
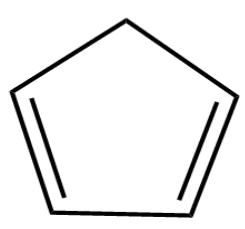
What is the structure of B in the following reaction?
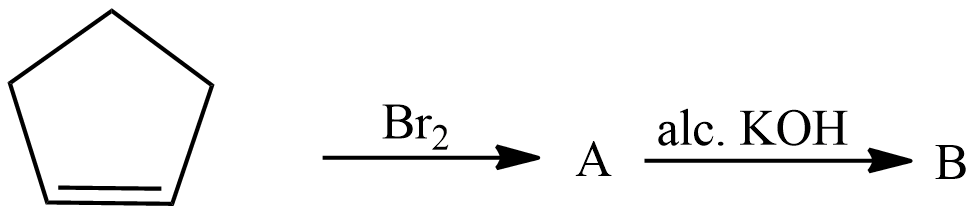
(A)
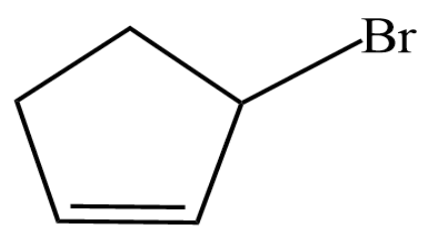
(B)
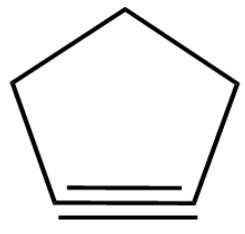
(C)
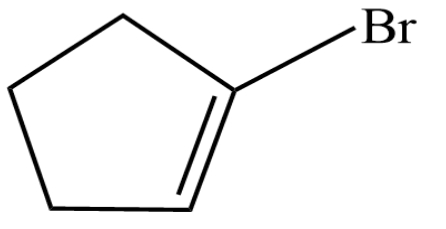
(D)
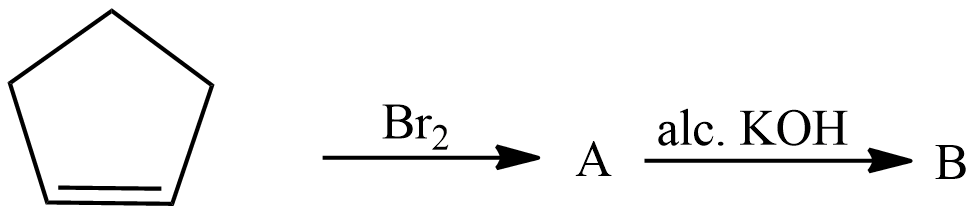




Answer
510.6k+ views
Hint: The organic compound given here is Cyclopentene which is undergoing two reactions to form a product B. In first reaction Cyclopentene reacts with bromine to give product A which then reacts with alcoholic Potassium hydroxide to give product B. We will see both reactions and discuss in detail what they are used for.
Complete answer:
The first reaction is electrophilic addition of bromine with alkenes. Alkenes react with pure liquid bromine or a solution of bromine in cold conditions, the double bond of alkenes breaks and a bromine atom is attached to each carbon which is forming a double bond. The bromine loses its original red-brown colour to give a colourless liquid. The reaction taking place is written as
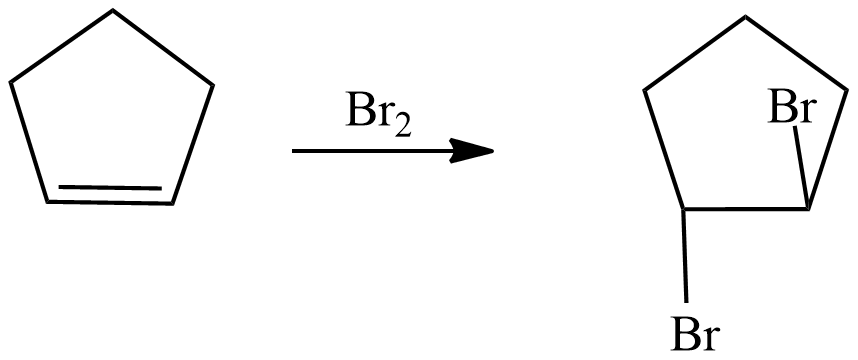
The above reaction shows the double bond in cyclopentane breaks and two bromines are attached to each carbon which is making double bonds.
