
State converse of Pythagoras theorem. \[\]
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: We recall the Pythagoras theorem which states that “in a right-angled triangle the square of the hypotenuse is the sum of squares of other two sides”. We find the premise and conclusion of the statement. We take the conclusion as the premise and the premise as the conclusion to state the converse of Pythagoras theorem. \[\]
Complete step by step answer:
We know that in a right-angled triangle there is one right angle of measure ${{90}^{\circ }}$ and side opposite to it called the hypotenuse. The Pythagoras theorem states that “in a right-angled triangle the square of the length of the hypotenuse is the sum of squares of lengths of other two sides”.\[\]
We see in the statement of the Pythagoras theorem that the premise or assumption is the triangle is right-angled and the conclusion is the square of the length of the hypotenuse is the sum of squares of lengths of the other two sides.\[\]
In order to take converse, we take the conclusion of the Pythagoras theorem as the premise and the premise as the conclusion. We have a triangle and we do not know which one is the hypotenuse. So the converse statement will be “If the sum of squares of lengths of two sides in a triangle is equal to the square of the third side, then the triangle is right-angled.”\[\]
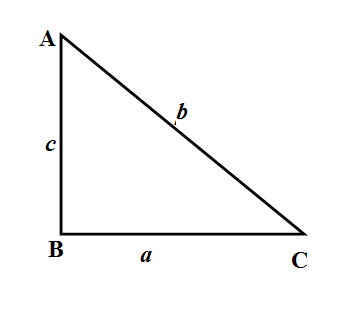
In symbols by Pythagoras theorem, if $\Delta ABC$ is a right-angled triangle and the length of the hypotenuse is $b$ and other two sides are of length $a,c$ then ${{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}$. The converse of this statement will be if the lengths of triangles $a,b,c$are related as ${{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}$ then triangle is right-angled. \[\]
Note:
We can use the converse of the Pythagoras theorem to check if the triangle is right-angled or not. Triplets of integers for example $\left( 3,4,5 \right),\left( 5,12,13 \right)$who satisfy Pythagoras theorem are called Pythagorean triples. If we know the mathematical logic the implication is symbolized as $p\to q$ where $p$ is called premise, antecedent or assumption, and $q$ is called consequence or conclusion. The converse of $p\to q$ is symbolized as $q\to p$.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that in a right-angled triangle there is one right angle of measure ${{90}^{\circ }}$ and side opposite to it called the hypotenuse. The Pythagoras theorem states that “in a right-angled triangle the square of the length of the hypotenuse is the sum of squares of lengths of other two sides”.\[\]
We see in the statement of the Pythagoras theorem that the premise or assumption is the triangle is right-angled and the conclusion is the square of the length of the hypotenuse is the sum of squares of lengths of the other two sides.\[\]
In order to take converse, we take the conclusion of the Pythagoras theorem as the premise and the premise as the conclusion. We have a triangle and we do not know which one is the hypotenuse. So the converse statement will be “If the sum of squares of lengths of two sides in a triangle is equal to the square of the third side, then the triangle is right-angled.”\[\]

In symbols by Pythagoras theorem, if $\Delta ABC$ is a right-angled triangle and the length of the hypotenuse is $b$ and other two sides are of length $a,c$ then ${{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}$. The converse of this statement will be if the lengths of triangles $a,b,c$are related as ${{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}$ then triangle is right-angled. \[\]
Note:
We can use the converse of the Pythagoras theorem to check if the triangle is right-angled or not. Triplets of integers for example $\left( 3,4,5 \right),\left( 5,12,13 \right)$who satisfy Pythagoras theorem are called Pythagorean triples. If we know the mathematical logic the implication is symbolized as $p\to q$ where $p$ is called premise, antecedent or assumption, and $q$ is called consequence or conclusion. The converse of $p\to q$ is symbolized as $q\to p$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




