
How do you solve the right triangle $a=117ft$, $b=16.35ft$?
Answer
537.9k+ views
Hint: We can assume the two lengths given to be the perpendicular and the base lengths respectively. The third side, the hypotenuse, can be determined by using the Pythagoras theorem. Then considering the sine of any of the angles of the triangle, apart from the right angle, we can determine the value of that angle. Finally, we can use the angle sum property to determine the value of the third angle as well.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that in a right triangle, one of the three angles is a right angle. One side is named as the perpendicular, the second as the base, and the third is the hypotenuse. Since the two given lengths of the sides a and b are not mentioned by these names, we assume a to be perpendicular length, and b to be the base length so that we can draw the triangle ABC as
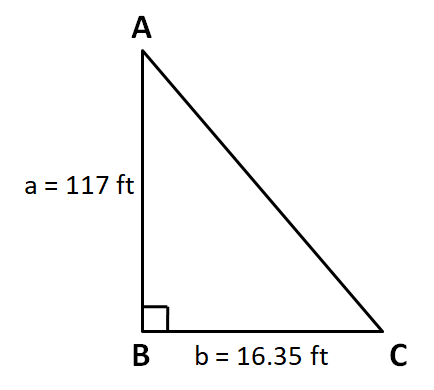
Let the dimension of the hypotenuse AC be $c\text{ }ft$.
Applying the Pythagoras theorem in the triangle ABC, we can write
$\Rightarrow A{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}$
Substituting $AB=a$, $BC=b$, and $AC=c$ in the above equation, we get
$\Rightarrow {{c}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}$
Now, according to the question, we can put $a=117ft$ and $b=16.35ft$ in the above equation to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{c}^{2}}={{117}^{2}}+{{16.35}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{c}^{2}}=13689+267.3225 \\
& \Rightarrow {{c}^{2}}=13965.3225 \\
\end{align}$
Taking square root both the sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow c=\sqrt{13965.3225} \\
& \Rightarrow c=118.17ft \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that the sine ratio is defined as
$\sin \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$
Therefore, for the triangle ABC we can write
$\Rightarrow \sin \angle BAC=\dfrac{BC}{AC}$
Putting $BC=b$ and $AC=c$
$\Rightarrow \sin \angle BAC=\dfrac{b}{c}$
Substituting $b=16.35ft$ and $c=118.17ft$ we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \sin \angle BAC=\dfrac{16.35}{118.17} \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \angle BAC=0.1384 \\
\end{align}$
Taking sine inverse both the sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle BAC={{\sin }^{-1}}\left( 0.1384 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \angle BAC={{7.95}^{\circ }}........\left( i \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, applying angle sum property in the triangle, we can write
$\Rightarrow \angle ABC+\angle ACB+\angle BAC={{180}^{\circ }}$
From the figure, we can see that $\angle ABC={{90}^{\circ }}$. Substituting this above, we get
$\Rightarrow {{90}^{\circ }}+\angle ACB+\angle BAC={{180}^{\circ }}$
Now, we substitute the equation (i) in the above equation to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{90}^{\circ }}+\angle ACB+{{7.95}^{\circ }}={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle ACB+{{97.95}^{\circ }}={{180}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
Finally, subtracting ${{97.95}^{\circ }}$ from both the sides, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle ACB+{{97.95}^{\circ }}-{{97.95}^{\circ }}={{180}^{\circ }}-{{97.95}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle ACB={{82.05}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Note: We must understand what the terms “perpendicular” and “base” mean in the definition of the trigonometric ratios. The perpendicular is the side opposite to the angle whose trigonometric ratio is being considered. And the base is the side adjacent to the angle.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that in a right triangle, one of the three angles is a right angle. One side is named as the perpendicular, the second as the base, and the third is the hypotenuse. Since the two given lengths of the sides a and b are not mentioned by these names, we assume a to be perpendicular length, and b to be the base length so that we can draw the triangle ABC as

Let the dimension of the hypotenuse AC be $c\text{ }ft$.
Applying the Pythagoras theorem in the triangle ABC, we can write
$\Rightarrow A{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}$
Substituting $AB=a$, $BC=b$, and $AC=c$ in the above equation, we get
$\Rightarrow {{c}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}$
Now, according to the question, we can put $a=117ft$ and $b=16.35ft$ in the above equation to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{c}^{2}}={{117}^{2}}+{{16.35}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{c}^{2}}=13689+267.3225 \\
& \Rightarrow {{c}^{2}}=13965.3225 \\
\end{align}$
Taking square root both the sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow c=\sqrt{13965.3225} \\
& \Rightarrow c=118.17ft \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that the sine ratio is defined as
$\sin \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$
Therefore, for the triangle ABC we can write
$\Rightarrow \sin \angle BAC=\dfrac{BC}{AC}$
Putting $BC=b$ and $AC=c$
$\Rightarrow \sin \angle BAC=\dfrac{b}{c}$
Substituting $b=16.35ft$ and $c=118.17ft$ we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \sin \angle BAC=\dfrac{16.35}{118.17} \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \angle BAC=0.1384 \\
\end{align}$
Taking sine inverse both the sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle BAC={{\sin }^{-1}}\left( 0.1384 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \angle BAC={{7.95}^{\circ }}........\left( i \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, applying angle sum property in the triangle, we can write
$\Rightarrow \angle ABC+\angle ACB+\angle BAC={{180}^{\circ }}$
From the figure, we can see that $\angle ABC={{90}^{\circ }}$. Substituting this above, we get
$\Rightarrow {{90}^{\circ }}+\angle ACB+\angle BAC={{180}^{\circ }}$
Now, we substitute the equation (i) in the above equation to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{90}^{\circ }}+\angle ACB+{{7.95}^{\circ }}={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle ACB+{{97.95}^{\circ }}={{180}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
Finally, subtracting ${{97.95}^{\circ }}$ from both the sides, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle ACB+{{97.95}^{\circ }}-{{97.95}^{\circ }}={{180}^{\circ }}-{{97.95}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle ACB={{82.05}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Note: We must understand what the terms “perpendicular” and “base” mean in the definition of the trigonometric ratios. The perpendicular is the side opposite to the angle whose trigonometric ratio is being considered. And the base is the side adjacent to the angle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
The draft of the Preamble of the Indian Constitution class 10 social science CBSE

Who gave "Inqilab Zindabad" slogan?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

What is the minimum age for fighting the election in class 10 social science CBSE

Write an application to the principal requesting five class 10 english CBSE

My birthday is June 27 a On b Into c Between d In class 10 english CBSE




