
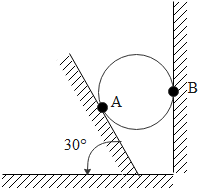
The 50 kg homogeneous smooth sphere rests on the ${30^ \circ }$ incline A and bears against the smooth vertical wall B. The contact force at B is ($g = 10\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}$)
\[\begin{array}{l}
A.\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;250N\\
B.\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;0N\\
C.\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\dfrac{{\;500}}{{\sqrt 3 }}N\\
D.\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;250N
\end{array}\]

Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this problem, first we need to draw a free body diagram which will show us the various forces acting on the system. Then comparing the directions of various forces, we can obtain the equations of motion for the system. By solving these equations, we may obtain the contact force.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first draw a free body diagram of the ball which involves two normal forces at A & B. These forces are perpendicular to walls from which they are applied and also to the gravitational force. Their magnitude is given to be equal to $50 \times 10 = 500N$ (where the gravitational force is equal to the product of the mass of the ball and the acceleration due to gravity.)
Let us call the normal from wall A to be ${N_A}$ and the normal from wall B to be ${N_B}$. Now by doing some simple calculations, we can find out the angle between the vertical and ${N_A}$ which is equal to the angle made by incline & floor which is equal to ${30^ \circ }$
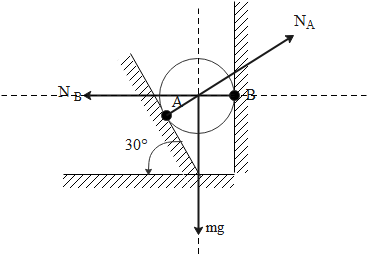
Now, we can resolve ${N_A}$ into its horizontal & vertical components which are given to be ${N_A}\cos {30^ \circ }$ & ${N_A}\sin {30^ \circ }$ which is equal to $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 {N_A}}}{2}$ & $\dfrac{{{N_A}}}{2}$ respectively.
Since the sphere is in equilibrium forces along vertical & horizontal should be balanced. On equating them we get
$mg = {N_A}\cos {30^ \circ }$
$\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 {N_A}}}{2} = 500$ … (1)
${N_B} = {N_A}\sin {30^ \circ }$
${N_B} = \dfrac{{{N_A}}}{2}$ … (2)
Putting value of ${N_A}$ from equation 1
${N_B} = \dfrac{{2 \times 500}}{{\sqrt 3 \times 2}} = \dfrac{{500}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$ N
Hence the correct option is C.
Note: Students often make mistakes while taking angle between components of force. The angle should be calculated carefully. Also, it must be remembered that normal always acts perpendicular to surface and point of contact. Hence in the case of a sphere it always passes from the center.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first draw a free body diagram of the ball which involves two normal forces at A & B. These forces are perpendicular to walls from which they are applied and also to the gravitational force. Their magnitude is given to be equal to $50 \times 10 = 500N$ (where the gravitational force is equal to the product of the mass of the ball and the acceleration due to gravity.)
Let us call the normal from wall A to be ${N_A}$ and the normal from wall B to be ${N_B}$. Now by doing some simple calculations, we can find out the angle between the vertical and ${N_A}$ which is equal to the angle made by incline & floor which is equal to ${30^ \circ }$

Now, we can resolve ${N_A}$ into its horizontal & vertical components which are given to be ${N_A}\cos {30^ \circ }$ & ${N_A}\sin {30^ \circ }$ which is equal to $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 {N_A}}}{2}$ & $\dfrac{{{N_A}}}{2}$ respectively.
Since the sphere is in equilibrium forces along vertical & horizontal should be balanced. On equating them we get
$mg = {N_A}\cos {30^ \circ }$
$\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 {N_A}}}{2} = 500$ … (1)
${N_B} = {N_A}\sin {30^ \circ }$
${N_B} = \dfrac{{{N_A}}}{2}$ … (2)
Putting value of ${N_A}$ from equation 1
${N_B} = \dfrac{{2 \times 500}}{{\sqrt 3 \times 2}} = \dfrac{{500}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$ N
Hence the correct option is C.
Note: Students often make mistakes while taking angle between components of force. The angle should be calculated carefully. Also, it must be remembered that normal always acts perpendicular to surface and point of contact. Hence in the case of a sphere it always passes from the center.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




