
How can you tell e and z isomers apart?
Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint: We can differentiate compounds as E and Z isomers easily just as in case of cis and trans – isomer but difference is that we have to check priorities instead of same substituent. When the higher priorities are on the same side of the double bond, then it is known as Z isomer and if higher priorities are on the opposite side, then it is called E isomer.
Complete step by step answer:
- E and Z isomers are described as follows:-
- E (taken from German word ‘entgegen’ which means opposite) isomers: alkenes are categorized as (E) – alkene if both the high priority groups are on the opposite side of the C=C.
- Z (taken from German word ‘zusammen’ which means together) isomers: alkenes are categorized as (Z) – alkene if both the high priority groups are on the same side of the C=C.
- To check which substituent is of higher priority, Cahn-Ingold-Prelog gave priority rules which are as follows:-
(A) Atoms with higher atomic number are given higher priority.
(B) If the first atom of both substituents is the same then move to the next atom and follow the above step again.
(C) Determine the relative position of both higher priority groups on either side of the double bond.
(D) If high priority groups are on the same side: E- alkene and if high priority groups are on the opposite sides: Z-alkene.
The example is shown below:-
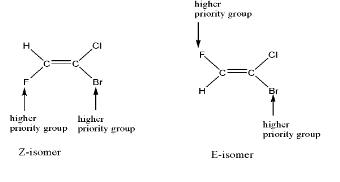
Note:
- There is a minor addition in the priority rule in case of isotopes which have the same atomic number but different atomic masses. We will give higher priority to the group or substituent having greater atomic mass than the other.
- Cis and trans-isomers can only categorize the alkenes which has atleast 2 same substituents on either side of the double bonds but E and Z-isomers are not limited to that.
Complete step by step answer:
- E and Z isomers are described as follows:-
- E (taken from German word ‘entgegen’ which means opposite) isomers: alkenes are categorized as (E) – alkene if both the high priority groups are on the opposite side of the C=C.
- Z (taken from German word ‘zusammen’ which means together) isomers: alkenes are categorized as (Z) – alkene if both the high priority groups are on the same side of the C=C.
- To check which substituent is of higher priority, Cahn-Ingold-Prelog gave priority rules which are as follows:-
(A) Atoms with higher atomic number are given higher priority.
(B) If the first atom of both substituents is the same then move to the next atom and follow the above step again.
(C) Determine the relative position of both higher priority groups on either side of the double bond.
(D) If high priority groups are on the same side: E- alkene and if high priority groups are on the opposite sides: Z-alkene.
The example is shown below:-

Note:
- There is a minor addition in the priority rule in case of isotopes which have the same atomic number but different atomic masses. We will give higher priority to the group or substituent having greater atomic mass than the other.
- Cis and trans-isomers can only categorize the alkenes which has atleast 2 same substituents on either side of the double bonds but E and Z-isomers are not limited to that.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




