
What is the strongest intermolecular force in methanol?
Answer
505.5k+ views
Hint: Methanol is an alcohol. Alcohols are compounds having the hydroxyl group $( - OH)$ attached to the alkyl group. The forces of attraction and repulsion between interacting particles are intermolecular forces. Intermolecular forces exist in all states of matter and are responsible for structural features and physical properties of matter.
Complete answer:
Hydrogen bond is the strongest intermolecular force in methanol.
Hydrogen bond is a case of dipole-dipole interaction. Hydrogen bond occurs when hydrogen is bonded to atoms of highly electronegative elements.
In methanol the oxygen of $ - OH$ group is bonded to $s{p^3}$ hybridised carbon by sigma bond. Three carbon $s{p^3}$ hybridised orbital overlap $1s$ hydrogen orbital, and in oxygen $1{\text{ s}}{{\text{p}}^3}$ hybrid orbital overlaps with $1s$ hydrogen orbital and the two $s{p^3}$ hybrid orbital contains lone pair of electrons.
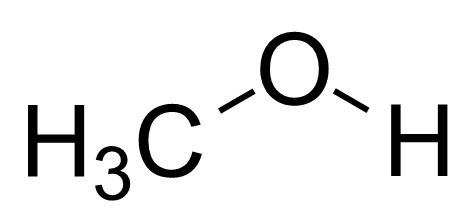
There is a large difference in electronegativities of oxygen and hydrogen atoms, as a result the$$$O - H$ bond is strongly polar and forms hydrogen bonds in alcohols (methanol).
Strong Hydrogen bonding is one of the reasons for the boiling points of alcohols to be higher than the corresponding isomeric ethers, aliphatic hydrocarbons and haloalkanes.
Note:
Methanol is also known as wood spirit as it was originally prepared by destructive distillation of wood. Methanol is a colorless liquid with boiling point $337{\text{ K}}$.It is miscible with water and also is highly poisonous in nature, it causes blindness or death. Methanol is used for denaturing ethyl alcohol that is making it unfit for drinking and it is also used as solvent for varnishes and manufacturing Formaldehyde, perfumes and drugs.
Complete answer:
Hydrogen bond is the strongest intermolecular force in methanol.
Hydrogen bond is a case of dipole-dipole interaction. Hydrogen bond occurs when hydrogen is bonded to atoms of highly electronegative elements.
In methanol the oxygen of $ - OH$ group is bonded to $s{p^3}$ hybridised carbon by sigma bond. Three carbon $s{p^3}$ hybridised orbital overlap $1s$ hydrogen orbital, and in oxygen $1{\text{ s}}{{\text{p}}^3}$ hybrid orbital overlaps with $1s$ hydrogen orbital and the two $s{p^3}$ hybrid orbital contains lone pair of electrons.

There is a large difference in electronegativities of oxygen and hydrogen atoms, as a result the$$$O - H$ bond is strongly polar and forms hydrogen bonds in alcohols (methanol).
Strong Hydrogen bonding is one of the reasons for the boiling points of alcohols to be higher than the corresponding isomeric ethers, aliphatic hydrocarbons and haloalkanes.
Note:
Methanol is also known as wood spirit as it was originally prepared by destructive distillation of wood. Methanol is a colorless liquid with boiling point $337{\text{ K}}$.It is miscible with water and also is highly poisonous in nature, it causes blindness or death. Methanol is used for denaturing ethyl alcohol that is making it unfit for drinking and it is also used as solvent for varnishes and manufacturing Formaldehyde, perfumes and drugs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




