
Splitting of light when it passes through prism is called as.
Answer
495k+ views
Hint:A rainbow is arguably the most well-known example of dispersion, in which dispersion causes the spatial separation of white light into components of different wavelengths (different colors). However, dispersion has an impact in a variety of different situations: for example, group velocity dispersion causes pulses to spread in optical fibres, diminishing messages over long distances; and soliton waves result from the cancellation of group velocity dispersion and nonlinear effects.
Complete step by step solution:
When white light passes through a glass prism, it separates into its spectrum of colours (in sequence violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, and red), a process known as dispersion.
Dispersion in a prism is the easiest method to describe dispersion.
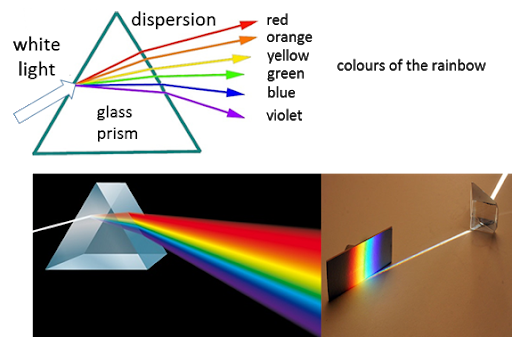
When light moves from one medium to another, the speed at which it propagates varies, and it bends or refracts as a result. Light is now refracted towards the triangle's base as it passes through a prism. The diagram above clearly depicts the refraction of light via a prism.
The wavelengths of different colours in the spectrum of light are varied. As a result, the rate at which they bend varies depending on the wavelength, with violet bending the most due to its shortest wavelength and red bending the least due to its longest wavelength.
When white light is refracted by a prism, it disperses into its spectrum of colours as a result of this.
Light does, in fact, spread into its range of colours on a glass slab. If we look at it in a certain manner, we can see it. Before we begin, you should be familiar with refractive indices. They aren't always the same. They are affected by the frequency of light and, as a result, the wavelength.
White light is now refracted not once, but twice when it passes through a glass slab or a glass prism. It goes from the air to the glass, then back to the air. It slows down in the first occurrence of refraction and accelerates up in the second
Note:
Dispersion is a phenomenon in optics where the phase velocity of a wave is affected by its frequency. Newton was the first to experiment with light flowing through a prism. He let sunlight pass through the prism, expecting to see white light on the other side of the screen, but instead saw a spectrum of light after dispersion.
Complete step by step solution:
When white light passes through a glass prism, it separates into its spectrum of colours (in sequence violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, and red), a process known as dispersion.
Dispersion in a prism is the easiest method to describe dispersion.

When light moves from one medium to another, the speed at which it propagates varies, and it bends or refracts as a result. Light is now refracted towards the triangle's base as it passes through a prism. The diagram above clearly depicts the refraction of light via a prism.
The wavelengths of different colours in the spectrum of light are varied. As a result, the rate at which they bend varies depending on the wavelength, with violet bending the most due to its shortest wavelength and red bending the least due to its longest wavelength.
When white light is refracted by a prism, it disperses into its spectrum of colours as a result of this.
Light does, in fact, spread into its range of colours on a glass slab. If we look at it in a certain manner, we can see it. Before we begin, you should be familiar with refractive indices. They aren't always the same. They are affected by the frequency of light and, as a result, the wavelength.
White light is now refracted not once, but twice when it passes through a glass slab or a glass prism. It goes from the air to the glass, then back to the air. It slows down in the first occurrence of refraction and accelerates up in the second
Note:
Dispersion is a phenomenon in optics where the phase velocity of a wave is affected by its frequency. Newton was the first to experiment with light flowing through a prism. He let sunlight pass through the prism, expecting to see white light on the other side of the screen, but instead saw a spectrum of light after dispersion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