Now the second reaction shows dehydrohalogenation which means removal of the halogen group as well as water. It is an elimination reaction, Alcoholic Potassium hydroxide $ \left( {alc.} \right)KOH $ breaks into hydroxide ions and it removes the halogen atoms. Halogen is removed from the alpha carbon and hydrogen is removed from beta carbon.
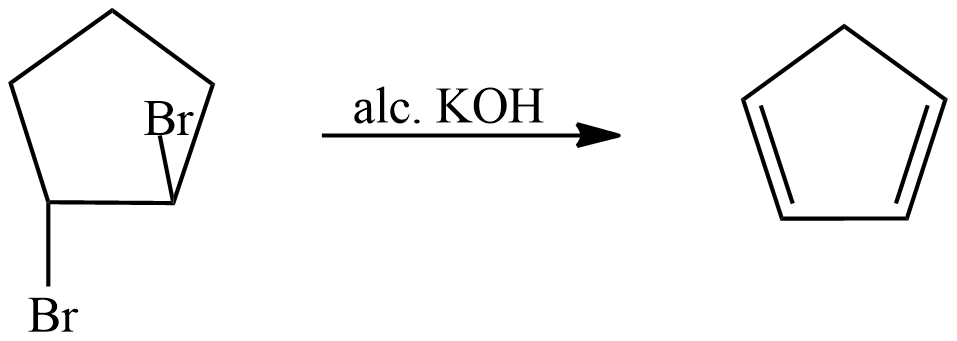
The above reaction shows the elimination of Bromines and hydrogen, two double bonds are created because of two bromines.
So, option four is the $ \left( D \right) $ is the correct answer.
Note:
Dehydrohalogenation is done in presence of a strong base, its general products are alkene and alkyne. In the case of simple alkyl halide with two bromines alkyne is formed but a triple bond will destroy the cyclicity and stability of the compound so instead double bonds are formed.
Complete answer:
The first reaction is electrophilic addition of bromine with alkenes. Alkenes react with pure liquid bromine or a solution of bromine in cold conditions, the double bond of alkenes breaks and a bromine atom is attached to each carbon which is forming a double bond. The bromine loses its original red-brown colour to give a colourless liquid. The reaction taking place is written as
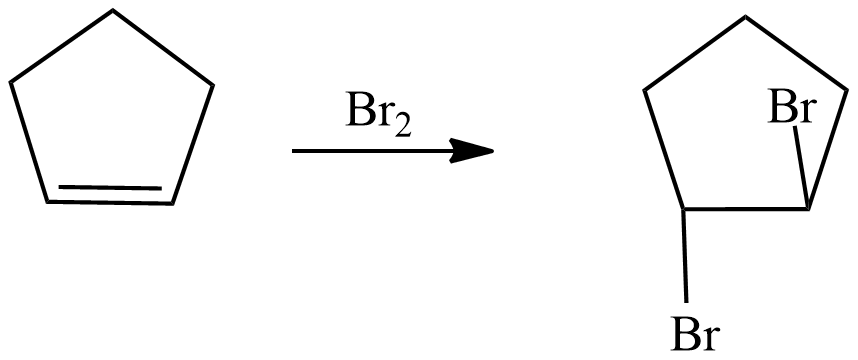
The above reaction shows the double bond in cyclopentane breaks and two bromines are attached to each carbon which is making double bonds.
Now the second reaction shows dehydrohalogenation which means removal of the halogen group as well as water. It is an elimination reaction, Alcoholic Potassium hydroxide $ \left( {alc.} \right)KOH $ breaks into hydroxide ions and it removes the halogen atoms. Halogen is removed from the alpha carbon and hydrogen is removed from beta carbon.

The above reaction shows the elimination of Bromines and hydrogen, two double bonds are created because of two bromines.
So, option four is the $ \left( D \right) $ is the correct answer.
Note:
Dehydrohalogenation is done in presence of a strong base, its general products are alkene and alkyne. In the case of simple alkyl halide with two bromines alkyne is formed but a triple bond will destroy the cyclicity and stability of the compound so instead double bonds are formed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




