
Straight chain silicones are prepared by hydrolysis by:
A. ${R_2}SiC{l_2}$
B. ${R_3}SiCl$
C. $RSiC{l_3}$
D. ${R_2}Si$
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: Silicones are the organosilicon compounds containing Si-O-Si linkages. These are called high-temperature polymers due to the high thermal stability of Si-O-Si linkages. General formula of silicones is ${\left( {{R_2}SiO} \right)_x}$ where $R = C{H_3}$or ${C_2}{H_5}$ or ${C_6}{H_5}$. The name silicone has been given to these materials because their empirical formula resembles the general formula of ketones $\left( {{R_2}CO} \right)$. These are of three types- Linear, cyclic, and cross-linked.
Complete step by step answer:
Linear or straight silicones are prepared by the action of alkyl halides with silicon in presence of copper powder at $570K$ followed by hydrolysis and polymerization.
$2C{H_3}Cl + Si\xrightarrow[{570K}]{{Cu}}{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}SiC{l_2}$
Hydrolysis: ${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}SiC{l_2} + 2{H_2}O \to {\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}Si{\left( {OH} \right)_2} + 2HCl$
The product formed is dimethyl silanol which on polymerization gives straight chain or linear silicones.
Polymerisation: The polymerisation of dimethyl silanol through the elimination of a molecule of water from two hydroxyl group of the adjacent dimethyl silanol results in the formation of a linear silicone as:
$4{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}Si{\left( {OH} \right)_2}\xrightarrow{{Polymerisation}}$
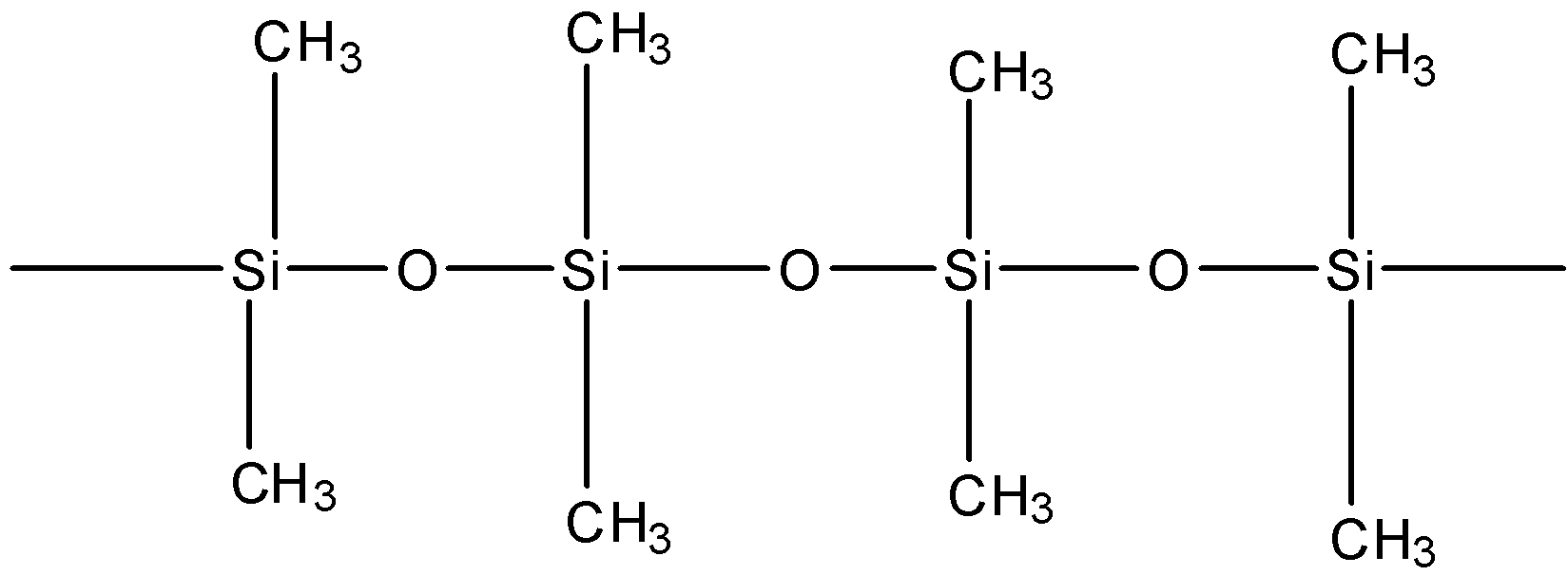
The chain length of the polymer can be controlled by adding ${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}SiCl$ due to which the blocks ends.
Therefore we can conclude that straight chain silicones are prepared by ${R_2}SiC{l_2}$ .
So, the correct answer is Option A .
Note: Properties of silicones:
1.They are highly soluble to heat.
2.They are stable towards chemical reagents and are not affected by weak acids, alkalies, and salt solutions.
3.Low molecular weight silicones are soluble in organic solvents such as benzene, ether, carbon tetrachloride, etc.
4.They are water repellent because of the presence of organic side chains.
5.They are non-toxic.
6.They are good electrical insulators.
7.The viscosity of silicon oils does not change with a temperature change. Hence, silicon oils do not thicken in cold weather.
8.They are resistant to oxidation. However, on heating at $350 - {400^ \circ }C$ in the presence of air, silicones get rapidly oxidized and this leads to a cross-linking polymer chain.
Complete step by step answer:
Linear or straight silicones are prepared by the action of alkyl halides with silicon in presence of copper powder at $570K$ followed by hydrolysis and polymerization.
$2C{H_3}Cl + Si\xrightarrow[{570K}]{{Cu}}{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}SiC{l_2}$
Hydrolysis: ${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}SiC{l_2} + 2{H_2}O \to {\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}Si{\left( {OH} \right)_2} + 2HCl$
The product formed is dimethyl silanol which on polymerization gives straight chain or linear silicones.
Polymerisation: The polymerisation of dimethyl silanol through the elimination of a molecule of water from two hydroxyl group of the adjacent dimethyl silanol results in the formation of a linear silicone as:
$4{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}Si{\left( {OH} \right)_2}\xrightarrow{{Polymerisation}}$

(Straight chain or Linear Silicon)
The chain length of the polymer can be controlled by adding ${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}SiCl$ due to which the blocks ends.
Therefore we can conclude that straight chain silicones are prepared by ${R_2}SiC{l_2}$ .
So, the correct answer is Option A .
Note: Properties of silicones:
1.They are highly soluble to heat.
2.They are stable towards chemical reagents and are not affected by weak acids, alkalies, and salt solutions.
3.Low molecular weight silicones are soluble in organic solvents such as benzene, ether, carbon tetrachloride, etc.
4.They are water repellent because of the presence of organic side chains.
5.They are non-toxic.
6.They are good electrical insulators.
7.The viscosity of silicon oils does not change with a temperature change. Hence, silicon oils do not thicken in cold weather.
8.They are resistant to oxidation. However, on heating at $350 - {400^ \circ }C$ in the presence of air, silicones get rapidly oxidized and this leads to a cross-linking polymer chain.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




