
State the numerical value of the frequency of oscillation of a second’s pendulum? Does it depend on the amplitude of the oscillation?
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: We all know that the time period of the pendulum the amount of time a pendulum takes to come to the initial position when starting from the same initial mean position. While completing a 1-time period, the pendulum goes to two extreme positions also.
Formula Used:
The formula for calculating the frequency is of the pendulum is:
$f = \dfrac{1}{T}$
Complete step by step answer:
The formula for calculating the frequency is:
$f = \dfrac{1}{T}$
Put the value of time period (T) as 2 seconds in the above equation.
$\begin{array}{c}
f = \dfrac{1}{{2\,{\rm{s}}}}\\
= 0.5\,
\end{array}$
We can refer to the below figure for the diagram of the pendulum which is the length l of the pendulum and the mass of the bob is m.
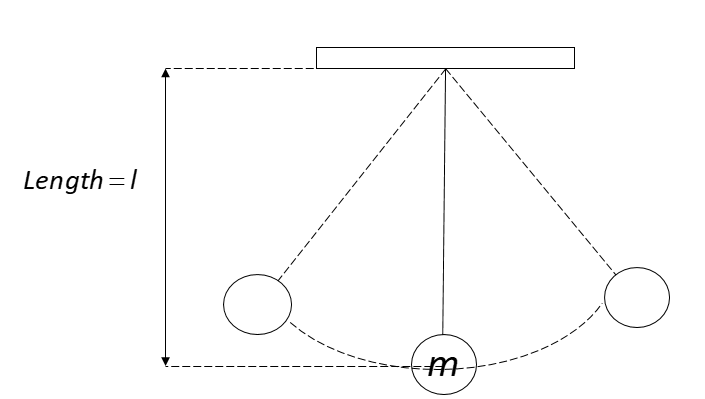
The frequency of the oscillation of a second’s pendulum depends on the time period of the oscillation. The time period further depends on the length of the pendulum and the acceleration due to gravity. Hence, the oscillation of a second’s pendulum is independent of the amplitude of the oscillation.
Additional Information:
The time period of the pendulum is also constant if there is no air drag or atmospheric friction. The time period of a pendulum in the moon will increase as the value of acceleration due to gravity g is less in the moon.
Note:
The effective length of the second’s pendulum, at a place where the value of acceleration due to gravity is g=9.8 m/$s^2$ (the average value), is nearly one meter. Here the string is considered as massless and only the mass of the bob is considered.
Formula Used:
The formula for calculating the frequency is of the pendulum is:
$f = \dfrac{1}{T}$
Complete step by step answer:
The formula for calculating the frequency is:
$f = \dfrac{1}{T}$
Put the value of time period (T) as 2 seconds in the above equation.
$\begin{array}{c}
f = \dfrac{1}{{2\,{\rm{s}}}}\\
= 0.5\,
\end{array}$
We can refer to the below figure for the diagram of the pendulum which is the length l of the pendulum and the mass of the bob is m.

The frequency of the oscillation of a second’s pendulum depends on the time period of the oscillation. The time period further depends on the length of the pendulum and the acceleration due to gravity. Hence, the oscillation of a second’s pendulum is independent of the amplitude of the oscillation.
Additional Information:
The time period of the pendulum is also constant if there is no air drag or atmospheric friction. The time period of a pendulum in the moon will increase as the value of acceleration due to gravity g is less in the moon.
Note:
The effective length of the second’s pendulum, at a place where the value of acceleration due to gravity is g=9.8 m/$s^2$ (the average value), is nearly one meter. Here the string is considered as massless and only the mass of the bob is considered.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




