
State two differences that might be seen in the graph if there had been a strong wind opposing the runners in the race.
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Velocity is rate of change of displacement with respect to the time. For a particular path we can define instantaneous velocity and average velocity. Velocity at a particular time instant is called instantaneous velocity and velocity over a certain duration of time is average velocity. Speed is the magnitude of velocity. In the given plot we will find out what is the variation of speed to answer this question.
Formula used:
$a = \dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity. Both velocity and acceleration are the vectors.
$a = \dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}$ where ‘a’ is an acceleration and ‘v’ is the velocity and ‘t’ is the time
If we clearly see the plot given below the plot is made between the speed of the person and time. We have to assume that there is a cross wind which will obstruct the man who is running. The slope of the below plot gives us the magnitude of acceleration as speed is the magnitude of velocity. Due to the opposing wind the man will face the opposing force and he will slow down. His acceleration will reduce and automatically the slope of the plot below upto 3 seconds will reduce.
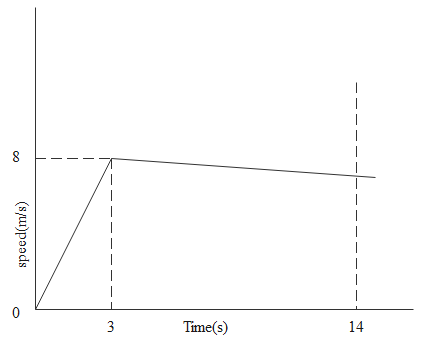
After three second the curve has steepen down and if there is opposing wind force then the curve will steep down below the 8 meter per second itself.
More over the time taken to finish the race will increase as speed is reduced and the acceleration is decreased.
Hence these will be the changes that happen.
Note: If we are asked to find out the time instant where instantaneous acceleration of a particle is zero then we should find out a point where slope of the speed time graph will be equal to zero as slope is nothing but the rate of change of speed with respect to time which gives magnitude of instantaneous acceleration. Even though acceleration is vector If the magnitude of it is zero, then the entire acceleration vector will be zero.
Formula used:
$a = \dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity. Both velocity and acceleration are the vectors.
$a = \dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}$ where ‘a’ is an acceleration and ‘v’ is the velocity and ‘t’ is the time
If we clearly see the plot given below the plot is made between the speed of the person and time. We have to assume that there is a cross wind which will obstruct the man who is running. The slope of the below plot gives us the magnitude of acceleration as speed is the magnitude of velocity. Due to the opposing wind the man will face the opposing force and he will slow down. His acceleration will reduce and automatically the slope of the plot below upto 3 seconds will reduce.

After three second the curve has steepen down and if there is opposing wind force then the curve will steep down below the 8 meter per second itself.
More over the time taken to finish the race will increase as speed is reduced and the acceleration is decreased.
Hence these will be the changes that happen.
Note: If we are asked to find out the time instant where instantaneous acceleration of a particle is zero then we should find out a point where slope of the speed time graph will be equal to zero as slope is nothing but the rate of change of speed with respect to time which gives magnitude of instantaneous acceleration. Even though acceleration is vector If the magnitude of it is zero, then the entire acceleration vector will be zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




