
Sycon belongs to a group of animals which are best described as
a) Unicellular or acellular
b) Multicellular without any tissue organization
c) Multicellular with a gastrovascular system
d) Multicellular having tissue organization, but nobody cavity
Answer
607.2k+ views
Hint: Sycons are the sponges with the cellular level of body organization with numerous pores on their calceiform body and have canal systems. In Sycon each cell acts independently and shows very little coordination.
Complete answer:
Sycon belongs to phylum-Porifera (cellular sponges) and is the most primitive group of multicellular organisms. They belong to class Calcarea having spicules made of calcium carbonate in the form of calcite. They have a cellular level of organization where the cells do not form tissues and more or less work independently with very little coordination. Thus, Sycons are the multicellular sponges without any tissue organization.
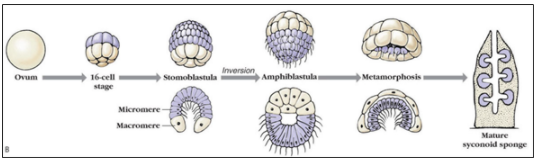
Figure 1: Development of Sycon
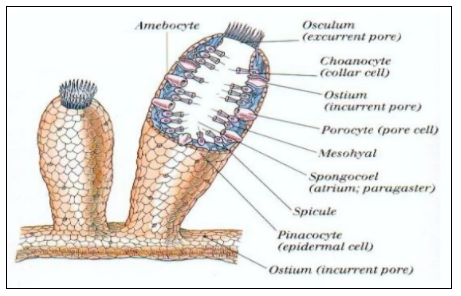
Figure 2: Sycon cellular level of organization
Additional information
1)Though the cellular level of organization in Sycon shows the independent working of each cell with little coordination, there is some division of labor present among the cells, based on which the cells work independently performing only the function assigned to them.
2)Another important feature of Sycon includes the presence of the Canal system, formed from pores on the walls that penetrate into the body forming the water channels and spongocoel (the large central canal).
Therefore the correct answer ‘Multicellular without any tissue organization’.
Note: Sycon is a member of Porifera phylum known as pore bearers as their body is made up of body walls that possess many tiny pores (known as Ostia), giving it a sponge-like look. They exhibit cell aggregate body plan and thus are included in the sub-kingdom of Parazoa.
Complete answer:
Sycon belongs to phylum-Porifera (cellular sponges) and is the most primitive group of multicellular organisms. They belong to class Calcarea having spicules made of calcium carbonate in the form of calcite. They have a cellular level of organization where the cells do not form tissues and more or less work independently with very little coordination. Thus, Sycons are the multicellular sponges without any tissue organization.

Figure 1: Development of Sycon

Figure 2: Sycon cellular level of organization
Additional information
1)Though the cellular level of organization in Sycon shows the independent working of each cell with little coordination, there is some division of labor present among the cells, based on which the cells work independently performing only the function assigned to them.
2)Another important feature of Sycon includes the presence of the Canal system, formed from pores on the walls that penetrate into the body forming the water channels and spongocoel (the large central canal).
Therefore the correct answer ‘Multicellular without any tissue organization’.
Note: Sycon is a member of Porifera phylum known as pore bearers as their body is made up of body walls that possess many tiny pores (known as Ostia), giving it a sponge-like look. They exhibit cell aggregate body plan and thus are included in the sub-kingdom of Parazoa.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




