
Sum of alpha-hydrogen in $ A+B+C $ is:
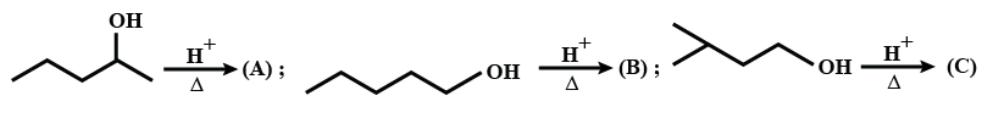
(A) $ 17 $
(B) $ 18 $
(C) $ 19 $
(D) $ 20 $

Answer
528.9k+ views
Hint: We know that the first carbon atom in an organic molecule that attaches to a functional group such as carbonyl is known as the alpha carbon and represented as $ C\alpha . $ The hydrogen atom which is attached to an alpha carbon is called alpha hydrogen and represented as $ H\alpha . $
Complete answer:
The second carbon atom in an organic molecule which attaches to the alpha carbon is known as the beta carbon and represented as $ C\beta . $ The hydrogen atom which is attached to a beta carbon is called beta hydrogen and represented as $ H\beta . $ Let us open and draw the structure given in the question and try identifying the alpha hydrogens and alpha carbons in the molecule;
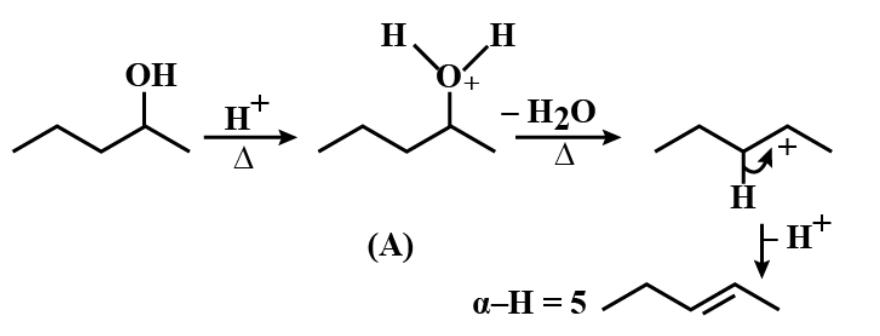
The carbons marked with black stars are the alpha carbons and the hydrogens attached to hybridized alpha carbon which is directly attached to $ s{{p}^{3}} $ the carbocation are called the alpha hydrogens.
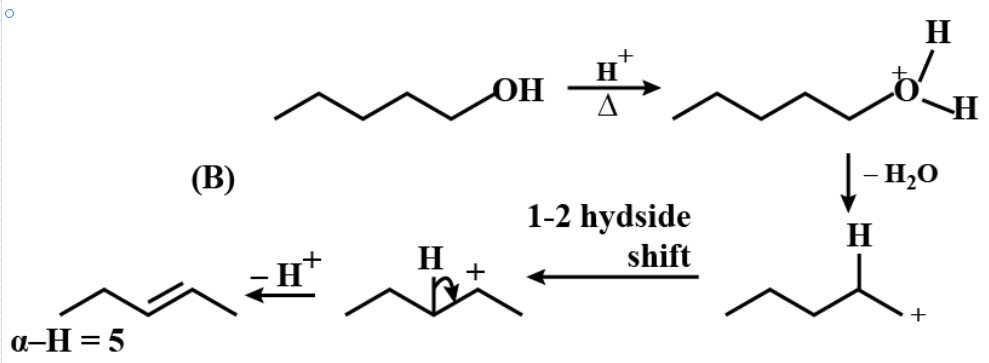
Similarly,
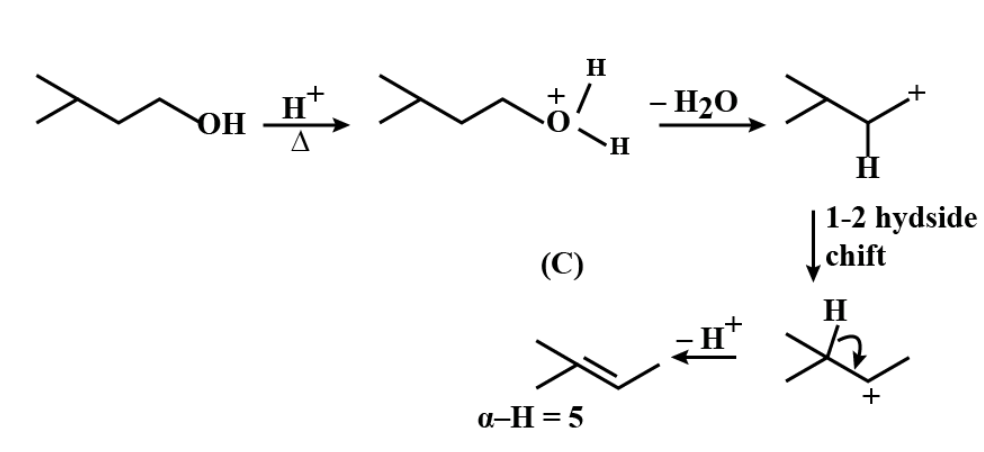
Therefore, Sum of alpha-hydrogen in $ A+B+C $ is $ 19. $
Note:
Remember that due to the acidic nature of alpha hydrogens in aldehydes and ketones, they undergo many reactions. The acidity of alpha hydrogen of ketones or aldehydes is due to the strong electron-withdrawing nature of the carbonyl groups and resonance stabilization of the conjugate base.
Complete answer:
The second carbon atom in an organic molecule which attaches to the alpha carbon is known as the beta carbon and represented as $ C\beta . $ The hydrogen atom which is attached to a beta carbon is called beta hydrogen and represented as $ H\beta . $ Let us open and draw the structure given in the question and try identifying the alpha hydrogens and alpha carbons in the molecule;

The carbons marked with black stars are the alpha carbons and the hydrogens attached to hybridized alpha carbon which is directly attached to $ s{{p}^{3}} $ the carbocation are called the alpha hydrogens.

Similarly,

Therefore, Sum of alpha-hydrogen in $ A+B+C $ is $ 19. $
Note:
Remember that due to the acidic nature of alpha hydrogens in aldehydes and ketones, they undergo many reactions. The acidity of alpha hydrogen of ketones or aldehydes is due to the strong electron-withdrawing nature of the carbonyl groups and resonance stabilization of the conjugate base.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




