
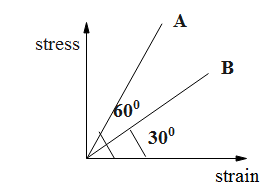
Stress-strain curves for wire A & B are shown in figure then the product of Young’s modulus of \[{{Y}_{A}}\times {{Y}_{B}}\]is.

Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: The stress-strain curve for a material gives the slope equal to that of Young’s modulus of that material. And, the slope is the angle of tan function. So, we will find the tan of angles of the wires A and B and then, we will multiply both to find the product of Young’s modulus of \[{{Y}_{A}}\times {{Y}_{B}}\].
Formula used:
\[\begin{align}
& Y=\dfrac{\text{stress}}{\text{strain}} \\
& \dfrac{\text{stress}}{\text{strain}}=\tan \theta \\
\end{align}\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
The Young’s modulus of a material in terms of stress and strain is given as follows.
\[Y=\dfrac{\text{stress}}{\text{strain}}\]….. (1)
As the curve of any graph is represented by the trigonometric function, that is, tan function, so, we have,
\[\dfrac{\text{stress}}{\text{strain}}=\tan \theta \]…… (2)
Equate the equations (1) and (2) to obtain the value of the slope of the function in terms of Young’s modulus of wires.
\[Y=\tan \theta \]
As we are given with the two wires, so, we have,
For the wire A,
\[{{Y}_{A}}=\tan {{\theta }_{A}}\]
And, for the wire B,
\[{{Y}_{B}}=\tan {{\theta }_{B}}\]
Substitute the given values in the above equations to find the values of the Young’s modulus of wires. So, we get,
The Young’s modulus of wire A as follows.
\[\begin{align}
& {{Y}_{A}}=\tan 60{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow {{Y}_{A}}=\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}\]…… (3)
The Young’s modulus of wire B is as follows.
\[\begin{align}
& {{Y}_{B}}=\tan 30{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow {{Y}_{B}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \\
\end{align}\]…… (4)
Multiply the equations (3) and (4) to obtain the product of the Young’s modulus of wires A and B.
\[\begin{align}
& {{Y}_{A}}\times {{Y}_{B}}=\sqrt{3}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{Y}_{A}}\times {{Y}_{B}}=1 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the product of Young’s modulus of \[{{Y}_{A}}\times {{Y}_{B}}\]is 1.
Note: This is a neither tricky nor simple question. The curves are drawn to make the question a bit complicated. We only need the value of the slope of the angle made by the stress-strain curve to solve this type of question.
Formula used:
\[\begin{align}
& Y=\dfrac{\text{stress}}{\text{strain}} \\
& \dfrac{\text{stress}}{\text{strain}}=\tan \theta \\
\end{align}\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
The Young’s modulus of a material in terms of stress and strain is given as follows.
\[Y=\dfrac{\text{stress}}{\text{strain}}\]….. (1)
As the curve of any graph is represented by the trigonometric function, that is, tan function, so, we have,
\[\dfrac{\text{stress}}{\text{strain}}=\tan \theta \]…… (2)
Equate the equations (1) and (2) to obtain the value of the slope of the function in terms of Young’s modulus of wires.
\[Y=\tan \theta \]
As we are given with the two wires, so, we have,
For the wire A,
\[{{Y}_{A}}=\tan {{\theta }_{A}}\]
And, for the wire B,
\[{{Y}_{B}}=\tan {{\theta }_{B}}\]
Substitute the given values in the above equations to find the values of the Young’s modulus of wires. So, we get,
The Young’s modulus of wire A as follows.
\[\begin{align}
& {{Y}_{A}}=\tan 60{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow {{Y}_{A}}=\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}\]…… (3)
The Young’s modulus of wire B is as follows.
\[\begin{align}
& {{Y}_{B}}=\tan 30{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow {{Y}_{B}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \\
\end{align}\]…… (4)
Multiply the equations (3) and (4) to obtain the product of the Young’s modulus of wires A and B.
\[\begin{align}
& {{Y}_{A}}\times {{Y}_{B}}=\sqrt{3}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{Y}_{A}}\times {{Y}_{B}}=1 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the product of Young’s modulus of \[{{Y}_{A}}\times {{Y}_{B}}\]is 1.
Note: This is a neither tricky nor simple question. The curves are drawn to make the question a bit complicated. We only need the value of the slope of the angle made by the stress-strain curve to solve this type of question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




