
Why is tertiary carbocation more stable than secondary?
Answer
516k+ views
Hint: Carbocations are the species in which the carbon atom attains a positive charge. It is an electron deficient species and its structure is planar. Carbocations are generally of three types which are: Primary carbocation $({1^o})$ , secondary carbocation $({2^o})$ and the tertiary carbocation $({3^o})$ . We will now discuss their stability.
Complete answer:
Carbocation is a species which has a positive charge on the carbon atom and is electron-deficient in nature. So, if we compare the tertiary carbocation and secondary carbocation.
So, there are two criteria for the stability of carbocations, one is the inductive effect and the second one is the hyperconjugation effect.
Inductive effect $( + I)$ : The tendency of some compounds to donate their electron tendency is known as inductive effect. For example: Alkyl groups have positive inductive effects $( + I)$ .
So, in tertiary carbocations, three alkyl groups are present which applies the $ + I$effect while in secondary carbocation there are only two alkyl groups.
Thus, according to the inductive effect, tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary carbocation.
Hyperconjugation effect: Hyperconjugation refers to the delocalization of electrons with the by participation of sigma bonds. It is also known as sigma bond resonance.
More the hyperconjugation, more will be the stability of carbocation.
Now, let us see hyperconjugation in tertiary carbocation:
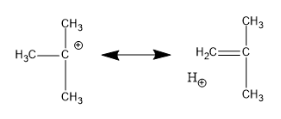
Following this type of sigma bond resonance, there can be a total of nine structures.
Now, hyperconjugation for secondary carbocation:
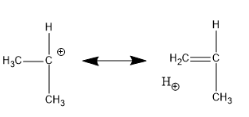
Hence, in secondary carbocation, there are only six hyperconjugation structures.
So, we can say that tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary carbocation.
Note:
We should remember that the tertiary carbocations are those in which three alkyl groups are present on carbocation and in secondary, two alkyl groups are present on carbocation. And primary carbocation is in which only one alkyl group is attached to the carbocation. There is one more type of carbocation which is methyl carbocation in which there is no alkyl group attached to carbocation.
Complete answer:
Carbocation is a species which has a positive charge on the carbon atom and is electron-deficient in nature. So, if we compare the tertiary carbocation and secondary carbocation.
So, there are two criteria for the stability of carbocations, one is the inductive effect and the second one is the hyperconjugation effect.
Inductive effect $( + I)$ : The tendency of some compounds to donate their electron tendency is known as inductive effect. For example: Alkyl groups have positive inductive effects $( + I)$ .
So, in tertiary carbocations, three alkyl groups are present which applies the $ + I$effect while in secondary carbocation there are only two alkyl groups.
Thus, according to the inductive effect, tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary carbocation.
Hyperconjugation effect: Hyperconjugation refers to the delocalization of electrons with the by participation of sigma bonds. It is also known as sigma bond resonance.
More the hyperconjugation, more will be the stability of carbocation.
Now, let us see hyperconjugation in tertiary carbocation:

Following this type of sigma bond resonance, there can be a total of nine structures.
Now, hyperconjugation for secondary carbocation:

Hence, in secondary carbocation, there are only six hyperconjugation structures.
So, we can say that tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary carbocation.
Note:
We should remember that the tertiary carbocations are those in which three alkyl groups are present on carbocation and in secondary, two alkyl groups are present on carbocation. And primary carbocation is in which only one alkyl group is attached to the carbocation. There is one more type of carbocation which is methyl carbocation in which there is no alkyl group attached to carbocation.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE

Explain sex determination in humans with line diag class 12 biology CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE




