.e., the group which consist of an atom with greater atomic number will be given first priority.
After assigning priorities, on moving from first towards second via fourth group if the arrow is heading in clockwise direction then the configuration is R while if the arrow is heading in anticlockwise direction, then the configuration is S.
Let us check the allocation of priorities and absolute configuration of each chiral centre separately for the given compound.

As the arrow moves in the clockwise direction on moving from the first priority group towards second. So, the configuration is R for considered chiral carbon.

The arrow moves in the anticlockwise direction on moving from first priority group towards second that means the configuration must be S but the group with fourth priority is present above the plane. So, the configuration will be inverted and will be R for considered chiral carbon.
Hence, the absolute configuration of the given compound is R, R. Thus, option (D) is the correct answer.
Note :
While finding the absolute configuration of a chiral molecule, make sure that the least priority group must always present below the plane. If it is not present below the plane, then the rotation of the molecule takes place due to which the configuration of the molecule also gets inverted. Always remember that if there are odd numbers of rotations, then only inversion of configuration will be observed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




