
State whether true or false.
The image formed by a plane mirror is always real.
Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: In case of mirrors usually there are three types used. Plain mirror, concave mirror and convex mirror. All will serve different purposes. Properties of different mirrors are different. In case of convex mirrors they always form virtual images. While concave mirrors form both virtual and real images and we will see about plain mirrors.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Complete answer:
In case of convex or concave mirrors the focal length of the mirror determines the type and size of the image formed. Same with the case of plane mirrors also.
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$ This is the mirror formula
Where v is the image distance while u is the object distance and f is the focal length.
But here the focal length of the plane mirror will be infinity. Mathematically the inverse of infinity will be zero. From the above formula we get
$v = - u$
If we consider only the magnitude distance of the object from the mirror will be equal to the distance of image from the mirror and magnification of the mirror will be $\dfrac{{ - v}}{u}$ which is one in this case and it is positive.
Hence if magnification is positive then image formed will be erected and rule is when only one mirror is present and image formed is erected then that image must be virtual.
Hence an image formed by a plane mirror is always virtually erect and laterally inverted.
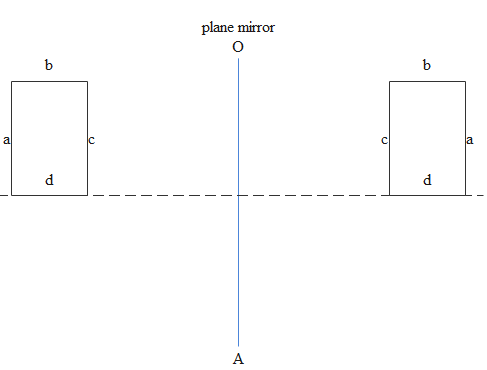
In the above image formed due to the plane mirror it is laterally inverted i.e left portion of object becomes right side portion for the mirror.
Hence the answer will be false.
Note:
In case of plane mirrors the magnification is always one i.e size of image will be always equal to size of an object let it be longitudinal size or the lateral size. Real image can never be formed by the plane mirror that’s why the image formed by the plane mirror can’t be caught on the screen.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Complete answer:
In case of convex or concave mirrors the focal length of the mirror determines the type and size of the image formed. Same with the case of plane mirrors also.
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$ This is the mirror formula
Where v is the image distance while u is the object distance and f is the focal length.
But here the focal length of the plane mirror will be infinity. Mathematically the inverse of infinity will be zero. From the above formula we get
$v = - u$
If we consider only the magnitude distance of the object from the mirror will be equal to the distance of image from the mirror and magnification of the mirror will be $\dfrac{{ - v}}{u}$ which is one in this case and it is positive.
Hence if magnification is positive then image formed will be erected and rule is when only one mirror is present and image formed is erected then that image must be virtual.
Hence an image formed by a plane mirror is always virtually erect and laterally inverted.

In the above image formed due to the plane mirror it is laterally inverted i.e left portion of object becomes right side portion for the mirror.
Hence the answer will be false.
Note:
In case of plane mirrors the magnification is always one i.e size of image will be always equal to size of an object let it be longitudinal size or the lateral size. Real image can never be formed by the plane mirror that’s why the image formed by the plane mirror can’t be caught on the screen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




