
State the function of a reservoir in a nutrient cycle. Explain the simplified model of carbon cycle in nature.
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint:To compensate for the imbalance created by the lack of equilibrium in the efflux and influx of minerals (deficit). The carbon cycle is a gaseous cycle with the atmosphere and oceans as its source and sink.
Complete answer:
First let’s answer the function of a reservoir in a nutrient cycle. The role of a nutrient cycle reservoir: it meets the deficit that exists because of the imbalances in the state of nutrient influx and efflux.
Now, let’s explain the simplified model of carbon cycle in nature. Carbon exists in the air through respiration (breathing) and combustion (burning) as carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is consumed by producers by the method of photosynthesis to create carbohydrates. Then oxygen is given out by these producers. There are many animals living on plants. They transfer the carbon compounds down the food chain. However, the rest of the carbon that these animals eat is exhaled as carbon dioxide. This is via the respiration process. Then the animals and plants die eventually. In the soil, the dead organisms are eaten by decomposers. The carbon that is in their bodies is then brought back as carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. In some situations, the decomposition process is prevented. Decomposed plants and animals may then be available for combustion as fossil fuels in the future.
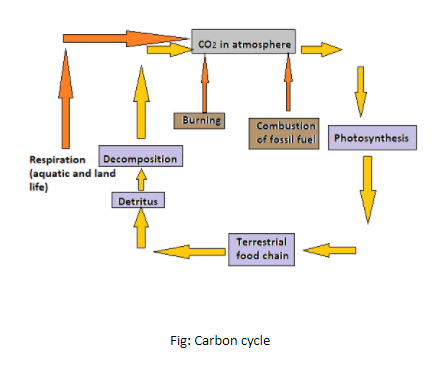
Note:An important aspect of the survival of all life on earth is the Carbon Cycle. From an environmental standpoint, by absorbing the heat of the sun, carbon creates insulation. Carbon is the building block of life from a biological perspective and establishes stable bonds with other components essential for life.
Complete answer:
First let’s answer the function of a reservoir in a nutrient cycle. The role of a nutrient cycle reservoir: it meets the deficit that exists because of the imbalances in the state of nutrient influx and efflux.
Now, let’s explain the simplified model of carbon cycle in nature. Carbon exists in the air through respiration (breathing) and combustion (burning) as carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is consumed by producers by the method of photosynthesis to create carbohydrates. Then oxygen is given out by these producers. There are many animals living on plants. They transfer the carbon compounds down the food chain. However, the rest of the carbon that these animals eat is exhaled as carbon dioxide. This is via the respiration process. Then the animals and plants die eventually. In the soil, the dead organisms are eaten by decomposers. The carbon that is in their bodies is then brought back as carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. In some situations, the decomposition process is prevented. Decomposed plants and animals may then be available for combustion as fossil fuels in the future.

Note:An important aspect of the survival of all life on earth is the Carbon Cycle. From an environmental standpoint, by absorbing the heat of the sun, carbon creates insulation. Carbon is the building block of life from a biological perspective and establishes stable bonds with other components essential for life.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




