
How do you solve the system of equations $2x + y = 6$ and $ - 2x - y = 6$?
Answer
547.5k+ views
Hint: First we have to make the first linear equation in Slope-intercept form and then calculate the value of $y$ for any two arbitrary values of $x$. Next make a table of these values of $x$ and $y$. Next plot the obtained points on the graph paper and draw a line passing through these points. Now repeat the process with the second equation and determine the solution of the given system of equations using the graph obtained.
Formula used:
Slope Intercept of a line:
The equation of a line with slope $m$ and making an intercept $c$ on $y$-axis is $y = mx + c$.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we have to move $2x$ to the right side of the equation, $2x + y = 6$. Thus, subtracting $2x$ from both sides of the equation.
$y = 6 - 2x$
Now, we have to calculate the value of $y$ for any two arbitrary values of $x$. Thus, finding the value of $y$ when $x = 1$ and $x = 2$.
When $x = 1$, $y = 6 - 2 = 4$
When $x = 2$, $y = 6 - 4 = 2$
Now we have to make a table of these values of $x$ and $y$.
Now we have to plot the points $A\left( {1,4} \right)$ and $B\left( {2,2} \right)$ on the graph paper and draw a line passing through $A$ and $B$.
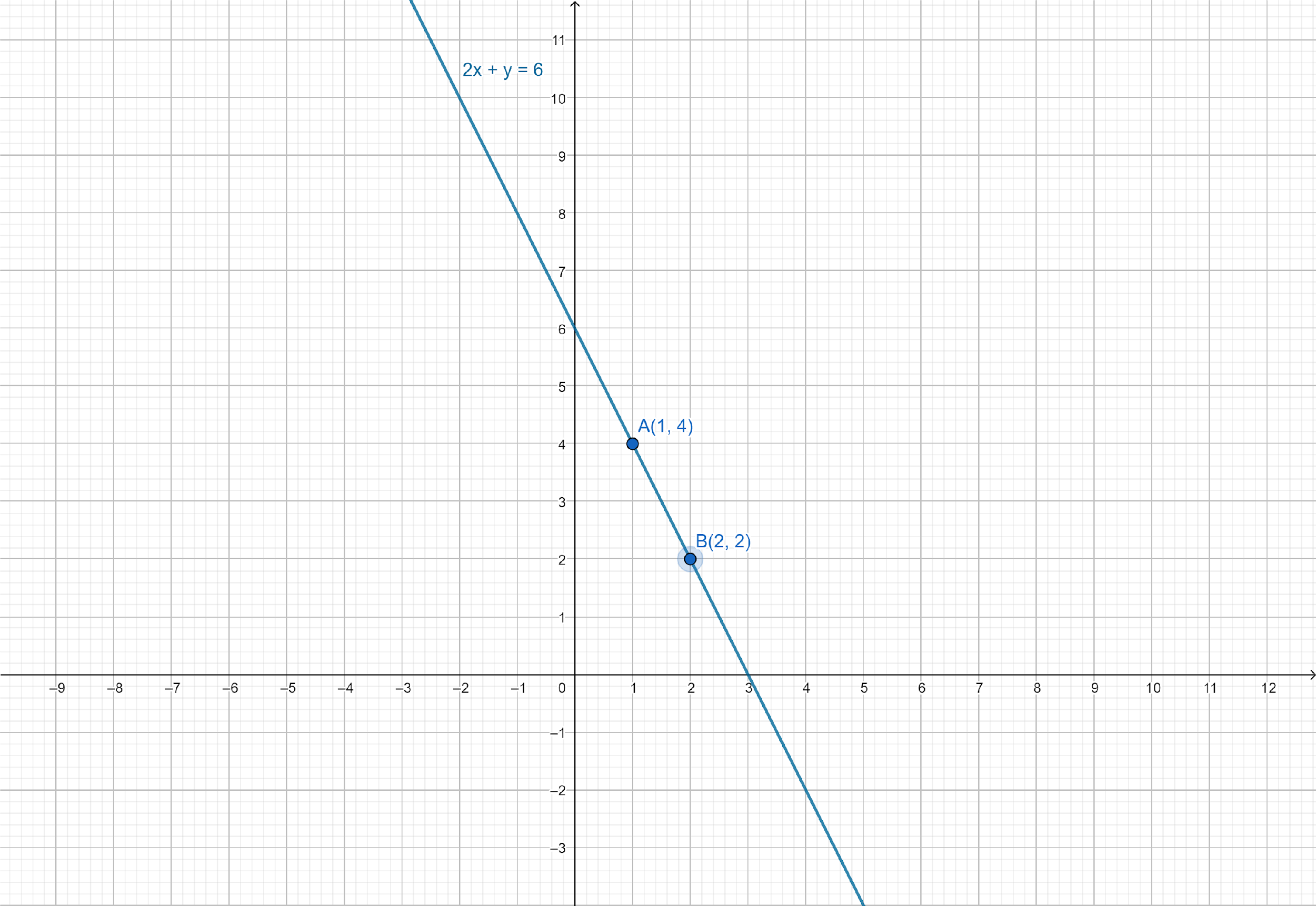
Now we have to make the second equation in Slope-intercept form. Thus, multiply both sides of the equation by $ - 1$.
