
State the main function of guard cells.
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: The stomatal pore is encircled by two guard cells that aid stomatal opening driven by bloat of guard cells. Guard cells control opening and shutting of stomata by admission of potassium particles and water. It helps in return of gases.
Complete step by step answer:
Guard cells will be cells surrounding every stoma. They help to control the pace of happening by opening and shutting the stomata. Light is the fundamental trigger for the opening or shutting. Each guard cell has a generally thick fingernail skin on the pore-side. As water enters the cell, the slim side lumps outward like an inflatable and draws the thick side alongside it, shaping a bow.
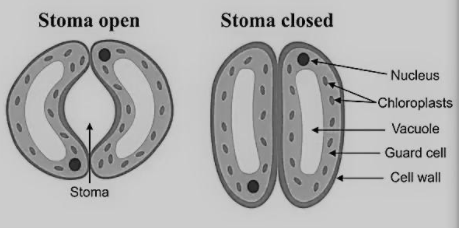
Guard cells contain phototropin proteins which are serine and threonine kinases with blue-light photoreceptor movement. The phototropins trigger numerous reactions, for example, phototropism, chloroplast development and leaf extension just as stomatal opening.
Note: Opening and conclusion of the stomatal pore is interceded by changes in the turgor weight of the two Guard cells.The turgor weight of guard cells is constrained by developments of huge amounts of particles and sugars into and out of the Guard cells. Guard cells have cell dividers of shifting thickness and distinctively situated cellulose microfibers, making them twist outward when they are bloated, which thus causes stomata to open. Stomata close when there is an osmotic loss of water, happening from the loss of $K^+$ to neighboring cells, mainly potassium ($K^+$) particles.
Complete step by step answer:
Guard cells will be cells surrounding every stoma. They help to control the pace of happening by opening and shutting the stomata. Light is the fundamental trigger for the opening or shutting. Each guard cell has a generally thick fingernail skin on the pore-side. As water enters the cell, the slim side lumps outward like an inflatable and draws the thick side alongside it, shaping a bow.

Guard cells contain phototropin proteins which are serine and threonine kinases with blue-light photoreceptor movement. The phototropins trigger numerous reactions, for example, phototropism, chloroplast development and leaf extension just as stomatal opening.
Note: Opening and conclusion of the stomatal pore is interceded by changes in the turgor weight of the two Guard cells.The turgor weight of guard cells is constrained by developments of huge amounts of particles and sugars into and out of the Guard cells. Guard cells have cell dividers of shifting thickness and distinctively situated cellulose microfibers, making them twist outward when they are bloated, which thus causes stomata to open. Stomata close when there is an osmotic loss of water, happening from the loss of $K^+$ to neighboring cells, mainly potassium ($K^+$) particles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




