
How do you solve the system of equations \[x+y=3\] , \[x-y=1\] by graphing?
Answer
561k+ views
Hint: The given equations are of straight lines in the \[x-y\], \[2-D\] coordinate system. From the given two equations we clearly observe that with a little manipulation we can convert them into the “Intercept form” of the equations, whose general form is defined by:
\[\dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}=1\]
Here, \[a\] and \[b\] are \[x\] and \[y\] intercepts respectively. The two equations hence transformed into the standard form, makes the graph plotting simpler. After plotting the respective lines on the graph paper, their point of intersection is located. This point of intersection of the two straight lines is the solution of the system of linear equations.
Complete step by step answer:
The two equations are first transformed into the "Intercept form", by dividing the first equation by \[3\] and the second equation by \[1\] . After transformation, we write the equations as:
\[\dfrac{x}{3}+\dfrac{y}{3}=1\text{ }\cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \text{ eqn 1}\]
\[\dfrac{x}{1}-\dfrac{y}{1}=1\text{ }\cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \text{ eqn 2}\]
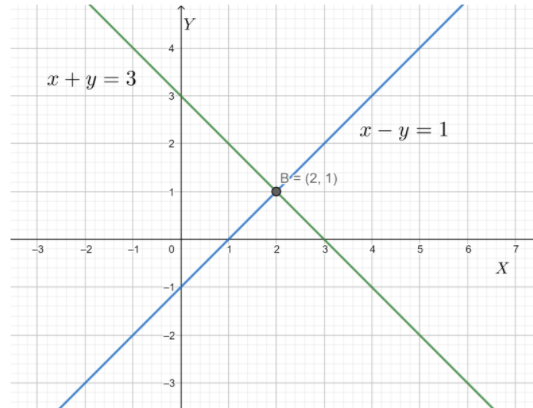
We can further transform the second equation as \[\dfrac{x}{1}+\dfrac{y}{-1}=1\] . Therefore, we draw the first line with x and y intercepts as \[3\] each and the second line with x-intercept \[1\] and y-intercept \[\left( -1 \right)\] . We thus plot the graph on Geogebra, providing the “Intercept form” of the two linear equations. The point of intersection of the pair of straight lines is located on the graph and is noted down. It comes out to be \[\left( 2,1 \right)\] . The point of intersection of two straight lines, is the only point that lies on both the lines. In other words, it is the only point that satisfies both the linear equations, i.e. it is the only solution of the given system of linear equations.
Note:
We must be very careful while transforming the given equations into their standardized form, especially with the negative and positive signs. Apart from the intercept form, other forms may also be considered for transformation, which depends solely on the equation. For example, this problem can also be solved using the slope-intercept form, but the above-shown method is the simplest and easy to understand. The proper scale must be used for accurate identification of the point of intersection.
\[\dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}=1\]
Here, \[a\] and \[b\] are \[x\] and \[y\] intercepts respectively. The two equations hence transformed into the standard form, makes the graph plotting simpler. After plotting the respective lines on the graph paper, their point of intersection is located. This point of intersection of the two straight lines is the solution of the system of linear equations.
Complete step by step answer:
The two equations are first transformed into the "Intercept form", by dividing the first equation by \[3\] and the second equation by \[1\] . After transformation, we write the equations as:
\[\dfrac{x}{3}+\dfrac{y}{3}=1\text{ }\cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \text{ eqn 1}\]
\[\dfrac{x}{1}-\dfrac{y}{1}=1\text{ }\cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \text{ eqn 2}\]
We can further transform the second equation as \[\dfrac{x}{1}+\dfrac{y}{-1}=1\] . Therefore, we draw the first line with x and y intercepts as \[3\] each and the second line with x-intercept \[1\] and y-intercept \[\left( -1 \right)\] . We thus plot the graph on Geogebra, providing the “Intercept form” of the two linear equations. The point of intersection of the pair of straight lines is located on the graph and is noted down. It comes out to be \[\left( 2,1 \right)\] . The point of intersection of two straight lines, is the only point that lies on both the lines. In other words, it is the only point that satisfies both the linear equations, i.e. it is the only solution of the given system of linear equations.

Note:
We must be very careful while transforming the given equations into their standardized form, especially with the negative and positive signs. Apart from the intercept form, other forms may also be considered for transformation, which depends solely on the equation. For example, this problem can also be solved using the slope-intercept form, but the above-shown method is the simplest and easy to understand. The proper scale must be used for accurate identification of the point of intersection.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