$2x + y = - 6$
Subtract $2x$ from both sides of the equation, we get
$y = - 6 - 2x$
Now, we have to calculate the value of $y$ for any two arbitrary values of $x$. Thus, finding the value of $y$ when $x = 0$ and $x = - 1$.
When $x = 0$, $y = - 6$
When $x = - 1$, $y = - 6 + 2 = - 4$
Now we have to make a table of these values of $x$ and $y$.
Now we have to plot the points $C\left( {0, - 6} \right)$ and $D\left( { - 1, - 4} \right)$ on the graph paper and draw a line passing through $C$ and $D$.
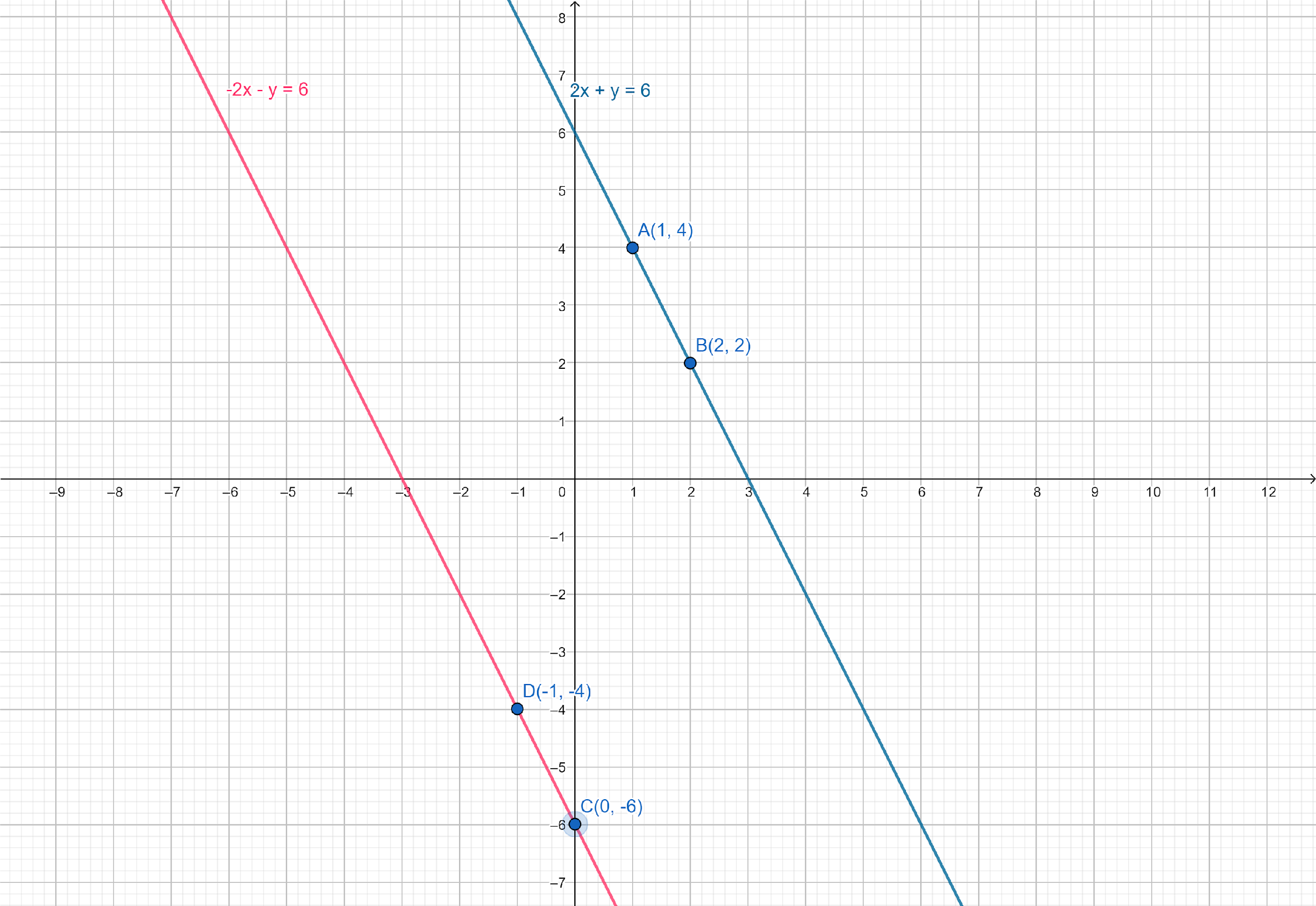
We find the lines represented by equations $2x + y = 6$ and $ - 2x - y = 6$ are parallel. So, the two lines have no common point.
Hence, the given system of equations has no solution.
