
How many sulphur atoms in $N{{a}_{2}}{{S}_{4}}{{O}_{6}}$ have zero oxidation state?
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: The oxidation states of each element can help to find more about its structure. Once the structure is understood we can know our required answer.
Complete step by step solution:
Oxidation state of an atom of any element in a molecule is defined as the charge on that atom when it leaves that particular molecule through heterolytic cleavage. The relative electronegativity of the atoms in a molecule and their positions are the most crucial clue about their oxidation state.
For example the structure of $C{{O}_{2}}$ or carbon dioxide is$O=C=O$. Oxygen being more electronegative than carbon has an oxidation state of “$-2$ ” while that on carbon is “$+4$ ” due to two oxygen atoms.
Let’s decipher the structure of sodium tetrathionate ($N{{a}_{2}}{{S}_{4}}{{O}_{6}}$).
Finding the atom which can behave as the central atom in a molecule is very important, as it holds clues to the overall structure and geometry of the molecule. Here oxygen and sodium cannot show multiple oxidation states but sulphur can. The one with the highest oxidation states is most likely the central atom. Here sulphur fits perfectly to this role.
The most electronegative atom here is oxygen and there are 6 of them. The least electronegative is sodium. Therefore the oxidation state of all six of the oxygen atoms is “$-12$ ” and that of the two sodium atoms are “$+2$ ”.
Oxidation state of sulphur cannot be calculated in a similar manner because it can be present in multiple states. So taking sulphur’s oxidation state as x and overall charge of the molecule to be zero, we get the following equation:
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x+2-12=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=10 \\
\end{align}\]
There are 4 sulphur atoms meaning that each atom has “$+2.5$ ” oxidation state. Now this is wrong because oxidation states are never in fraction, this can only mean a bond between two sulphur units or in technical terms a “disulphide bridge”.
If there is a disulphide bridge then the oxidation states of both the sulphur atoms involved is “$0$ ” (because both of them have the same electronegativity) which implies the other two sulphur atoms both have a “$+5$ ” oxidation state. And now through hit and trial method and by carefully satisfying everyone’s valency (as derived from their oxidation states) we obtain the structure as:
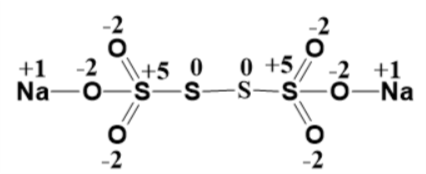
(Oxidation state of each atom is marked over them)
Therefore there are two sulphur atoms with zero oxidation states.
Note: Zero oxidation state does not mean they have lost all their electrons or their property has changed in reality. Oxidation states are a human interpretation of the state of an atom when it is part of a molecule. A “zero” implies the neighbouring atom has a similar electronic state.
Complete step by step solution:
Oxidation state of an atom of any element in a molecule is defined as the charge on that atom when it leaves that particular molecule through heterolytic cleavage. The relative electronegativity of the atoms in a molecule and their positions are the most crucial clue about their oxidation state.
For example the structure of $C{{O}_{2}}$ or carbon dioxide is$O=C=O$. Oxygen being more electronegative than carbon has an oxidation state of “$-2$ ” while that on carbon is “$+4$ ” due to two oxygen atoms.
Let’s decipher the structure of sodium tetrathionate ($N{{a}_{2}}{{S}_{4}}{{O}_{6}}$).
Finding the atom which can behave as the central atom in a molecule is very important, as it holds clues to the overall structure and geometry of the molecule. Here oxygen and sodium cannot show multiple oxidation states but sulphur can. The one with the highest oxidation states is most likely the central atom. Here sulphur fits perfectly to this role.
The most electronegative atom here is oxygen and there are 6 of them. The least electronegative is sodium. Therefore the oxidation state of all six of the oxygen atoms is “$-12$ ” and that of the two sodium atoms are “$+2$ ”.
Oxidation state of sulphur cannot be calculated in a similar manner because it can be present in multiple states. So taking sulphur’s oxidation state as x and overall charge of the molecule to be zero, we get the following equation:
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x+2-12=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=10 \\
\end{align}\]
There are 4 sulphur atoms meaning that each atom has “$+2.5$ ” oxidation state. Now this is wrong because oxidation states are never in fraction, this can only mean a bond between two sulphur units or in technical terms a “disulphide bridge”.
If there is a disulphide bridge then the oxidation states of both the sulphur atoms involved is “$0$ ” (because both of them have the same electronegativity) which implies the other two sulphur atoms both have a “$+5$ ” oxidation state. And now through hit and trial method and by carefully satisfying everyone’s valency (as derived from their oxidation states) we obtain the structure as:

(Oxidation state of each atom is marked over them)
Therefore there are two sulphur atoms with zero oxidation states.
Note: Zero oxidation state does not mean they have lost all their electrons or their property has changed in reality. Oxidation states are a human interpretation of the state of an atom when it is part of a molecule. A “zero” implies the neighbouring atom has a similar electronic state.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




