
What is the speed of the block when it has moved a distance of 0.0200m from its initial position?(At this point the spring is compressed 0.0190m.See details.
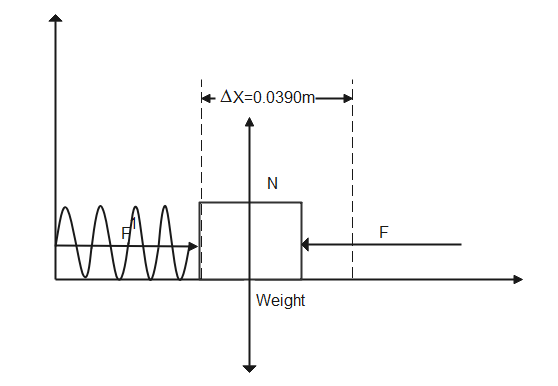
A 2.55 kg block on a horizontal floor is attached to a horizontal spring that is initially compressed 0.0390 m. The spring has a force constant of$815N{{m}^{-1}}$. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the floor and the block is 0.35. The block and spring are released from rest and the block slides along the floor

Answer
516.3k+ views
Hint: Speed is defined as the distance covered per unit time and speed is a scalar quantity. SI unit of speed is . Displacement is defined as the process in which objects' positions are changed and in displacement the initial position of objects are changed. Displacement is also defined as change in initial position of objects to the final position and displacement is denoted as S.
Complete answer:
The potential energy is stored if a spring is compressed by a Force of F,
Potential energy turns into kinetic energy when spring is realized
By the call-back force the objects are repulsed which happens on the spring
$F=K\cdot \Delta x$
From the data we know the values of $K=815N{{m}^{-1}}$
$\Delta x$=0.0190 m
F=815⋅0.019=15.48 N
${{F}_{F}}=K\cdot mg$
Friction force (${{F}_{F}}$) =0.35⋅2.55⋅9.81=8.76N
Acceleration of object is given by:
$a=\dfrac{F-{{F}_{F}}}{m}$
Where mass of object m=2.55kg
After substituting
$\begin{align}
& a=\dfrac{15.48-8.76}{2.55} \\
& a=2.64m{{s}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}$
$\begin{align}
& {{v}^{2}}=2\cdot a\cdot displacement \\
& {{v}^{2}}=2\cdot 2.64\cdot 0.0200 \\
& {{v}^{2}}=0.1056 \\
& v=\sqrt{0.1056} \\
& v=0.32m{{s}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}$
The speed of the block is $v=0.32m{{s}^{-1}}$.
Note: Students kinetic energy is a property of a moving particle and depends on its mass and motion. Acceleration depends on the mass and also on the force. The force velocity, acceleration and momentum have both magnitude and a direction. Heavier objects have less acceleration compared to lighter objects.
Complete answer:
The potential energy is stored if a spring is compressed by a Force of F,
Potential energy turns into kinetic energy when spring is realized
By the call-back force the objects are repulsed which happens on the spring
$F=K\cdot \Delta x$
From the data we know the values of $K=815N{{m}^{-1}}$
$\Delta x$=0.0190 m
F=815⋅0.019=15.48 N
${{F}_{F}}=K\cdot mg$
Friction force (${{F}_{F}}$) =0.35⋅2.55⋅9.81=8.76N
Acceleration of object is given by:
$a=\dfrac{F-{{F}_{F}}}{m}$
Where mass of object m=2.55kg
After substituting
$\begin{align}
& a=\dfrac{15.48-8.76}{2.55} \\
& a=2.64m{{s}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}$
$\begin{align}
& {{v}^{2}}=2\cdot a\cdot displacement \\
& {{v}^{2}}=2\cdot 2.64\cdot 0.0200 \\
& {{v}^{2}}=0.1056 \\
& v=\sqrt{0.1056} \\
& v=0.32m{{s}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}$
The speed of the block is $v=0.32m{{s}^{-1}}$.
Note: Students kinetic energy is a property of a moving particle and depends on its mass and motion. Acceleration depends on the mass and also on the force. The force velocity, acceleration and momentum have both magnitude and a direction. Heavier objects have less acceleration compared to lighter objects.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




