
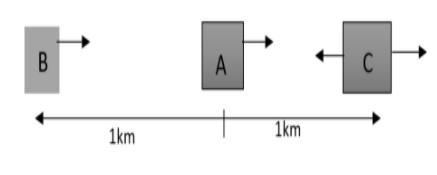
Suppose that on a two lane road, car A is travelling with a speed of $36km{{h}^{-1}}$. This time two cars B and C approach car A in the opposite directions with a speed of $54km{{h}^{-1}}$each. At a specific moment, if the distance AB is equal to AC, both being $1km$, B decides to overtake A before C does. Calculate the minimum acceleration of car B is required to avoid an accident?
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Convert the velocities in terms of metre per second. Find the relative speed of the car A with respect to the car C. calculate the time taken by car C to overtake A. Then the distance travelled by the car A should be found. Use the third equation of motion finally to find the answer. This all will help you in answering this question.
Complete step by step answer:
The speed of the car A has been given as,
${{S}_{A}}=36km{{h}^{-1}}=36\times \dfrac{5}{18}=10m{{s}^{-1}}$
The speed of the car B and car C has been given as,
${{S}_{B}}={{S}_{C}}=54km{{h}^{-1}}=54\times \dfrac{5}{18}=15m{{s}^{-1}}$
The relative speed of A with respect to C will be,
${{S}_{AC}}={{S}_{C}}+{{S}_{A}}=10+15=25m{{s}^{-1}}$
Therefore the time taken by C in order to overtake A is given as,
$t=\dfrac{1000}{25}=40s$
The distance travelled by A all this time can be found as,
${{d}_{A}}=10\times 40=400m$
From this we can understand that car B has to travel a distance which is the sum of the distances covered by A and C.
$\begin{align}
& {{d}_{A}}=400m \\
& {{d}_{C}}=1km=1000m \\
\end{align}$
That is,
${{d}_{B}}=1000+400=1400m$
That is $1400m$ to take over A before C has been done in $40s$. Apply this in the equation of motion,
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Substituting the values in it will give,
$\begin{align}
& 1400=15\times 40+\dfrac{1}{2}a\times {{\left( 40 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 800=a\times 800 \\
\end{align}$
Rearranging the equation gives,
$a=1m{{s}^{-2}}$
Note: The velocity is the time rate of variation of the displacement. Distance covered is the total length of the path traversed by a body. The displacement is the shortest distance between the initial and final points. Time rate of variation of distance is known as speed. Acceleration is the time rate of variation of velocity.
Complete step by step answer:
The speed of the car A has been given as,
${{S}_{A}}=36km{{h}^{-1}}=36\times \dfrac{5}{18}=10m{{s}^{-1}}$
The speed of the car B and car C has been given as,
${{S}_{B}}={{S}_{C}}=54km{{h}^{-1}}=54\times \dfrac{5}{18}=15m{{s}^{-1}}$
The relative speed of A with respect to C will be,
${{S}_{AC}}={{S}_{C}}+{{S}_{A}}=10+15=25m{{s}^{-1}}$
Therefore the time taken by C in order to overtake A is given as,
$t=\dfrac{1000}{25}=40s$
The distance travelled by A all this time can be found as,
${{d}_{A}}=10\times 40=400m$
From this we can understand that car B has to travel a distance which is the sum of the distances covered by A and C.
$\begin{align}
& {{d}_{A}}=400m \\
& {{d}_{C}}=1km=1000m \\
\end{align}$
That is,
${{d}_{B}}=1000+400=1400m$
That is $1400m$ to take over A before C has been done in $40s$. Apply this in the equation of motion,
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Substituting the values in it will give,
$\begin{align}
& 1400=15\times 40+\dfrac{1}{2}a\times {{\left( 40 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 800=a\times 800 \\
\end{align}$
Rearranging the equation gives,
$a=1m{{s}^{-2}}$

Note: The velocity is the time rate of variation of the displacement. Distance covered is the total length of the path traversed by a body. The displacement is the shortest distance between the initial and final points. Time rate of variation of distance is known as speed. Acceleration is the time rate of variation of velocity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 11 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




