
Tautomerism is exhibited by:
This question has multiple correct options.
(A) $ {(M{e_3}CCO)_3}CH $
(B)
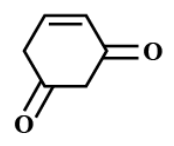
(C)
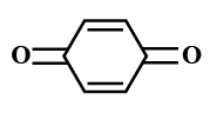
(D)
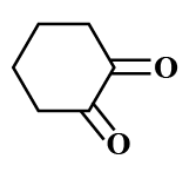



Answer
527.4k+ views
Hint: Tautomers are isomers of a compound which differ only in the position of the protons and electrons. Molecules that exhibit tautomerism have the same molecular formula and they interconvert rapidly.
Complete answer:
Tautomerism is exhibited by those compounds which have $ \alpha - $ hydrogen atoms. The $ \alpha - $ carbon in an organic molecule refers to the first carbon atom that attaches to a functional group, such as a carbonyl group. A hydrogen atom attached to an $ \alpha - $ carbon atom is called an alpha-hydrogen atom. In tautomerism, there is an exchange of a hydrogen atom between two other atoms while forming a covalent bond to either one.
Now, if we look in the above given options, we can see that in option A,
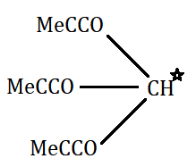
there is one $ \alpha - $ hydrogen atom in $ {(M{e_3}CCO)_3}CH $ . While in option B and option D, there are two $ \alpha - $ hydrogen atoms.
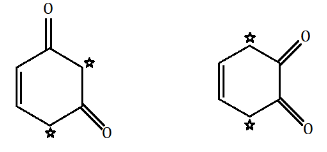
There is no $ \alpha - $ hydrogen atom present in option C.
Hence, tautomerism is exhibited by compounds of option A, option B and option D.
The $ \alpha - $ hydrogen atoms are represented using star marks and they enable the compounds to show keto-enol tautomerism.
To exhibit tautomerism, a compound must contain polar molecules and weak acidic functional groups. Tautomerism provides more stability to a compound. Tautomerism is a reversible process. Some examples of tautomerism are keto-enol, enamine-imine, lactam-lactim configurations etc.
Note:
Tautomerism involves proton transfer in an intramolecular fashion. Tautomerism has no effects on bond length or any such features. Tautomerism generally occurs in planar or non-planar molecules. Students should be careful not to confuse tautomers with depictions of "contributing structures" in chemical resonance. Resonance structures are merely convenient depictions and do not physically exist.
Complete answer:
Tautomerism is exhibited by those compounds which have $ \alpha - $ hydrogen atoms. The $ \alpha - $ carbon in an organic molecule refers to the first carbon atom that attaches to a functional group, such as a carbonyl group. A hydrogen atom attached to an $ \alpha - $ carbon atom is called an alpha-hydrogen atom. In tautomerism, there is an exchange of a hydrogen atom between two other atoms while forming a covalent bond to either one.
Now, if we look in the above given options, we can see that in option A,

there is one $ \alpha - $ hydrogen atom in $ {(M{e_3}CCO)_3}CH $ . While in option B and option D, there are two $ \alpha - $ hydrogen atoms.

There is no $ \alpha - $ hydrogen atom present in option C.
Hence, tautomerism is exhibited by compounds of option A, option B and option D.
The $ \alpha - $ hydrogen atoms are represented using star marks and they enable the compounds to show keto-enol tautomerism.
To exhibit tautomerism, a compound must contain polar molecules and weak acidic functional groups. Tautomerism provides more stability to a compound. Tautomerism is a reversible process. Some examples of tautomerism are keto-enol, enamine-imine, lactam-lactim configurations etc.
Note:
Tautomerism involves proton transfer in an intramolecular fashion. Tautomerism has no effects on bond length or any such features. Tautomerism generally occurs in planar or non-planar molecules. Students should be careful not to confuse tautomers with depictions of "contributing structures" in chemical resonance. Resonance structures are merely convenient depictions and do not physically exist.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




