
State and prove interior angle bisector theorem.
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: We know that a line segment that bisects one of the vertex angles of a triangle is called the angle bisector of triangle. This angle bisector of an angle of a triangle divides the opposite side into two segments. The interior bisector theorem gives the relation between these two segments and other two sides of the triangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Interior angle bisector theorem states that the angle bisector of an angle of a triangle divides the opposite side into two segments that are proportional to the other two sides of the triangle.
Now, we will prove the interior angle bisector theorem.
Given: In $ \vartriangle ABC $ , $ \overline {BD} $ bisects $ \angle ABC $ .
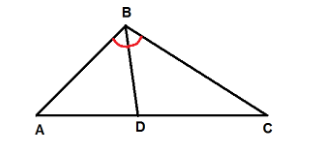
To prove: $ \dfrac{{AD}}{{CD}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{CB}} $
Proof:
It is given that in $ \vartriangle ABC $ , $ \overline {BD} $ bisects $ \angle ABC $ .
We know that an angle bisector is a ray in the interior of an angle which forms two congruent angles.
$ \Rightarrow \angle ABD \cong \angle CBD $
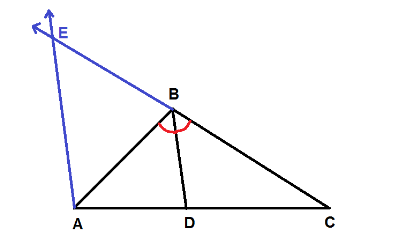
Now, we will draw an auxiliary line through $ A $ parallel to bisector $ \overline {BD} $ which intersects the extension of $ \overline {CB} $ at point $ E $ as shown in figure.
If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, the corresponding angles are congruent angles.
$ \Rightarrow \angle CBD \cong \angle AEB $
If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, the alternate interior angles are congruent angles.
$ \Rightarrow \angle CBD \cong \angle BAE $
Now, substitute $ \angle CBD \cong \angle AEB $
$ \Rightarrow \angle AEB \cong \angle BAE $
We know from the Side Splitter Theorem that If a line is parallel to one side of a triangle and intersects the other two sides, it divides the sides proportionally.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AD}}{{CD}} = \dfrac{{EB}}{{CB}} $
The sides opposite the angles are congruent if two angles of a triangle are congruent.
\[ \Rightarrow \overline {AB} = \overline {EB} \]
Also, congruent segments have equal lengths.
\[ \Rightarrow AB = EB\]
Substituting this in the equation $ \dfrac{{AD}}{{CD}} = \dfrac{{EB}}{{CB}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AD}}{{CD}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{CB}} $
Hence, the theorem is proved.
Note: We can understand the application of the interior angle bisector by solving one simple example.
Suppose we are asked to find the value of $ x $ in the given figure where $ \overline {BD} $ bisects $ \angle ABC $ in $ \vartriangle ABC $ .
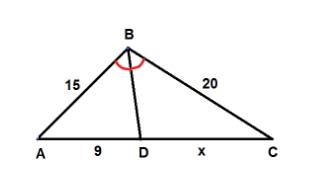
We will apply the interior angle bisector theorem here, then
$
\dfrac{{AD}}{{CD}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{CB}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{9}{{15}} = \dfrac{x}{{20}} \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{9 \times 20}}{{15}} \\
\Rightarrow x = 12 \;
$
Thus, we can find the missing value of a segment by applying this theorem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Interior angle bisector theorem states that the angle bisector of an angle of a triangle divides the opposite side into two segments that are proportional to the other two sides of the triangle.
Now, we will prove the interior angle bisector theorem.
Given: In $ \vartriangle ABC $ , $ \overline {BD} $ bisects $ \angle ABC $ .

To prove: $ \dfrac{{AD}}{{CD}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{CB}} $
Proof:

It is given that in $ \vartriangle ABC $ , $ \overline {BD} $ bisects $ \angle ABC $ .
We know that an angle bisector is a ray in the interior of an angle which forms two congruent angles.
$ \Rightarrow \angle ABD \cong \angle CBD $
Now, we will draw an auxiliary line through $ A $ parallel to bisector $ \overline {BD} $ which intersects the extension of $ \overline {CB} $ at point $ E $ as shown in figure.
If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, the corresponding angles are congruent angles.
$ \Rightarrow \angle CBD \cong \angle AEB $
If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, the alternate interior angles are congruent angles.
$ \Rightarrow \angle CBD \cong \angle BAE $
Now, substitute $ \angle CBD \cong \angle AEB $
$ \Rightarrow \angle AEB \cong \angle BAE $
We know from the Side Splitter Theorem that If a line is parallel to one side of a triangle and intersects the other two sides, it divides the sides proportionally.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AD}}{{CD}} = \dfrac{{EB}}{{CB}} $
The sides opposite the angles are congruent if two angles of a triangle are congruent.
\[ \Rightarrow \overline {AB} = \overline {EB} \]
Also, congruent segments have equal lengths.
\[ \Rightarrow AB = EB\]
Substituting this in the equation $ \dfrac{{AD}}{{CD}} = \dfrac{{EB}}{{CB}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AD}}{{CD}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{CB}} $
Hence, the theorem is proved.
Note: We can understand the application of the interior angle bisector by solving one simple example.
Suppose we are asked to find the value of $ x $ in the given figure where $ \overline {BD} $ bisects $ \angle ABC $ in $ \vartriangle ABC $ .

We will apply the interior angle bisector theorem here, then
$
\dfrac{{AD}}{{CD}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{CB}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{9}{{15}} = \dfrac{x}{{20}} \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{9 \times 20}}{{15}} \\
\Rightarrow x = 12 \;
$
Thus, we can find the missing value of a segment by applying this theorem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





