
Statement-1: The internal angle bisector of angle C of triangle ABC with sides AB, BC and AC are $y=0,3x+2y=0$ and $2x+3y+6=0$ respectively is, $5x+5y+6=0$ .
Statement-2: Image of point A with respect to $5x+5y+6=0$ lies on side BC of the triangle.
(a). Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is correct explanation for statement 1.
(b). Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is not correct explanation for statement 1.
(c). Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is false.
(d). Statement 1 is false, statement 2 is true.
Answer
607.8k+ views
Hint: First find the points A, B, C by intersection of sides given in the question. So given an internal angular bisector, the bisector bisects the angle into 2 equal halves hence, it divides the side opposite into 2 parts with ratio of corresponding sides. Equation of angular bisector of two equation of line $ax+by+c=0,dx+ey+f=0$ is given by
$\dfrac{ax+by+c}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}=\pm \dfrac{dx+ey+f}{\sqrt{{{d}^{2}}+{{e}^{2}}}}$
These 2 lines become the equations of bisectors.
Complete step-by-sep answer:
If two lines from an angle then they have 2 angles bisectors because between 2 lines there are 2 angles possible which are acute and obtuse. So, the 2 lines bisecting these 2 angles between lines $ax+by+c=0,dx+ey+f=0$ are given by
$\dfrac{ax+by+c}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}=\pm \dfrac{dx+ey+f}{\sqrt{{{d}^{2}}+{{e}^{2}}}}$
So, the symbol plus or minus denotes 2 equations of bisectors. Out of both any of them may be acute and may be obtuse if one is acute the other is obtuse and vice versa.
Here, B is the intersection of $y=0,3x+2y=0$. So, substituting y in $3x+2y=0$ we get $x=0$
So, $B=\left( 0,0 \right)$
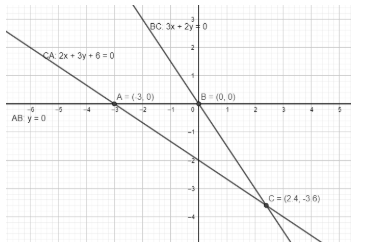
Similarly, we calculate A is intersection of $y=0,2x+3y+6=0$
So, substituting y in $2x+3y+6=0$ , we get
$2x+6=0\text{ }\Rightarrow x=-3$
So, $A=\left( -3,0 \right)$ similarly we get $C=\left( \dfrac{12}{5},\dfrac{-18}{5} \right)$
By bisector equation, we get
$\dfrac{3x+2y}{\sqrt{9+4}}=\pm \dfrac{2x+3y+6}{\sqrt{9+4}}$
By simplifying, we get as follows the equation:
$3x+2y=2x+3y+6$ ; $3x+2y=-2x-3y-6$
By simplifying both equations, we get bisector:
$x-y-6=0$ ; $5x+5y+6=0$
Image of $\left( p,q \right)$ in $ax+by+c=0$ is $\left( h,k \right)$ then
$\dfrac{x-h}{a}=\dfrac{y-k}{b}=\dfrac{2\left( ap+bq+c \right)}{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$
By substituting $\left( 0,0 \right)$ in $5x+5y+6=0$ we get,
$\dfrac{+x+0}{5}=\dfrac{+y+0}{5}=\dfrac{-2\left( 6 \right)}{{{5}^{2}}+{{5}^{2}}}=\dfrac{-6}{25}$
By above equation we can say $x=\dfrac{-6}{25},y=\dfrac{6}{25}$
Given this statement this point lies on BC.
Equation of BC is $2x+3y+6=0$
Substituting that point, we get
$2\left( \dfrac{-6}{5} \right)+3\left( \dfrac{-6}{5} \right)+6=0$
$5\left( \dfrac{-6}{5} \right)+6=0$
By simplifying, we get
$-6+6=0$
So, that point lies on side BC.
So, both are true but don't depend on each other.
So, option (b) is the correct answer.
Note: Be careful while calculating angular bisectors. Remember the $''\pm ''$ sign, you must get 2 bisector equations. The point specifying that the foot of the bisector equation always lies on the opposite side is very important because this idea will give us the point we require. So whenever you need a point find the conditions on that point such as the line equations which pass through this point.
$\dfrac{ax+by+c}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}=\pm \dfrac{dx+ey+f}{\sqrt{{{d}^{2}}+{{e}^{2}}}}$
These 2 lines become the equations of bisectors.
Complete step-by-sep answer:
If two lines from an angle then they have 2 angles bisectors because between 2 lines there are 2 angles possible which are acute and obtuse. So, the 2 lines bisecting these 2 angles between lines $ax+by+c=0,dx+ey+f=0$ are given by
$\dfrac{ax+by+c}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}=\pm \dfrac{dx+ey+f}{\sqrt{{{d}^{2}}+{{e}^{2}}}}$
So, the symbol plus or minus denotes 2 equations of bisectors. Out of both any of them may be acute and may be obtuse if one is acute the other is obtuse and vice versa.
Here, B is the intersection of $y=0,3x+2y=0$. So, substituting y in $3x+2y=0$ we get $x=0$
So, $B=\left( 0,0 \right)$

Similarly, we calculate A is intersection of $y=0,2x+3y+6=0$
So, substituting y in $2x+3y+6=0$ , we get
$2x+6=0\text{ }\Rightarrow x=-3$
So, $A=\left( -3,0 \right)$ similarly we get $C=\left( \dfrac{12}{5},\dfrac{-18}{5} \right)$
By bisector equation, we get
$\dfrac{3x+2y}{\sqrt{9+4}}=\pm \dfrac{2x+3y+6}{\sqrt{9+4}}$
By simplifying, we get as follows the equation:
$3x+2y=2x+3y+6$ ; $3x+2y=-2x-3y-6$
By simplifying both equations, we get bisector:
$x-y-6=0$ ; $5x+5y+6=0$
Image of $\left( p,q \right)$ in $ax+by+c=0$ is $\left( h,k \right)$ then
$\dfrac{x-h}{a}=\dfrac{y-k}{b}=\dfrac{2\left( ap+bq+c \right)}{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$
By substituting $\left( 0,0 \right)$ in $5x+5y+6=0$ we get,
$\dfrac{+x+0}{5}=\dfrac{+y+0}{5}=\dfrac{-2\left( 6 \right)}{{{5}^{2}}+{{5}^{2}}}=\dfrac{-6}{25}$
By above equation we can say $x=\dfrac{-6}{25},y=\dfrac{6}{25}$
Given this statement this point lies on BC.
Equation of BC is $2x+3y+6=0$
Substituting that point, we get
$2\left( \dfrac{-6}{5} \right)+3\left( \dfrac{-6}{5} \right)+6=0$
$5\left( \dfrac{-6}{5} \right)+6=0$
By simplifying, we get
$-6+6=0$
So, that point lies on side BC.
So, both are true but don't depend on each other.
So, option (b) is the correct answer.
Note: Be careful while calculating angular bisectors. Remember the $''\pm ''$ sign, you must get 2 bisector equations. The point specifying that the foot of the bisector equation always lies on the opposite side is very important because this idea will give us the point we require. So whenever you need a point find the conditions on that point such as the line equations which pass through this point.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




