
Study the roadmap for preparation of washing soda and fill up the blanks:
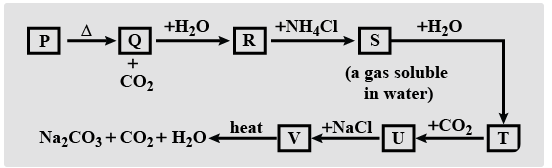
A. $\text{P-CaC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{, Q-Cao, R-Ca(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\text{, S-N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{, T-N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH, U-N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{, V-NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$
B. \[\text{P-CaC}{{\text{l}}_{2}}\text{, Q-Cao, R-Ca(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\text{, S-HCl, T-HCl, U-NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{3}}\text{, V-HCl}\]
C. \[\text{P-CaC}{{\text{l}}_{2}}\text{, Q-Cao, R-CaC}{{\text{O}}_{3}}\text{, S-N}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{, T-HCl, U-N}{{\text{H}}_{4}}\text{Cl, V-NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{3}}\]
D. \[\text{P-CaC}{{\text{O}}_{3}}\text{, Q-Cao, R-Ca(OH}{{\text{)}}_{2}}\text{, S-HCl, T-C}{{\text{l}}_{2}}\text{, U-CaC}{{\text{l}}_{2}}\text{, V-NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{3}}\]

Answer
600.9k+ views
Hint: Washing soda is a sodium carbonate which has 10 molecules of water of crystallization. It is also called sodium carbonate decahydrate.
Complete step by step answer:
- The formula of washing soda is $\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{.10}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$ so our main purpose is to get sodium carbonate. Now let us see how we will do this.
- Take some amount of calcium carbonate (\[\text{CaC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\]) heat it to give calcium oxide($\text{CaO}$) and carbon dioxide (as residual).
- Now react this calcium oxide ($\text{CaO}$) with water to give calcium hydroxide ($\text{Ca(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}$).
- Calcium hydroxide ($\text{Ca(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}$) in the presence of ammonium chloride($\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl}$) will give us ammonia($\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$).
- The ammonia obtain in the last step reacts with water to give us ammonium hydroxide$\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH}$.
- This ammonium hydroxide in the presence of carbon dioxide changes into ammonium bicarbonate ($\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{HC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$).
- This ammonium bicarbonate reacts with sodium chloride to give sodium bicarbonate hydrogen ($\text{NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$).
- This sodium bicarbonate is heated to give sodium carbonate ($\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$).
- This sodium bicarbonate is recrystallized to give washing soda ($\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{.10}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$).
So, we can conclude that option A is correct.
Note: Whenever sodium carbonate crystals are exposed to air efflorescence takes place. Efflorescence is the phenomenon by which sodium carbonate losses water of crystallization and turns into white powder when exposed to air.
Complete step by step answer:
- The formula of washing soda is $\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{.10}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$ so our main purpose is to get sodium carbonate. Now let us see how we will do this.
- Take some amount of calcium carbonate (\[\text{CaC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\]) heat it to give calcium oxide($\text{CaO}$) and carbon dioxide (as residual).
- Now react this calcium oxide ($\text{CaO}$) with water to give calcium hydroxide ($\text{Ca(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}$).
- Calcium hydroxide ($\text{Ca(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}$) in the presence of ammonium chloride($\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl}$) will give us ammonia($\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$).
- The ammonia obtain in the last step reacts with water to give us ammonium hydroxide$\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH}$.
- This ammonium hydroxide in the presence of carbon dioxide changes into ammonium bicarbonate ($\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{HC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$).
- This ammonium bicarbonate reacts with sodium chloride to give sodium bicarbonate hydrogen ($\text{NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$).
- This sodium bicarbonate is heated to give sodium carbonate ($\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$).
- This sodium bicarbonate is recrystallized to give washing soda ($\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{.10}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$).
So, we can conclude that option A is correct.
Note: Whenever sodium carbonate crystals are exposed to air efflorescence takes place. Efflorescence is the phenomenon by which sodium carbonate losses water of crystallization and turns into white powder when exposed to air.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




