
How do you solve ${{x}^{2}}-12x+36=25$ by completing the square?
Answer
546k+ views
Hint: In the problem they have mentioned to use the method of completing the square. We know that the method of completing the square is used to solve or find the roots of a quadratic equation. So first we will check whether the given equation is a quadratic equation or not. We can observe that some value is there at RHS, so we will shift it to LHS and simplify it. If the given equation is a quadratic equation and which is in the form of $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$, then we will go to the further steps. In the first step we will divide the given equation with the coefficient of ${{x}^{2}}$ to get the coefficient of ${{x}^{2}}$ as $1$. In the step two we will add and subtract the square of the half of the coefficient of $x$ in the above equation and rearrange the obtained equation, then we will apply the formula either ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+2ab+{{b}^{2}}$ or ${{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-2ab+{{b}^{2}}$ based the obtained equation in step two. In step three we will simplify and move the constants to another side of the equation. In step four we will apply square roots on both sides of the equation and simplify it to get the value of $x$.
Complete step by step solution:
Given equation, ${{x}^{2}}-12x+36=25$
Shifting the term $25$ which is right hand side to left hand side, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-12x+36-25=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-12x+11=0 \\
\end{align}$
We can clearly see that the above equation is a quadratic equation, so we can use the method of completing squares to solve the given equation.
Comparing the given equation with $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$, then we will get
$a=1$, $b=-12$, $c=11$.
We have the value $a=1$, so there is no need to divide the given equation with any other coefficient.
In the above equation the coefficient of $x$ is $-12$. Adding the square of half of the coefficient of $x$ in the above equation, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-12x+11+{{\left( -\dfrac{12}{2} \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( -\dfrac{12}{2} \right)}^{2}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-12x+11+{{6}^{2}}-{{6}^{2}}=0 \\
\end{align}$
Rearranging and rewriting the terms in the above equation, then we will get
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-2\left( 6 \right)\left( x \right)+{{6}^{2}}+11-36=0$
We know that ${{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-2ab+{{b}^{2}}$, then we will get
$\Rightarrow {{\left( x-6 \right)}^{2}}-25=0$
Taking the constants in the above equation to the other side of the equation, then we will get
$\Rightarrow {{\left( x-6 \right)}^{2}}=25$
Applying square root on both side of the above equation, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{{{\left( x-6 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{25} \\
& \Rightarrow x-6=\pm 5 \\
\end{align}$
From the above equation, we will get
$x-6=5$ or $x-6=-5$
Simplifying the above equations, then
$\begin{align}
& x=5+6 \\
& \Rightarrow x=11 \\
\end{align}$ or $\begin{align}
& x=-5+6 \\
& \Rightarrow x=1 \\
\end{align}$
Hence the roots of the given equation ${{x}^{2}}-12x+36=25$ are $x=1,11$. The graph of the given equation with the roots is given below
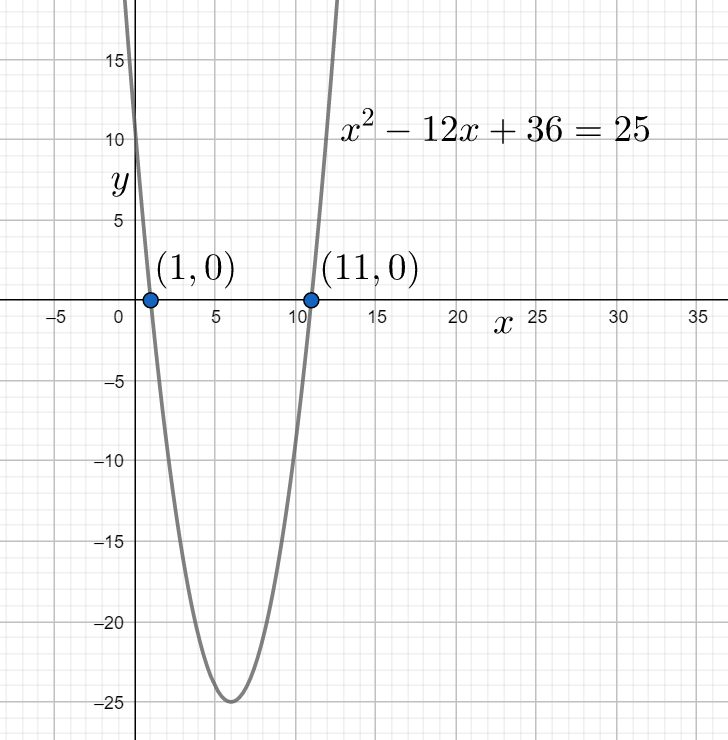
Note: In the method of completing squares most of the students forget to consider the $\pm $ sign after applying the square root to the equation. It is not the correct way to solve the equation since if you don’t consider the sign then we only get one root, but for a quadratic equation we have two roots. So, it is necessary to consider the $\pm $ sign in method of completing squares.
Complete step by step solution:
Given equation, ${{x}^{2}}-12x+36=25$
Shifting the term $25$ which is right hand side to left hand side, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-12x+36-25=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-12x+11=0 \\
\end{align}$
We can clearly see that the above equation is a quadratic equation, so we can use the method of completing squares to solve the given equation.
Comparing the given equation with $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$, then we will get
$a=1$, $b=-12$, $c=11$.
We have the value $a=1$, so there is no need to divide the given equation with any other coefficient.
In the above equation the coefficient of $x$ is $-12$. Adding the square of half of the coefficient of $x$ in the above equation, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-12x+11+{{\left( -\dfrac{12}{2} \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( -\dfrac{12}{2} \right)}^{2}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-12x+11+{{6}^{2}}-{{6}^{2}}=0 \\
\end{align}$
Rearranging and rewriting the terms in the above equation, then we will get
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-2\left( 6 \right)\left( x \right)+{{6}^{2}}+11-36=0$
We know that ${{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-2ab+{{b}^{2}}$, then we will get
$\Rightarrow {{\left( x-6 \right)}^{2}}-25=0$
Taking the constants in the above equation to the other side of the equation, then we will get
$\Rightarrow {{\left( x-6 \right)}^{2}}=25$
Applying square root on both side of the above equation, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{{{\left( x-6 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{25} \\
& \Rightarrow x-6=\pm 5 \\
\end{align}$
From the above equation, we will get
$x-6=5$ or $x-6=-5$
Simplifying the above equations, then
$\begin{align}
& x=5+6 \\
& \Rightarrow x=11 \\
\end{align}$ or $\begin{align}
& x=-5+6 \\
& \Rightarrow x=1 \\
\end{align}$
Hence the roots of the given equation ${{x}^{2}}-12x+36=25$ are $x=1,11$. The graph of the given equation with the roots is given below

Note: In the method of completing squares most of the students forget to consider the $\pm $ sign after applying the square root to the equation. It is not the correct way to solve the equation since if you don’t consider the sign then we only get one root, but for a quadratic equation we have two roots. So, it is necessary to consider the $\pm $ sign in method of completing squares.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




