
Technically porous wood is _______ wood.
(a) Hard
(b) Soft
(c) Sap
(d) Heart
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: Porous wood is found in deciduous trees mainly that have a complex structure and possess various vessels. This wood has larger pores that form a band or ring along the earlywood zone.
Complete answer:
Technically porous wood is hardwood. They contain vessels which when viewed from the end-grain appear like holes and give the wood a porous appearance. Vessel cells are the largest type of cells and can be viewed individually, sometimes even without magnification, unlike other hardwood cells.
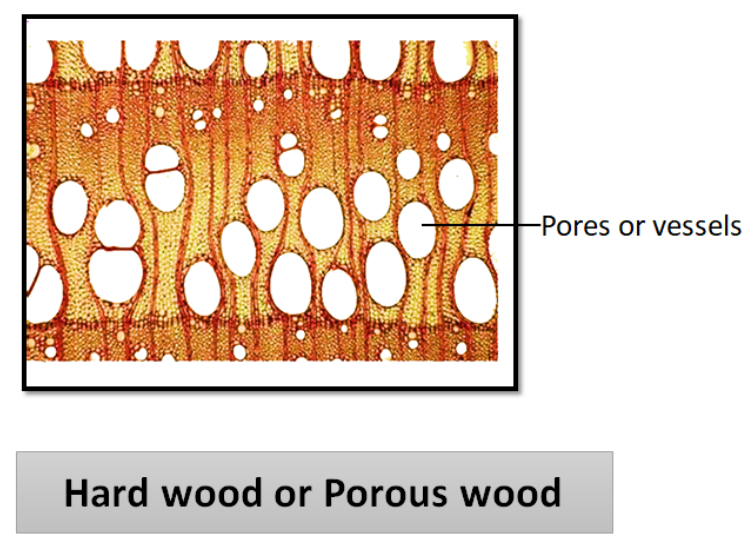
Additional Information:
In hardwood, the axial system is mainly composed of fibers and vessel elements. Vessels are specialized for water conduction. Root hair is abundant in hardwoods, making them more competent, in terms of absorption of water, as compared to other trees in its surroundings.
Hardwood is of three types depending upon its porosity -
> Ring porous - Pores from two to four rows wide, rings or bands, for example - European Ash.
> Diffuse porous - Earlywood and latewood pore size and arrangement is similar, cannot be differentiated, for example - Afzelia.
> Semi ring-porous - Size gradually decreases from earlywood to latewood, but no distinct rows are present, for example - Butternut.
Hardwood is generally found in deciduous trees and broadleaved evergreen trees.
So, the correct answer is ‘Hard’.
Notes:
- Softwood also known as non-porous wood does not have prominent vessels.
- Softwoods have a much more uniform structure than hardwoods and they have no vessels.
- Dendrochronology is the study of the age of the tree depending on the number of annual rings, which comprise the springwood and winter wood.
- Vessels are a characteristic feature of angiosperms and are absent in gymnosperms.
Complete answer:
Technically porous wood is hardwood. They contain vessels which when viewed from the end-grain appear like holes and give the wood a porous appearance. Vessel cells are the largest type of cells and can be viewed individually, sometimes even without magnification, unlike other hardwood cells.

Additional Information:
In hardwood, the axial system is mainly composed of fibers and vessel elements. Vessels are specialized for water conduction. Root hair is abundant in hardwoods, making them more competent, in terms of absorption of water, as compared to other trees in its surroundings.
Hardwood is of three types depending upon its porosity -
> Ring porous - Pores from two to four rows wide, rings or bands, for example - European Ash.
> Diffuse porous - Earlywood and latewood pore size and arrangement is similar, cannot be differentiated, for example - Afzelia.
> Semi ring-porous - Size gradually decreases from earlywood to latewood, but no distinct rows are present, for example - Butternut.
Hardwood is generally found in deciduous trees and broadleaved evergreen trees.
So, the correct answer is ‘Hard’.
Notes:
- Softwood also known as non-porous wood does not have prominent vessels.
- Softwoods have a much more uniform structure than hardwoods and they have no vessels.
- Dendrochronology is the study of the age of the tree depending on the number of annual rings, which comprise the springwood and winter wood.
- Vessels are a characteristic feature of angiosperms and are absent in gymnosperms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




