
Soni says that the acceleration in an object could be zero even when several forces are acting on it. Do you agree with her? Why?
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint
There is a possibility for the objects with the zero acceleration, for all the static objects the acceleration is zero. If the moving object will show zero acceleration, then that means the object stops. There is no zero acceleration for the dynamic objects.
Complete step by step answer
$\Rightarrow F=ma$, where $F$ is the force acting on the object, $m$ is the mass of the object and $a$ is the acceleration of the object. In this equation, the force acting on the object is directly proportional to the acceleration when the mass of the object is constant. Usually, there is no change in the mass of the object, so that the force is always directly proportional to the acceleration. In the force equation, the mass of the object is never zero because every object must have the mass, so the mass never is zero. So, there is only one possibility to make the acceleration zero by using the force only. The object is moving with some force in one direction, to make the force zero, there must be the same amount of force in the opposite direction.
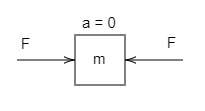
For example, if the book is on the table, one student moves the book by giving some amount of force in one direction, in that case there is an acceleration of the book. If suppose there are two students, both are giving the same amount of force on the book but in different directions, in this condition the book will never move on either side, so there is no acceleration. In the second case two equal forces are acting in opposite directions, so the force will become zero $F = 0$, then the force equation is, $0 = ma$, from this equation, $a = 0$ .
So, I agree with Soni's statement.
Note
From the diagram mentioned above it is very clear that both the same amount of the force is acting in opposite directions to each other, so the magnitude of the one force is solved by the magnitude of the other force. In this diagram, both the forces push the mass. In other cases, if both the forces pull the mass when the two forces are in opposite directions, then also the acceleration is zero.
There is a possibility for the objects with the zero acceleration, for all the static objects the acceleration is zero. If the moving object will show zero acceleration, then that means the object stops. There is no zero acceleration for the dynamic objects.
Complete step by step answer
$\Rightarrow F=ma$, where $F$ is the force acting on the object, $m$ is the mass of the object and $a$ is the acceleration of the object. In this equation, the force acting on the object is directly proportional to the acceleration when the mass of the object is constant. Usually, there is no change in the mass of the object, so that the force is always directly proportional to the acceleration. In the force equation, the mass of the object is never zero because every object must have the mass, so the mass never is zero. So, there is only one possibility to make the acceleration zero by using the force only. The object is moving with some force in one direction, to make the force zero, there must be the same amount of force in the opposite direction.

For example, if the book is on the table, one student moves the book by giving some amount of force in one direction, in that case there is an acceleration of the book. If suppose there are two students, both are giving the same amount of force on the book but in different directions, in this condition the book will never move on either side, so there is no acceleration. In the second case two equal forces are acting in opposite directions, so the force will become zero $F = 0$, then the force equation is, $0 = ma$, from this equation, $a = 0$ .
So, I agree with Soni's statement.
Note
From the diagram mentioned above it is very clear that both the same amount of the force is acting in opposite directions to each other, so the magnitude of the one force is solved by the magnitude of the other force. In this diagram, both the forces push the mass. In other cases, if both the forces pull the mass when the two forces are in opposite directions, then also the acceleration is zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




