
State the major functions of the following: Asters of centrosome.
Answer
516k+ views
Hint: Asters, found only in animal cells, are made up of filaments of tubulin protein. The main function of asters is to hold the two centrioles at the two opposite poles and help the spindle apparatus to position during nuclear division.
Complete Answer:
An aster is a star-shaped cellular structure, consisting of a centrosome and its associated microtubules. It is seen during the early stages of mitosis in animal cells. Astral rays, composed of microtubules, radiate from the centrosphere in a cloud-like appearance. They are one variant of microtubules that come out of the centrosome; others include kinetochore microtubules and polar microtubules.
Astral microtubules are a subpopulation of microtubules that exist during and immediately before mitosis. They are defined as any microtubule originating from the centrosome which does not connect to a kinetochore. Astral microtubules develop in the actin skeleton and along with the cell cortex aids in spindle orientation. They are organized into radial arrays around the centrosomes.
The role of astral microtubules is assisted by dyneins that are specific to this role. The light chains (static portion) of these dyneins are attached to the cell membrane and their globular parts (dynamic portions) are attached to the microtubules. The globular chains attempt to move towards the centrosome, but as they are bound to the cell membrane, they pull the centrosomes towards the membrane.
Thus, astral microtubules assist in cytokinesis.
Note:
Astral microtubules are not actually required for the progression of mitosis, but are necessary to ensure the fidelity of the process. The function of astral microtubules is generally to determine the cell geometry. Astral microtubules are absent in plant cells.
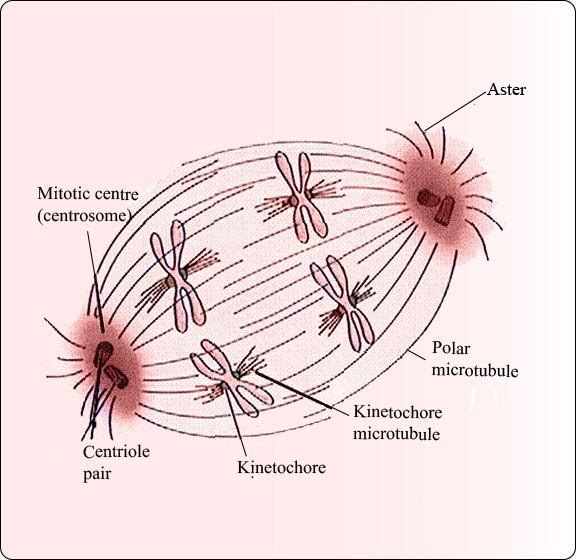
Figure: Asters of centrosome
Complete Answer:
An aster is a star-shaped cellular structure, consisting of a centrosome and its associated microtubules. It is seen during the early stages of mitosis in animal cells. Astral rays, composed of microtubules, radiate from the centrosphere in a cloud-like appearance. They are one variant of microtubules that come out of the centrosome; others include kinetochore microtubules and polar microtubules.
Astral microtubules are a subpopulation of microtubules that exist during and immediately before mitosis. They are defined as any microtubule originating from the centrosome which does not connect to a kinetochore. Astral microtubules develop in the actin skeleton and along with the cell cortex aids in spindle orientation. They are organized into radial arrays around the centrosomes.
The role of astral microtubules is assisted by dyneins that are specific to this role. The light chains (static portion) of these dyneins are attached to the cell membrane and their globular parts (dynamic portions) are attached to the microtubules. The globular chains attempt to move towards the centrosome, but as they are bound to the cell membrane, they pull the centrosomes towards the membrane.
Thus, astral microtubules assist in cytokinesis.
Note:
Astral microtubules are not actually required for the progression of mitosis, but are necessary to ensure the fidelity of the process. The function of astral microtubules is generally to determine the cell geometry. Astral microtubules are absent in plant cells.

Figure: Asters of centrosome
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




