
What is the structural formula for $ 2 - {\text{methyl propane}} $ ?
Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint: 2-methyl propane ends with suffix ‘ane’ which tells us that it belongs to the alkane family of hydrocarbons and is substituted with a methyl group that is placed at the second position of the carbon chain. On attaching a group, the chain becomes branched.
Complete answer:
The structural formula of a given hydrocarbon can be obtained by identifying the family it belongs to and the number of substituents it contains.
The prefix “prop” suggests that the given hydrocarbon contains a total of three carbon atoms connected to each other in the parent chain through covalent bonds represented by straight lines.
The suffix “ane” is an indicator of the fact that the given hydrocarbon belongs to the alkane family.
The methyl group with the formula $ C{H_3} $ is substituent and is not a direct part of the parent chain. The numeral written prior to the methyl group indicates the position of the substituent on the parent chain causing a branching of the chain at that position. Hence, the methyl group is attached to the second carbon of the propane chain.
The three carbons are attached in a linear fashion. Since carbons are tetravalent in nature, the remaining valencies are satisfied by placing hydrogens atoms at vacant positions. Thus the first and the last carbon contains three hydrogens each while the second carbon is attached to a single hydrogen and a methyl group.
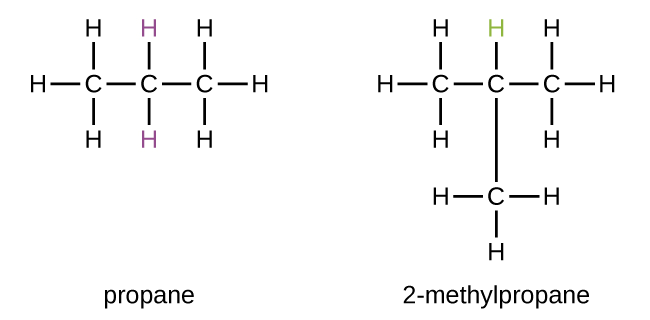
Therefore the structural formula of $ 2 - {\text{methyl propane}} $ is as follows:
Note:
The structural formula is not the same as the molecular formula of any hydrocarbon. The molecular formula only gives the information about the number of different atoms present in the hydrocarbon but the structural formula helps visualize the position of the various groups attached to the parent chain.
Complete answer:
The structural formula of a given hydrocarbon can be obtained by identifying the family it belongs to and the number of substituents it contains.
The prefix “prop” suggests that the given hydrocarbon contains a total of three carbon atoms connected to each other in the parent chain through covalent bonds represented by straight lines.
The suffix “ane” is an indicator of the fact that the given hydrocarbon belongs to the alkane family.
The methyl group with the formula $ C{H_3} $ is substituent and is not a direct part of the parent chain. The numeral written prior to the methyl group indicates the position of the substituent on the parent chain causing a branching of the chain at that position. Hence, the methyl group is attached to the second carbon of the propane chain.
The three carbons are attached in a linear fashion. Since carbons are tetravalent in nature, the remaining valencies are satisfied by placing hydrogens atoms at vacant positions. Thus the first and the last carbon contains three hydrogens each while the second carbon is attached to a single hydrogen and a methyl group.
Therefore the structural formula of $ 2 - {\text{methyl propane}} $ is as follows:

Note:
The structural formula is not the same as the molecular formula of any hydrocarbon. The molecular formula only gives the information about the number of different atoms present in the hydrocarbon but the structural formula helps visualize the position of the various groups attached to the parent chain.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




