
State Hooke’s law. Hence draw a typical stress-strain curve for a metallic wire and label the parts.
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint
Hooke’s law shows that the force needed to the material to expand or compress by some distance. The stress and strain diagram shows that the behaviour of the material under the gradual increase of the load. The stress and diagram can be drawn for all the material, to know its behaviour under different load conditions.
Complete step by step answer
Hooke’s law:
Hooke’s law states that for relatively small deformation of the object, the displacement of the deformation is directly proportional to the force applied to the object.
$\Rightarrow F = kX$
Where, $F$ is the force applied to the object, $k$ is the spring constant for the object and $X$ is the spring stretch or compression.
The Stress vs Strain graph for the metallic wire is:
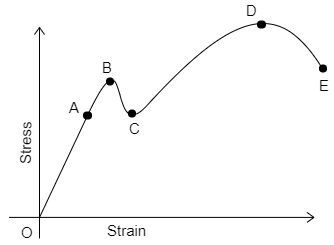
From the stress and strain curve,
1. The line OA is the proportional limit, which means that the stress is directly proportional to the strain. And the material behaves like rubber, which means after the removal of the load the material comes to the original shape. There is no change in the shape and size of the material of the metallic wire.
2. The point B is the upper yield point, which means that the material can withstand and does not undergo the deformation until this point. So, the point B is the maximum stress that the metallic wire doesn’t undergo deformation.
3. The point C is the lower yield point, which means to maintain the plastic behaviour of the material. After the point B, the material changes to the plastic deformation. To maintain the plastic behaviour the point C is required.
4. The point D is the Ultimate stress point; it is the peak point in the stress and strain graph. At this point the material reaches the maximum plastic behaviour limit. After this point very several force only the material with stand.
5. The point E is the breaking point, where the material breaks into two or more parts.
Note
The ratio of the stress and the strain is called Young’s modulus. So, this graph is also known as the Young’s modulus graph of the metallic wire. When load is applied to the material, first it acts like elastic material up to some limit, after that limit it converts to the plastic behaviour on further it will break.
Hooke’s law shows that the force needed to the material to expand or compress by some distance. The stress and strain diagram shows that the behaviour of the material under the gradual increase of the load. The stress and diagram can be drawn for all the material, to know its behaviour under different load conditions.
Complete step by step answer
Hooke’s law:
Hooke’s law states that for relatively small deformation of the object, the displacement of the deformation is directly proportional to the force applied to the object.
$\Rightarrow F = kX$
Where, $F$ is the force applied to the object, $k$ is the spring constant for the object and $X$ is the spring stretch or compression.
The Stress vs Strain graph for the metallic wire is:

From the stress and strain curve,
1. The line OA is the proportional limit, which means that the stress is directly proportional to the strain. And the material behaves like rubber, which means after the removal of the load the material comes to the original shape. There is no change in the shape and size of the material of the metallic wire.
2. The point B is the upper yield point, which means that the material can withstand and does not undergo the deformation until this point. So, the point B is the maximum stress that the metallic wire doesn’t undergo deformation.
3. The point C is the lower yield point, which means to maintain the plastic behaviour of the material. After the point B, the material changes to the plastic deformation. To maintain the plastic behaviour the point C is required.
4. The point D is the Ultimate stress point; it is the peak point in the stress and strain graph. At this point the material reaches the maximum plastic behaviour limit. After this point very several force only the material with stand.
5. The point E is the breaking point, where the material breaks into two or more parts.
Note
The ratio of the stress and the strain is called Young’s modulus. So, this graph is also known as the Young’s modulus graph of the metallic wire. When load is applied to the material, first it acts like elastic material up to some limit, after that limit it converts to the plastic behaviour on further it will break.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




