
Stomochord is not similar to notochord because it is
(a) Hollow
(b) Outgrowth of gut
(c) Outgrowth of the nerve cord
(d) Ingrowth of body wall
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: ‘Stomochord’ has ‘stomo’ which is related to the digestive system. This is a conspicuous dorsal extension of the pharynx from an anterior buccal tube or stomochord and this lacks the fibrous sheath of the chordates notochord.
Complete step by step answer:
Hemichordates have pharyngeal slits and dorsal nerve cord which may not be hollow. However, they do not appear to have a notochord merely a stomocord and have no post- anal tail. The stomochord is a short hollow diverticulum of the foregut.
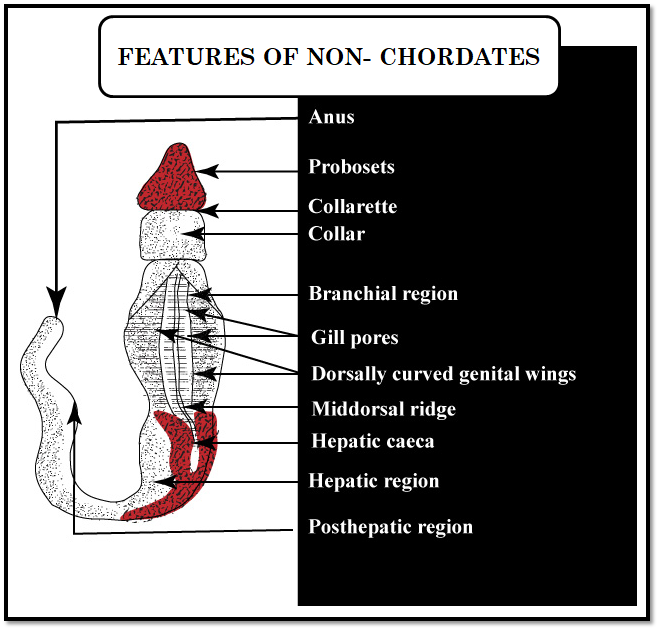
- Acorn worm is an example which belongs to Phylum - Hemichordata and, from class 1- Enteropneusta.
- Their body is divided into three parts: Proboscis, collar, and trunk.
- The anterior end is a muscular, extensible proboscis used to burrow and collect food.
- The presence of slender stalks supported by cartilage skeleton joins proboscis to the collar.
- The trunk is behind the collar and consists of many pairs of small external gills slits through which water exits.
- Mouth is located at the proboscis collar junction, which directly joins into a pharynx.
- Acorn worms have well- developed gill slits and stomochord.
- They have a dorsal strand of nerve cells that are the precursor of dorsal hollow nerve cord.
So, the correct answer is ‘(b) outgrowth of the gut.’
Note:
Chordates are distinguished from non- chordates based on three main characteristics:
- Notochord: A strong but flexible rod present beneath the nerve cord called the notochord.
- A dorsal tubular central nervous system or dorsal tubular nerve cord.
- Pharyngeal gill clefts: Embryos have gill slits on the walls of pharynx functions in both feeding and respiration.
Complete step by step answer:
Hemichordates have pharyngeal slits and dorsal nerve cord which may not be hollow. However, they do not appear to have a notochord merely a stomocord and have no post- anal tail. The stomochord is a short hollow diverticulum of the foregut.

- Acorn worm is an example which belongs to Phylum - Hemichordata and, from class 1- Enteropneusta.
- Their body is divided into three parts: Proboscis, collar, and trunk.
- The anterior end is a muscular, extensible proboscis used to burrow and collect food.
- The presence of slender stalks supported by cartilage skeleton joins proboscis to the collar.
- The trunk is behind the collar and consists of many pairs of small external gills slits through which water exits.
- Mouth is located at the proboscis collar junction, which directly joins into a pharynx.
- Acorn worms have well- developed gill slits and stomochord.
- They have a dorsal strand of nerve cells that are the precursor of dorsal hollow nerve cord.
So, the correct answer is ‘(b) outgrowth of the gut.’
Note:
Chordates are distinguished from non- chordates based on three main characteristics:
- Notochord: A strong but flexible rod present beneath the nerve cord called the notochord.
- A dorsal tubular central nervous system or dorsal tubular nerve cord.
- Pharyngeal gill clefts: Embryos have gill slits on the walls of pharynx functions in both feeding and respiration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




