
Suggest reasons why the BF bond lengths in $B{{F}_{3}}$(130 pm) and $B{{F}_{4}}^{-}$(143 pm) differ.
Answer
542.4k+ views
Hint: $B{{F}_{3}}$ molecule involves backbonding, which induces a minimal double bond character, and due to this, bond length is less.
Complete answer:
In order to answer the question, we need to learn about the nature of both the compounds and their hybridisation nature. Let us talk about $s{{p}^{2}}$ and $s{{p}^{3}}$hybridisation:
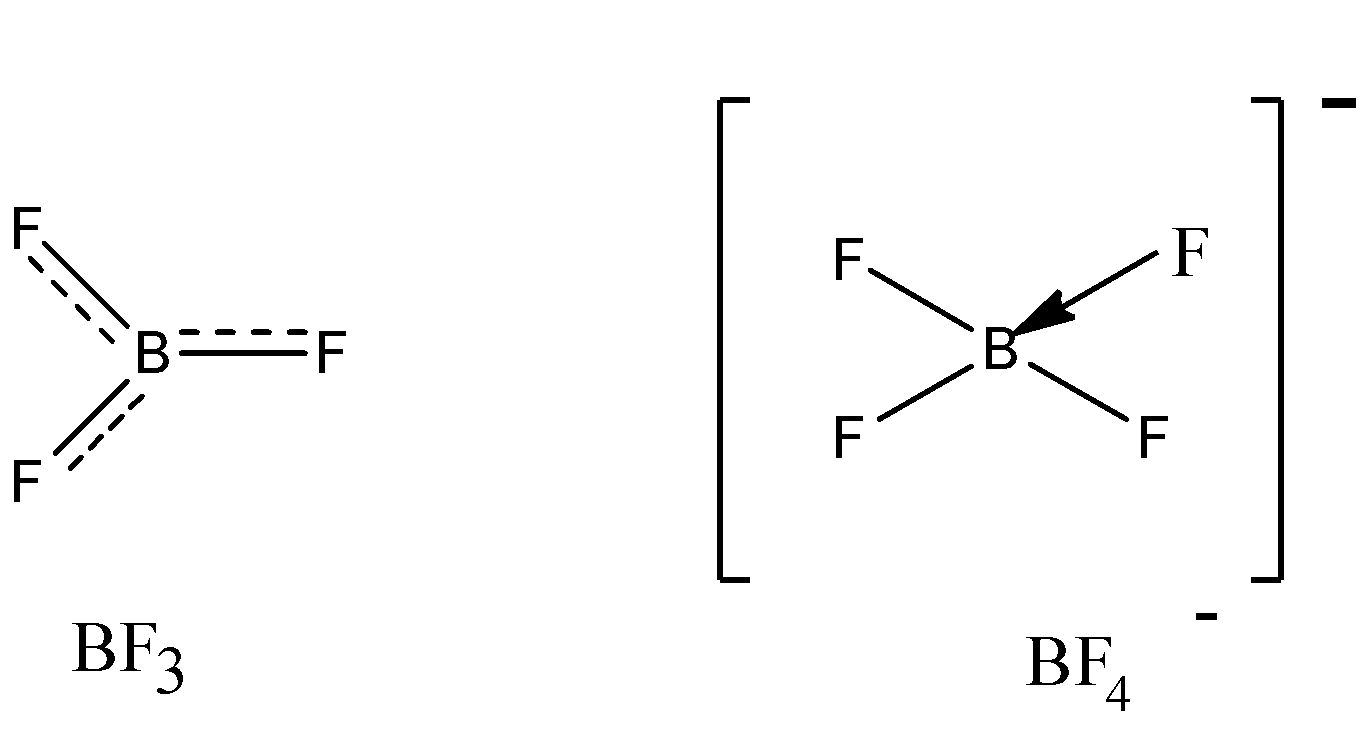
$\mathbf{s}{{\mathbf{p}}^{\mathbf{2}}}$Hybridisation: In $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridisation one s and two p (${{p}_{x}}$ and ${{p}_{y}}$) orbitals of one atom hybridize to give three equivalent $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals. These three $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals are directed towards the three corners of an equilateral triangle with an angle of ${{120}^{0}}$ and give a triangular geometry to the molecule. In $B{{F}_{3}}$ boron is the central atom. Its electronic configuration in the ground state and excited state are one half filled 2s orbital and two half filled 2p orbital undergo hybridisation and produce three equivalent half filled $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals are trigonal planar and are oriented at an angle of ${{120}^{0}}$ to each other. These three $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals overlap with half filled 2p orbitals of three fluorine atoms to form three B-F sigma bonds. The resultant geometry of $B{{F}_{3}}$ molecule is trigonal planar
$\mathbf{s}{{\mathbf{p}}^{\mathbf{3}}}$Hybridisation: In this hybridisation one s and three p-orbitals intermix to form $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybrid orbitals of equivalent energy and identical shape. These four $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybrid orbitals are directed towards the four comers of a tetrahedron separated by an angle of ${{109}^{0}}28'$.
