
State Chargaff’s rule.
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: It tells about the ratio of the different nitrogenous bases that are present inside the DNA molecule as it helps in determining the various structure and composition of DNA in different organisms. It is constant for a species.
Complete answer:
The DNA of any organism should have purine and pyrimidine bases in a 1:1 ratio. This, the Chargaff’s rule is also known as the base pair rule. It states that guanine and cytosine amount should be the same while the ratio of adenine and thiamine should be the same. This rule was named after its discoverer in 1950, Erwin Chargaff. This ratio of nitrogenous bases is found in both the DNA strands.
The Chargaff rule is dependent on the DNA structure presented by Watson and Crick. This model shows that the percentage of the nitrogenous base pairs is equal to the double-stranded DNA. This is called the first parity rule. The second parity rule states that the percentage of adenine is equal to the percentage of thiamine while the percentage of thymine is equal to the percentage of cytosine. This is the case of both the single strands of DNA.
The percentage of nitrogenous bases is found to be different in different organisms resulting in the variation of various species. This changing ability of the DNA makes it compatible to be genetic material. This makes the study of the DNA structure easier.
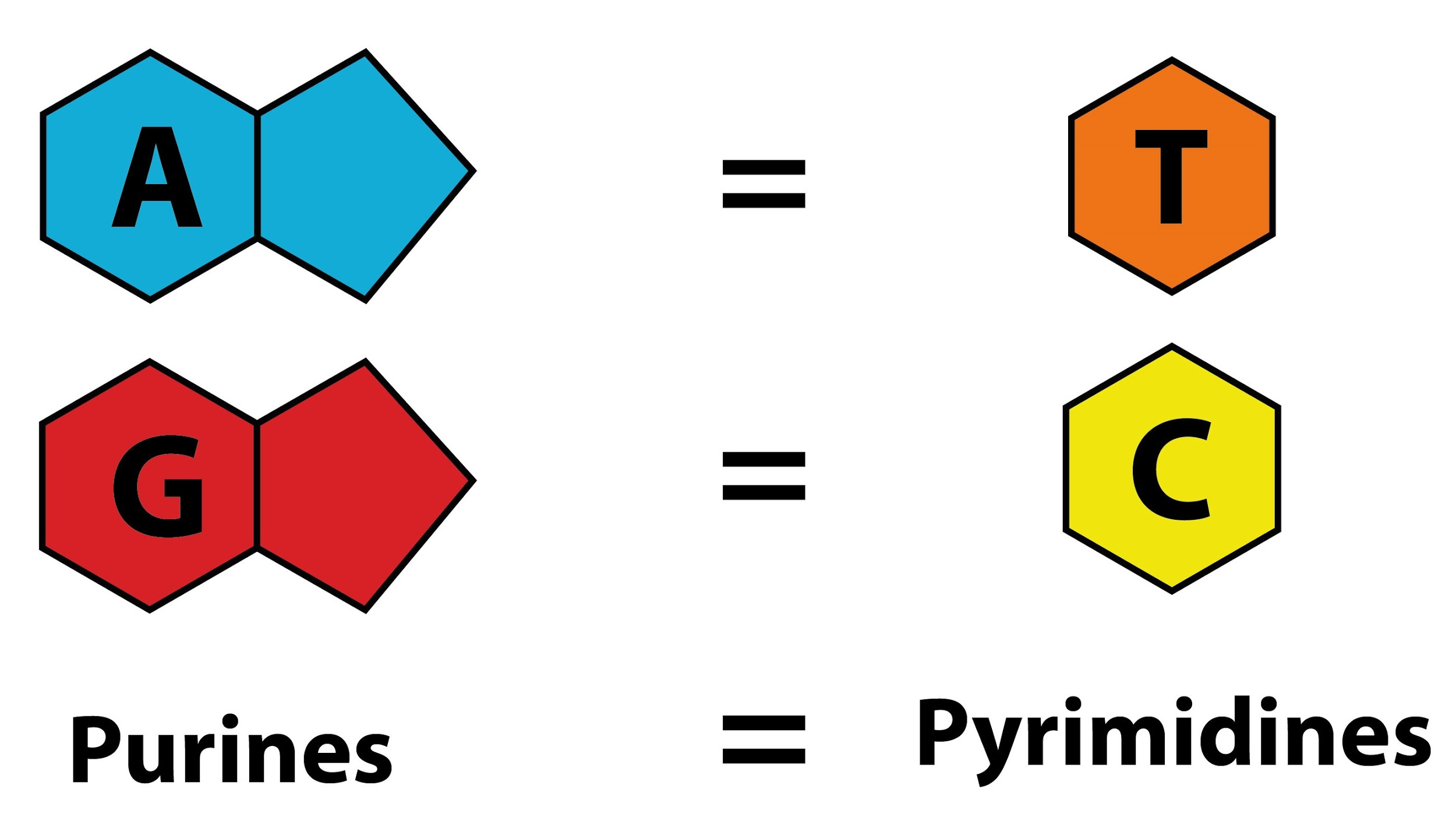
Note: Chargaff’s rule is also known as the ‘grammar of biology’ because it states the features that maintain the structure of DNA and specifies the rules which govern them. Purines and pyrimidine are the nitrogenous bases that help in holding the structure of the DNA in a place with hydrogen bonds. The adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine are present in the DNA while Uracil instead of thymine is present in the case of RNA.
Complete answer:
The DNA of any organism should have purine and pyrimidine bases in a 1:1 ratio. This, the Chargaff’s rule is also known as the base pair rule. It states that guanine and cytosine amount should be the same while the ratio of adenine and thiamine should be the same. This rule was named after its discoverer in 1950, Erwin Chargaff. This ratio of nitrogenous bases is found in both the DNA strands.
The Chargaff rule is dependent on the DNA structure presented by Watson and Crick. This model shows that the percentage of the nitrogenous base pairs is equal to the double-stranded DNA. This is called the first parity rule. The second parity rule states that the percentage of adenine is equal to the percentage of thiamine while the percentage of thymine is equal to the percentage of cytosine. This is the case of both the single strands of DNA.
The percentage of nitrogenous bases is found to be different in different organisms resulting in the variation of various species. This changing ability of the DNA makes it compatible to be genetic material. This makes the study of the DNA structure easier.

Note: Chargaff’s rule is also known as the ‘grammar of biology’ because it states the features that maintain the structure of DNA and specifies the rules which govern them. Purines and pyrimidine are the nitrogenous bases that help in holding the structure of the DNA in a place with hydrogen bonds. The adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine are present in the DNA while Uracil instead of thymine is present in the case of RNA.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




