
State true or false:
\[{\sin ^2}A + {\cos ^2}A = 1\]
Answer
573k+ views
Hint: Here we will first draw the right angled triangle \[ABC\]. Then we will find the value of \[\sin A\] and \[\cos A\] using the trigonometric ratios. We will find the square of \[\sin A\] and \[\cos A\] and then we will find their sum. We will use the Pythagoras theorem to simplify it further. If we will get the value as 1 after simplification then the above identity will be true otherwise false.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have to check whether the given identity \[{\sin ^2}A + {\cos ^2}A = 1\] is true or false.
First, we will draw a right angled triangle \[ABC\]
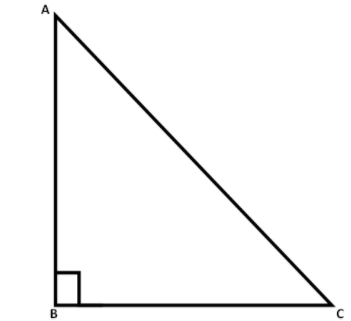
We will first find the value of \[\sin A\] using the trigonometric ratios.
We know that, \[\sin A = \dfrac{P}{H}\] , where \[P\] is perpendicular and \[H\] is hypotenuse.
From the right angled triangle, we have the hypotenuse \[AC\] and the perpendicular \[AB\]. Substituting these values here, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \sin A = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}\]
Squaring both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}A = {\left( {\dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{A{B^2}}}{{A{C^2}}}\] ……… \[\left( 1 \right)\]
We will now find the value of \[\cos A\] using the trigonometric ratios.
We know that \[\cos A = \dfrac{B}{H}\], where \[B\] is base and \[H\] is hypotenuse.
From the right angled triangle, we have the hypotenuse \[AC\] and the base \[BC\]. Substituting these values here, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \cos A = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AC}}\]
Squaring both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {\cos ^2}A = {\left( {\dfrac{{BC}}{{AC}}} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{B{C^2}}}{{A{C^2}}}\] ……… \[\left( 2 \right)\]
Now, We will add equation \[\left( 1 \right)\] and equation \[\left( 2 \right)\].
\[ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}A + {\cos ^2}A = \dfrac{{A{B^2}}}{{A{C^2}}} + \dfrac{{B{C^2}}}{{A{C^2}}}\]
Simplifying the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}A + {\cos ^2}A = \dfrac{{A{B^2} + B{C^2}}}{{A{C^2}}}\]
Using Pythagoras theorem for this right angled triangle here, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}A + {\cos ^2}A = \dfrac{{A{C^2}}}{{A{C^2}}} = 1\]
Hence, the given identity is correct or the given statement is true.
Note: We have used trigonometric ratios here to prove the given identity. We need to keep in mind that trigonometric ratios and trigonometric identities are different. Trigonometric identities means the formula which involves trigonometric functions and trigonometric ratios means the formula which shows the relation between angles and length of the right angled triangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have to check whether the given identity \[{\sin ^2}A + {\cos ^2}A = 1\] is true or false.
First, we will draw a right angled triangle \[ABC\]

We will first find the value of \[\sin A\] using the trigonometric ratios.
We know that, \[\sin A = \dfrac{P}{H}\] , where \[P\] is perpendicular and \[H\] is hypotenuse.
From the right angled triangle, we have the hypotenuse \[AC\] and the perpendicular \[AB\]. Substituting these values here, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \sin A = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}\]
Squaring both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}A = {\left( {\dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{A{B^2}}}{{A{C^2}}}\] ……… \[\left( 1 \right)\]
We will now find the value of \[\cos A\] using the trigonometric ratios.
We know that \[\cos A = \dfrac{B}{H}\], where \[B\] is base and \[H\] is hypotenuse.
From the right angled triangle, we have the hypotenuse \[AC\] and the base \[BC\]. Substituting these values here, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \cos A = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AC}}\]
Squaring both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {\cos ^2}A = {\left( {\dfrac{{BC}}{{AC}}} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{B{C^2}}}{{A{C^2}}}\] ……… \[\left( 2 \right)\]
Now, We will add equation \[\left( 1 \right)\] and equation \[\left( 2 \right)\].
\[ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}A + {\cos ^2}A = \dfrac{{A{B^2}}}{{A{C^2}}} + \dfrac{{B{C^2}}}{{A{C^2}}}\]
Simplifying the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}A + {\cos ^2}A = \dfrac{{A{B^2} + B{C^2}}}{{A{C^2}}}\]
Using Pythagoras theorem for this right angled triangle here, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}A + {\cos ^2}A = \dfrac{{A{C^2}}}{{A{C^2}}} = 1\]
Hence, the given identity is correct or the given statement is true.
Note: We have used trigonometric ratios here to prove the given identity. We need to keep in mind that trigonometric ratios and trigonometric identities are different. Trigonometric identities means the formula which involves trigonometric functions and trigonometric ratios means the formula which shows the relation between angles and length of the right angled triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