Now, let us come to our question.
In the $B{{F}_{3}}$ molecule, there is back bonding present between $B-F$, which results in formation of partial double bond character. Electron deficiency is removed, and so bond length gets reduced.
In $B{{F}_{4}}^{-}$, the hybridization becomes $s{{p}^{3}}$, the double bond character loose and single bond character takes place, which in turn increases the bond length. So, $B{{F}_{3}}$ has a lesser bond length than $B{{F}_{4}}^{-}$ due to backbonding.
Note:
It is to be noted that in the $B{{F}_{3}}$ molecule, there is no resonance, however, delocalisation occurs. Resonance and delocalisation enhances stability of the compound.
Complete answer:
In order to answer the question, we need to learn about the nature of both the compounds and their hybridisation nature. Let us talk about $s{{p}^{2}}$ and $s{{p}^{3}}$hybridisation:
$\mathbf{s}{{\mathbf{p}}^{\mathbf{2}}}$Hybridisation: In $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridisation one s and two p (${{p}_{x}}$ and ${{p}_{y}}$) orbitals of one atom hybridize to give three equivalent $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals. These three $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals are directed towards the three corners of an equilateral triangle with an angle of ${{120}^{0}}$ and give a triangular geometry to the molecule. In $B{{F}_{3}}$ boron is the central atom. Its electronic configuration in the ground state and excited state are one half filled 2s orbital and two half filled 2p orbital undergo hybridisation and produce three equivalent half filled $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals are trigonal planar and are oriented at an angle of ${{120}^{0}}$ to each other. These three $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals overlap with half filled 2p orbitals of three fluorine atoms to form three B-F sigma bonds. The resultant geometry of $B{{F}_{3}}$ molecule is trigonal planar
$\mathbf{s}{{\mathbf{p}}^{\mathbf{3}}}$Hybridisation: In this hybridisation one s and three p-orbitals intermix to form $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybrid orbitals of equivalent energy and identical shape. These four $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybrid orbitals are directed towards the four comers of a tetrahedron separated by an angle of ${{109}^{0}}28'$.
Now, let us come to our question.
In the $B{{F}_{3}}$ molecule, there is back bonding present between $B-F$, which results in formation of partial double bond character. Electron deficiency is removed, and so bond length gets reduced.
In $B{{F}_{4}}^{-}$, the hybridization becomes $s{{p}^{3}}$, the double bond character loose and single bond character takes place, which in turn increases the bond length. So, $B{{F}_{3}}$ has a lesser bond length than $B{{F}_{4}}^{-}$ due to backbonding.

Note:
It is to be noted that in the $B{{F}_{3}}$ molecule, there is no resonance, however, delocalisation occurs. Resonance and delocalisation enhances stability of the compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




