
Somaesthetic area lies in
(a) Frontal lobe
(b) Temporal lobe
(c) Parietal lobe
(d) Occipital lobe
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: The love has postcentral sulcus with the posterior boundary of the somatosensory cortex and the posterior zone with the remaining areas has a posterior parietal cortex. The lobe is divided into visual processing sulcus.
Complete answer:
The sensory area in the brain has four areas: primary sensory area, secondary sensory area, sensory association area, and higher association areas. The primary sensory areas are divided into three major parts: somesthetic area, visual area, and auditory area. The somesthetic area is further divided into two primary and secondary areas. The primary somesthetic area localizes, analyses, and discriminates in different modalities of cutaneous senses like touch, pressure, position, and vibration senses. The secondary somesthetic area receives pain sensation and other modalities of cutaneous sensation. The Somesthitic association area occupies the superior parietal lobule and extends onto the medical surface of Brodmann areas 5 and 7.
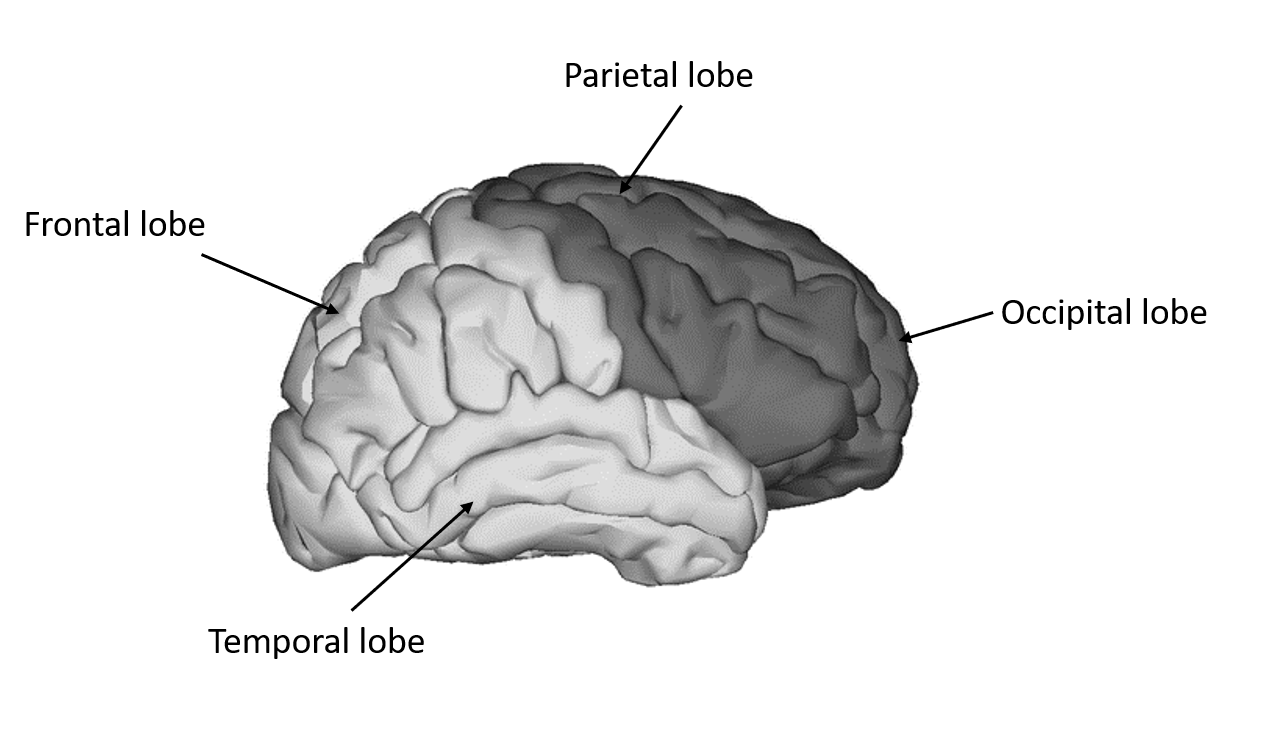
- The parietal cortex is considered as one of the most complex regions of the human brain which is responsible for the integration of various stimuli.
- The parietal cortex receives, correlates, analyze primary sensory information to interpret stimulus and aid in discrimination and recognition.
- The parietal lobes are subdivided into the postcentral sulcus and intraparietal sulcus.
- Boundaries of the parietal lobe
Dorsally by the cingulate gyrus
Posterior border: Parieto- Occipital sulcus
Anterior border: Central Fissure
Ventral border: Sylvian Fissure
So, the correct answer is, ‘(c) Parietal lobe.’
Note:
- Parietal lobe syndrome in the dominant hemisphere consists of two syndrome apraxias and Gerstmann’s syndrome.
- Apraxias is the inability to carry out an action in response to verbal command in the absence of problems with comparison, impairment of motor function.
- Gerstmann’s syndrome causes impaired calculation, left- right confusion, finger agnosia, dysgraphia.
Complete answer:
The sensory area in the brain has four areas: primary sensory area, secondary sensory area, sensory association area, and higher association areas. The primary sensory areas are divided into three major parts: somesthetic area, visual area, and auditory area. The somesthetic area is further divided into two primary and secondary areas. The primary somesthetic area localizes, analyses, and discriminates in different modalities of cutaneous senses like touch, pressure, position, and vibration senses. The secondary somesthetic area receives pain sensation and other modalities of cutaneous sensation. The Somesthitic association area occupies the superior parietal lobule and extends onto the medical surface of Brodmann areas 5 and 7.

- The parietal cortex is considered as one of the most complex regions of the human brain which is responsible for the integration of various stimuli.
- The parietal cortex receives, correlates, analyze primary sensory information to interpret stimulus and aid in discrimination and recognition.
- The parietal lobes are subdivided into the postcentral sulcus and intraparietal sulcus.
- Boundaries of the parietal lobe
Dorsally by the cingulate gyrus
Posterior border: Parieto- Occipital sulcus
Anterior border: Central Fissure
Ventral border: Sylvian Fissure
So, the correct answer is, ‘(c) Parietal lobe.’
Note:
- Parietal lobe syndrome in the dominant hemisphere consists of two syndrome apraxias and Gerstmann’s syndrome.
- Apraxias is the inability to carry out an action in response to verbal command in the absence of problems with comparison, impairment of motor function.
- Gerstmann’s syndrome causes impaired calculation, left- right confusion, finger agnosia, dysgraphia.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




