
Strong reducing behaviour of ${H_3}P{O_2}$ is due to:
a.) High oxidation state of phosphorus
b.) Presence of two $ - OH$ groups and one $P - H$ bond
c.) Presence of one $ - OH$ group and two $P - H$ bonds
d.) High electron gain enthalpy of phosphorus
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: In order to deal with this question first we will define the term reducing agent further according to its property and its structure we will find the required reason behind the strong reducing nature of hypophosphorous acid.
Complete step by step answer:
Reducing agent (also known as reductant or reducer) is an entity or compound that loses (or "donates") an electron in a redox chemical reaction to an electron receiver (oxidizing agent).
And a reduction agent is oxidized as electrons are lost in the redox reaction. Reducers have extra electrons (that is, they are reduced by themselves) in their pre-reaction states, whereas oxidizers lose electrons (that is, they are oxidized by themselves). A reducer usually occurs in one of the lowest potential oxidation states and is known as the donor of electrons. Earth elements, formic acid, oxalic acid, and sulphite derivatives are examples of reducing agents.
So, all oxyacids of phosphorus which have $P - H$ bonds act as strong reducing agents. ${H_3}P{O_2}$ has two bonds hence, it acts as a strong reducing agent.
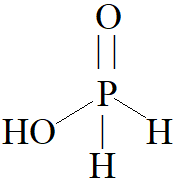
From the diagram it is quite clear that there is a presence of one $ - OH$ bond and two $P - H$ bonds.
Hence, strong reducing behaviour of ${H_3}P{O_2}$ is due to the presence of one $ - OH$ group and two $P - H$ bonds.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: On comparing the reducing nature of the acids ${H_3}P{O_2}$, ${H_3}P{O_3}$ and ${H_3}P{O_4}$. We find that the oxidation number of $P$ in ${H_3}P{O_2}$ and ${H_3}P{O_3}$ is +1 and +3 respectively, which can be further oxidised to the higher oxidation state while the $P$ of the ${H_3}P{O_4}$ is having +5 oxidation state which is the highest oxidation state of the $P$. Hence both ${H_3}P{O_2}$ and ${H_3}P{O_3}$ can be act as reducing agent while ${H_3}P{O_4}$ can’t be used as reducing agent. Among ${H_3}P{O_2}$ and ${H_3}P{O_3}$ the ${H_3}P{O_2}$ is more reducing in nature because of the lowest oxidation number of the $P$.
${H_3}P{O_2}$ (Hypophosphorous acid) is a compound having low-melting, colourless compounds and is soluble in water, dioxane, and alcohol. Due to its strong reducing agent it is commonly used to eliminate Cu, Hg and Ag etc. to test impurities like Nb, As and Ta, etc. Hypophosphorous acid also used in the manufacturing of some plastics (e.g. alkyl resins, polyamides, glycerol, polyester fibre, polyacrylonitrile, nylon fibres, epoxies, and fatty acid esters) as a decolourizing agent for colour stabilisation.
Complete step by step answer:
Reducing agent (also known as reductant or reducer) is an entity or compound that loses (or "donates") an electron in a redox chemical reaction to an electron receiver (oxidizing agent).
And a reduction agent is oxidized as electrons are lost in the redox reaction. Reducers have extra electrons (that is, they are reduced by themselves) in their pre-reaction states, whereas oxidizers lose electrons (that is, they are oxidized by themselves). A reducer usually occurs in one of the lowest potential oxidation states and is known as the donor of electrons. Earth elements, formic acid, oxalic acid, and sulphite derivatives are examples of reducing agents.
So, all oxyacids of phosphorus which have $P - H$ bonds act as strong reducing agents. ${H_3}P{O_2}$ has two bonds hence, it acts as a strong reducing agent.

From the diagram it is quite clear that there is a presence of one $ - OH$ bond and two $P - H$ bonds.
Hence, strong reducing behaviour of ${H_3}P{O_2}$ is due to the presence of one $ - OH$ group and two $P - H$ bonds.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: On comparing the reducing nature of the acids ${H_3}P{O_2}$, ${H_3}P{O_3}$ and ${H_3}P{O_4}$. We find that the oxidation number of $P$ in ${H_3}P{O_2}$ and ${H_3}P{O_3}$ is +1 and +3 respectively, which can be further oxidised to the higher oxidation state while the $P$ of the ${H_3}P{O_4}$ is having +5 oxidation state which is the highest oxidation state of the $P$. Hence both ${H_3}P{O_2}$ and ${H_3}P{O_3}$ can be act as reducing agent while ${H_3}P{O_4}$ can’t be used as reducing agent. Among ${H_3}P{O_2}$ and ${H_3}P{O_3}$ the ${H_3}P{O_2}$ is more reducing in nature because of the lowest oxidation number of the $P$.
${H_3}P{O_2}$ (Hypophosphorous acid) is a compound having low-melting, colourless compounds and is soluble in water, dioxane, and alcohol. Due to its strong reducing agent it is commonly used to eliminate Cu, Hg and Ag etc. to test impurities like Nb, As and Ta, etc. Hypophosphorous acid also used in the manufacturing of some plastics (e.g. alkyl resins, polyamides, glycerol, polyester fibre, polyacrylonitrile, nylon fibres, epoxies, and fatty acid esters) as a decolourizing agent for colour stabilisation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




