
How do you solve the polynomial inequality and state the answer in interval notation given $ 3{x^2} + 2x < {x^4} $ ?
Answer
543.9k+ views
Hint: In the given question, we are required to find the answer in interval notation to the inequality given to us in the problem itself. So, we first transpose or shift all the terms to one side of the equation and look for methods of simplification and factorization. We may also employ the wavy curve method that represents the graph of the function and helps us to solve the inequality graphically.
Complete step by step solution:
So, we are given the inequality $ 3{x^2} + 2x < {x^4} $ .
Shifting all the terms to the right side of the equation, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {x^4} - 3{x^2} - 2x > 0 $
$ \Rightarrow x\left( {{x^3} - 3x - 2} \right) > 0 $
Now, to solve the inequality, we first need to factorize the cubic expression written in brackets.
So, we have $ \left( {{x^3} - 3x - 2} \right) $ .
Hence, by hit and trial, we notice that for $ x = 2 $ , the value of the expression is $ 0 $ .
So, we infer that $ \left( {x - 2} \right) $ is a factor of $ \left( {{x^3} - 3x - 2} \right) $ .
So, we can divide $ \left( {{x^3} - 3x - 2} \right) $ by $ \left( {x - 2} \right) $ so as to find the other factors or we can either simply factorize $ \left( {{x^3} - 3x - 2} \right) $ .
So, $ \left( {{x^3} - 3x - 2} \right) = \left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {{x^2} + 2x + 1} \right) $
Condensing the quadratic factor $ \left( {{x^2} + 2x + 1} \right) $ into squares of binomial $ \left( {x + 1} \right) $ .
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^3} - 3x - 2} \right) = \left( {x - 2} \right){\left( {x + 1} \right)^2} $
Hence, getting back to the inequality, we get,
$ \Rightarrow x\left( {x - 2} \right){\left( {x + 1} \right)^2} > 0 $
Now, using the graphical method so as to find the intervals in which the inequality holds.
Graph of polynomial function $ x\left( {x - 2} \right){\left( {x + 1} \right)^2} $ is as follows:
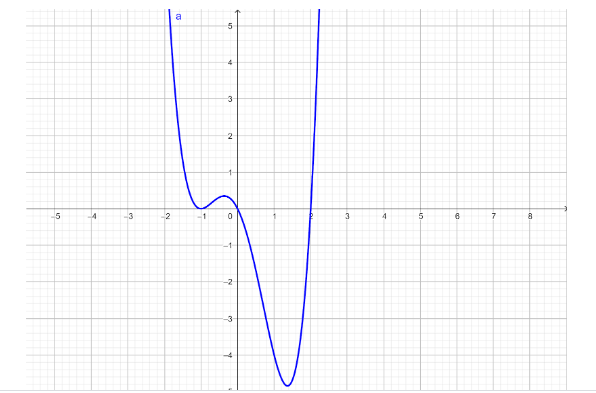
So, we can observe from the graph of polynomial function $ x\left( {x - 2} \right){\left( {x + 1} \right)^2} $ that the value of the function is positive for the intervals $ \left( { - \inf , - 1} \right) $ , $ \left( { - 1,0} \right) $ and $ \left( {2,\inf } \right) $ . We
So, the solution to the polynomial inequality $ 3{x^2} + 2x < {x^4} $ is the union of the intervals $ \left( { - \inf , - 1} \right) $ , $ \left( { - 1,0} \right) $ and $ \left( {2,\inf } \right) $ as the inequality $ 3{x^2} + 2x < {x^4} $ is same as $ {x^4} - 3{x^2} - 2x > 0 $ .
Note: So, these kinds of questions which require us to solve the two sided inequalities can be solved by following some basic algebraic rules such as transposition and factorization. Wavy curve methods may also be employed in some complex inequalities.
Complete step by step solution:
So, we are given the inequality $ 3{x^2} + 2x < {x^4} $ .
Shifting all the terms to the right side of the equation, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {x^4} - 3{x^2} - 2x > 0 $
$ \Rightarrow x\left( {{x^3} - 3x - 2} \right) > 0 $
Now, to solve the inequality, we first need to factorize the cubic expression written in brackets.
So, we have $ \left( {{x^3} - 3x - 2} \right) $ .
Hence, by hit and trial, we notice that for $ x = 2 $ , the value of the expression is $ 0 $ .
So, we infer that $ \left( {x - 2} \right) $ is a factor of $ \left( {{x^3} - 3x - 2} \right) $ .
So, we can divide $ \left( {{x^3} - 3x - 2} \right) $ by $ \left( {x - 2} \right) $ so as to find the other factors or we can either simply factorize $ \left( {{x^3} - 3x - 2} \right) $ .
So, $ \left( {{x^3} - 3x - 2} \right) = \left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {{x^2} + 2x + 1} \right) $
Condensing the quadratic factor $ \left( {{x^2} + 2x + 1} \right) $ into squares of binomial $ \left( {x + 1} \right) $ .
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^3} - 3x - 2} \right) = \left( {x - 2} \right){\left( {x + 1} \right)^2} $
Hence, getting back to the inequality, we get,
$ \Rightarrow x\left( {x - 2} \right){\left( {x + 1} \right)^2} > 0 $
Now, using the graphical method so as to find the intervals in which the inequality holds.
Graph of polynomial function $ x\left( {x - 2} \right){\left( {x + 1} \right)^2} $ is as follows:

So, we can observe from the graph of polynomial function $ x\left( {x - 2} \right){\left( {x + 1} \right)^2} $ that the value of the function is positive for the intervals $ \left( { - \inf , - 1} \right) $ , $ \left( { - 1,0} \right) $ and $ \left( {2,\inf } \right) $ . We
So, the solution to the polynomial inequality $ 3{x^2} + 2x < {x^4} $ is the union of the intervals $ \left( { - \inf , - 1} \right) $ , $ \left( { - 1,0} \right) $ and $ \left( {2,\inf } \right) $ as the inequality $ 3{x^2} + 2x < {x^4} $ is same as $ {x^4} - 3{x^2} - 2x > 0 $ .
Note: So, these kinds of questions which require us to solve the two sided inequalities can be solved by following some basic algebraic rules such as transposition and factorization. Wavy curve methods may also be employed in some complex inequalities.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





