
How do you solve the right triangle given the hypotenuse is 7 and it is a 45-45-90 triangle?
Answer
538.2k+ views
Hint: If we represent these angles diagrammatically, we can see that the acute angles are equal. If the acute angles in a right-angled triangle are equal, then the length of the two sides adjacent to the right angle are equal. We use the Pythagoras theorem to find the length of the remaining sides of a right-angled triangle.
Complete step by step solution:
The right-angled triangle in the question can be represented diagrammatically as follows:
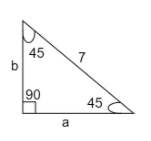
A 45-45-90 triangle has two $45{}^\circ$ angles and a $90{}^\circ$ angle.
We have been given a right-angled triangle whose length of hypotenuse is 7 and need to find the length of the remaining sides.
We will be using Pythagoras Theorem to find out the length of the remaining sides of a right-angled triangle.
Pythagoras Theorem:
This Theorem defines the relationship between the three sides of a right-angled triangle.
It states that the square of the hypotenuse of the right-angled triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides of a triangle.
The other two sides of a triangle are designated as the base and height of a triangle respectively.
According to Pythagoras Theorem,
$\Rightarrow {{\left( hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}={{\left( base \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( height \right)}^{2}}$
According to the given question,
The acute angles in the right-angled triangle are equal.
If the two acute angles of a right-angled triangle are equal, then the length of the two sides adjacent to the right angle are equal.
Here,
Hypotenuse = 7;
Base = a;
Height = b
From the above,
$\Rightarrow base=height$
which implies,
$\Rightarrow a=b$
Applying Pythagoras Theorem for the given right-angled triangle,
$\Rightarrow {{\left( hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}={{\left( base \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( height \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}={{\left( a \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( b \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( 7 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( a \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( b \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( 7 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( a \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( a \right)}^{2}}$
Let us now evaluate further.
$\Rightarrow {{\left( 7 \right)}^{2}}=2{{\left( a \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 49=2\times {{\left( a \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow a^2 = \dfrac{49}{2}$
$\Rightarrow a=\pm \sqrt{\dfrac{49}{2}}$
The negative value of $\sqrt{\dfrac{49}{2}}$is ignored because the length cannot be negative.
$\therefore a=\dfrac{7}{\sqrt{2}}$
As $a=b$,
$\therefore b=\dfrac{7}{\sqrt{2}}$
Therefore, the length of the base and height of the given right-angled triangle is $\dfrac{7}{\sqrt{2}}$.
Note: The length of the other two sides of 45-45-90 triangle can be easily found out by dividing the length of the hypotenuse by $\sqrt{2}$. The ratio of base: height: hypotenuse in 45-45-90 triangle is given by 1: 1:$\sqrt{2}$.Pythagoras theorem is valid only in the case of the right-angled triangle.
Complete step by step solution:
The right-angled triangle in the question can be represented diagrammatically as follows:

A 45-45-90 triangle has two $45{}^\circ$ angles and a $90{}^\circ$ angle.
We have been given a right-angled triangle whose length of hypotenuse is 7 and need to find the length of the remaining sides.
We will be using Pythagoras Theorem to find out the length of the remaining sides of a right-angled triangle.
Pythagoras Theorem:
This Theorem defines the relationship between the three sides of a right-angled triangle.
It states that the square of the hypotenuse of the right-angled triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides of a triangle.
The other two sides of a triangle are designated as the base and height of a triangle respectively.
According to Pythagoras Theorem,
$\Rightarrow {{\left( hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}={{\left( base \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( height \right)}^{2}}$
According to the given question,
The acute angles in the right-angled triangle are equal.
If the two acute angles of a right-angled triangle are equal, then the length of the two sides adjacent to the right angle are equal.
Here,
Hypotenuse = 7;
Base = a;
Height = b
From the above,
$\Rightarrow base=height$
which implies,
$\Rightarrow a=b$
Applying Pythagoras Theorem for the given right-angled triangle,
$\Rightarrow {{\left( hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}={{\left( base \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( height \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}={{\left( a \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( b \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( 7 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( a \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( b \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( 7 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( a \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( a \right)}^{2}}$
Let us now evaluate further.
$\Rightarrow {{\left( 7 \right)}^{2}}=2{{\left( a \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 49=2\times {{\left( a \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow a^2 = \dfrac{49}{2}$
$\Rightarrow a=\pm \sqrt{\dfrac{49}{2}}$
The negative value of $\sqrt{\dfrac{49}{2}}$is ignored because the length cannot be negative.
$\therefore a=\dfrac{7}{\sqrt{2}}$
As $a=b$,
$\therefore b=\dfrac{7}{\sqrt{2}}$
Therefore, the length of the base and height of the given right-angled triangle is $\dfrac{7}{\sqrt{2}}$.
Note: The length of the other two sides of 45-45-90 triangle can be easily found out by dividing the length of the hypotenuse by $\sqrt{2}$. The ratio of base: height: hypotenuse in 45-45-90 triangle is given by 1: 1:$\sqrt{2}$.Pythagoras theorem is valid only in the case of the right-angled triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Convert 40circ C to Fahrenheit A 104circ F B 107circ class 8 maths CBSE

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE





