
State any two illustrations for Newton’s third law of motion.
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Recall that Newton’s third law suggests that to every action, there is always an equal and opposite reaction. Using this principle, think of some everyday examples where a force exerted by body A on body B results in an opposite force exerted back on body A by body B.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us begin by establishing Newton’s Third Law of Motion.
According to this law, action is always accompanied by an equal reaction but both are directed in opposite directions to each other. Thus, this law gives a quantitative summary of how forces affect motion and the reaction they experience as a result of force exertion.
The forces in play have the following characteristics:
1. Forces always occur in pairs as action and reaction forces.
2. Both the action and reaction forces are equal in magnitude.
3. Both the action and reaction forces act in opposite directions.
4. Action and reaction forces act on different bodies.
Let us look at some examples of Newton’s third law.
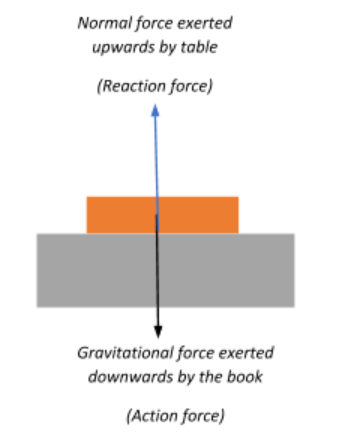
1. When a book is placed on the table it stays on the table as a consequence of Newton’s third law.
The book exerts its weight downwards on the table in the form of a gravitational force, in response to which the table produces a normal reaction force on the book by pushing it upwards. This action-reaction pair keeps the book balanced on the table.
2. When a bullet is fired from the gun, the recoil produced is another consequence of Newton’s third law. When a bullet is fired from the gun, the bullet experiences a force (action) produced in the forward direction by the gun, in response to which the bullet exerts a backward force (reaction) of the same magnitude on the gun which causes the gun to recoil upon firing.

Thus, in the above two examples, the action and reaction forces are consistent with the characteristics of these forces that we listed above, and can hence be classified as illustrations of Newton’s third law of motion.
Note: It is a common misconception that the force pairs should cancel, resulting in no motion. This is not true because the action and reaction forces are exerted on different systems. If the action and reaction were produced on the same system, it is only then that the forces will cancel out with no change in state of motion. Thus, the action-reaction forces do not cancel out if they act on different systems.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us begin by establishing Newton’s Third Law of Motion.
According to this law, action is always accompanied by an equal reaction but both are directed in opposite directions to each other. Thus, this law gives a quantitative summary of how forces affect motion and the reaction they experience as a result of force exertion.
The forces in play have the following characteristics:
1. Forces always occur in pairs as action and reaction forces.
2. Both the action and reaction forces are equal in magnitude.
3. Both the action and reaction forces act in opposite directions.
4. Action and reaction forces act on different bodies.
Let us look at some examples of Newton’s third law.
1. When a book is placed on the table it stays on the table as a consequence of Newton’s third law.
The book exerts its weight downwards on the table in the form of a gravitational force, in response to which the table produces a normal reaction force on the book by pushing it upwards. This action-reaction pair keeps the book balanced on the table.

2. When a bullet is fired from the gun, the recoil produced is another consequence of Newton’s third law. When a bullet is fired from the gun, the bullet experiences a force (action) produced in the forward direction by the gun, in response to which the bullet exerts a backward force (reaction) of the same magnitude on the gun which causes the gun to recoil upon firing.

Thus, in the above two examples, the action and reaction forces are consistent with the characteristics of these forces that we listed above, and can hence be classified as illustrations of Newton’s third law of motion.
Note: It is a common misconception that the force pairs should cancel, resulting in no motion. This is not true because the action and reaction forces are exerted on different systems. If the action and reaction were produced on the same system, it is only then that the forces will cancel out with no change in state of motion. Thus, the action-reaction forces do not cancel out if they act on different systems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