Note: We can directly check whether the system of equations is inconsistent or not using below property:
The system of equations ${a_1}x + {b_1}y + {c_1} = 0$ and ${a_2}x + {b_2}y + {c_2} = 0$ is inconsistent, if
$\dfrac{{{a_1}}}{{{a_2}}} = \dfrac{{{b_1}}}{{{b_2}}} \ne \dfrac{{{c_1}}}{{{c_2}}}$……(i)
Step by step solution:
First, we have to compare $2x + y = 6$ and $ - 2x - y = 6$ with ${a_1}x + {b_1}y + {c_1} = 0$ and ${a_2}x + {b_2}y + {c_2} = 0$.
${a_1} = 2,{b_1} = 1,{c_1} = - 6$ and ${a_2} = - 2,{b_2} = - 1,{c_2} = - 6$
Now we have to find $\dfrac{{{a_1}}}{{{a_2}}},\dfrac{{{b_1}}}{{{b_2}}},\dfrac{{{c_1}}}{{{c_2}}}$ and check whether it satisfy (i) or not.
$\dfrac{{{a_1}}}{{{a_2}}} = \dfrac{2}{{ - 2}} = - 1$, $\dfrac{{{b_1}}}{{{b_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{{ - 1}} = - 1$ and $\dfrac{{{c_1}}}{{{c_2}}} = \dfrac{{ - 6}}{{ - 6}} = 1$
Therefore, $\dfrac{{{a_1}}}{{{a_2}}} = \dfrac{{{b_1}}}{{{b_2}}} \ne \dfrac{{{c_1}}}{{{c_2}}}$.
Hence, the given system of equations has no solution.
Formula used:
Slope Intercept of a line:
The equation of a line with slope $m$ and making an intercept $c$ on $y$-axis is $y = mx + c$.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we have to move $2x$ to the right side of the equation, $2x + y = 6$. Thus, subtracting $2x$ from both sides of the equation.
$y = 6 - 2x$
Now, we have to calculate the value of $y$ for any two arbitrary values of $x$. Thus, finding the value of $y$ when $x = 1$ and $x = 2$.
When $x = 1$, $y = 6 - 2 = 4$
When $x = 2$, $y = 6 - 4 = 2$
Now we have to make a table of these values of $x$ and $y$.
| $x$ | $1$ | $2$ |
| $y$ | $4$ | $2$ |
Now we have to plot the points $A\left( {1,4} \right)$ and $B\left( {2,2} \right)$ on the graph paper and draw a line passing through $A$ and $B$.

Now we have to make the second equation in Slope-intercept form. Thus, multiply both sides of the equation by $ - 1$.
$2x + y = - 6$
Subtract $2x$ from both sides of the equation, we get
$y = - 6 - 2x$
Now, we have to calculate the value of $y$ for any two arbitrary values of $x$. Thus, finding the value of $y$ when $x = 0$ and $x = - 1$.
When $x = 0$, $y = - 6$
When $x = - 1$, $y = - 6 + 2 = - 4$
Now we have to make a table of these values of $x$ and $y$.
| $x$ | $0$ | $ - 1$ |
| $y$ | $ - 6$ | $ - 4$ |
Now we have to plot the points $C\left( {0, - 6} \right)$ and $D\left( { - 1, - 4} \right)$ on the graph paper and draw a line passing through $C$ and $D$.

We find the lines represented by equations $2x + y = 6$ and $ - 2x - y = 6$ are parallel. So, the two lines have no common point.
Hence, the given system of equations has no solution.
Note: We can directly check whether the system of equations is inconsistent or not using below property:
The system of equations ${a_1}x + {b_1}y + {c_1} = 0$ and ${a_2}x + {b_2}y + {c_2} = 0$ is inconsistent, if
$\dfrac{{{a_1}}}{{{a_2}}} = \dfrac{{{b_1}}}{{{b_2}}} \ne \dfrac{{{c_1}}}{{{c_2}}}$……(i)
Step by step solution:
First, we have to compare $2x + y = 6$ and $ - 2x - y = 6$ with ${a_1}x + {b_1}y + {c_1} = 0$ and ${a_2}x + {b_2}y + {c_2} = 0$.
${a_1} = 2,{b_1} = 1,{c_1} = - 6$ and ${a_2} = - 2,{b_2} = - 1,{c_2} = - 6$
Now we have to find $\dfrac{{{a_1}}}{{{a_2}}},\dfrac{{{b_1}}}{{{b_2}}},\dfrac{{{c_1}}}{{{c_2}}}$ and check whether it satisfy (i) or not.
$\dfrac{{{a_1}}}{{{a_2}}} = \dfrac{2}{{ - 2}} = - 1$, $\dfrac{{{b_1}}}{{{b_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{{ - 1}} = - 1$ and $\dfrac{{{c_1}}}{{{c_2}}} = \dfrac{{ - 6}}{{ - 6}} = 1$
Therefore, $\dfrac{{{a_1}}}{{{a_2}}} = \dfrac{{{b_1}}}{{{b_2}}} \ne \dfrac{{{c_1}}}{{{c_2}}}$.
Hence, the given system of equations has no solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What type of cell is found in the Seminiferous tub class 10 biology CBSE

What are the public facilities provided by the government? Also explain each facility




