
How do you solve the inequality\[\dfrac{1}{{x + 1}} \succ \dfrac{3}{{x - 2}}?\]
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint:The given question describes the operation of addition/ subtraction/ multiplication/ division. In this question, we have to find the value of\[x\]. At first, we would arrange the fraction terms to one side. After that, we have to find the final condition to find the value \[x\]. In this question, we have to use a number line to assume the value of\[x\] and compare it with the final condition.
Complete step by step solution:
In this question, we have to solve the following inequality terms,
\[\dfrac{1}{{x + 1}} \succ \dfrac{3}{{x - 2}}\]
First, we have to arrange the fraction terms into one side of the equation. So, the above
equation can also be written as,
\[
\dfrac{3}{{x - 2}} \prec \dfrac{1}{{x + 1}} \\
\dfrac{3}{{x - 2}} - \dfrac{1}{{x + 1}} \prec 0 \\
\]
Using cross-multiplication, we get
\[
\dfrac{{\left( {3\left( {x + 1} \right)} \right) - \left( {1\left( {x - 2} \right)} \right)}}{{\left( {x - 2}
\right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0 \\
\dfrac{{3x + 3 - x + 2}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0 \\
\]
Let’s solve the numerator using arithmetic operations,
\[
\dfrac{{3x + 3 - x + 2}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0 \\
\dfrac{{2x + 5}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0 \\
\]
So, the final condition is,
\[\dfrac{{2x + 5}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0\]\[ \to \left( 1 \right)\]
For finding the value of\[x\] we have to assume,
(Case: 1) \[2x + 5 = 0\]
(Case: 2) \[x - 2 = 0\]
(Case: 3) \[x + 1 = 0\]
In case: 1 we get,
\[
2x + 5 = 0 \\
2x = - 5 \\
x = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{2} \\
\]
In case: 2 we get,
\[
x - 2 = 0 \\
x = 2 \\
\]
In vase: 3 we get,
\[
x + 1 = 0 \\
x = - 1 \\
\]
So finally we have,
\[x = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{2},x = 2\]and\[x = - 1\]
Let’s mark the above-mentioned values in the number line,

We have three options for\[x\]value. Now we need to find the correct\[x\]value among the three answers. Here we have intervals \[\left( { - \infty ,\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}} \right),\left( {\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}, - 1} \right),\left( { - 1,2} \right)and\left( {2,\infty } \right)\]
To find the correct interval we have to assume anyone value with each interval and substitute that value in the equation\[\left( 1 \right)\]
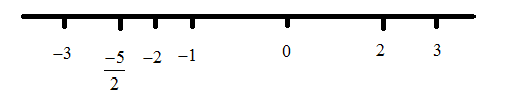
In the interval \[\left( { - \infty ,\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}} \right)\] we assume\[ - 3\]. So, the final
condition\[\left( 1 \right)\]becomes,
\[\left( 1 \right) \to \dfrac{{2x + 5}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0\]
Where, \[x = - 3\]
\[\dfrac{{2\left( { - 3} \right) + 5}}{{\left( { - 3 - 2} \right)\left( { - 3 + 1} \right)}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{{ - 6 + 5}}{{\left( { - 5} \right)\left( { - 2} \right)}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{{ - 1}}{{10}} \prec 0\]
The above equation satisfies the condition.
In the interval\[\left( {\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}, - 1} \right)\], we assume \[x = - 2\]
\[\left( 1 \right) \to \dfrac{{2x + 5}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{{2\left( { - 2} \right) + 5}}{{\left( { - 2 - 2} \right)\left( { - 2 + 1} \right)}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{{ - 4 + 5}}{{ - 1 \times - 4}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{1}{4} \prec 0\]
The above equation doesn’t satisfy the condition.
In the interval\[\left( { - 1,2} \right)\], we assume\[x = 0\]
\[\left( 1 \right) \to \dfrac{{2x + 5}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{{2\left( 0 \right) + 5}}{{\left( {0 - 2} \right)\left( {0 + 1} \right)}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2} \prec 0\]
The above equation satisfies the condition.
In the interval\[\left( {2,\infty } \right)\], we assume\[x = 3\]
\[\left( 1 \right) \to \dfrac{{2x + 5}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{{2\left( 3 \right) + 5}}{{\left( {3 - 2} \right)\left( {3 + 1} \right)}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{{6 + 5}}{{4 \times 1}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{{11}}{4} \prec 0\]
The above equation doesn’t satisfy the condition.
So, the final answer is\[x \in \left( { - \infty ,\left( {\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}} \right)} \right) \cup \left( { - 1,2} \right)\]
Note: The total limit of the number line is\[\left( { - \infty , + \infty } \right)\]. In this type of question we should use the arithmetic operation of addition/ subtraction/ multiplication/ division/ cross multiplication. Take care when assuming the value of\[x\]in the number line. If the\[x\]value is a fraction number, convert it into a decimal number for easy calculation.
Complete step by step solution:
In this question, we have to solve the following inequality terms,
\[\dfrac{1}{{x + 1}} \succ \dfrac{3}{{x - 2}}\]
First, we have to arrange the fraction terms into one side of the equation. So, the above
equation can also be written as,
\[
\dfrac{3}{{x - 2}} \prec \dfrac{1}{{x + 1}} \\
\dfrac{3}{{x - 2}} - \dfrac{1}{{x + 1}} \prec 0 \\
\]
Using cross-multiplication, we get
\[
\dfrac{{\left( {3\left( {x + 1} \right)} \right) - \left( {1\left( {x - 2} \right)} \right)}}{{\left( {x - 2}
\right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0 \\
\dfrac{{3x + 3 - x + 2}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0 \\
\]
Let’s solve the numerator using arithmetic operations,
\[
\dfrac{{3x + 3 - x + 2}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0 \\
\dfrac{{2x + 5}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0 \\
\]
So, the final condition is,
\[\dfrac{{2x + 5}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0\]\[ \to \left( 1 \right)\]
For finding the value of\[x\] we have to assume,
(Case: 1) \[2x + 5 = 0\]
(Case: 2) \[x - 2 = 0\]
(Case: 3) \[x + 1 = 0\]
In case: 1 we get,
\[
2x + 5 = 0 \\
2x = - 5 \\
x = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{2} \\
\]
In case: 2 we get,
\[
x - 2 = 0 \\
x = 2 \\
\]
In vase: 3 we get,
\[
x + 1 = 0 \\
x = - 1 \\
\]
So finally we have,
\[x = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{2},x = 2\]and\[x = - 1\]
Let’s mark the above-mentioned values in the number line,

We have three options for\[x\]value. Now we need to find the correct\[x\]value among the three answers. Here we have intervals \[\left( { - \infty ,\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}} \right),\left( {\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}, - 1} \right),\left( { - 1,2} \right)and\left( {2,\infty } \right)\]
To find the correct interval we have to assume anyone value with each interval and substitute that value in the equation\[\left( 1 \right)\]
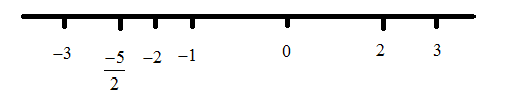
In the interval \[\left( { - \infty ,\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}} \right)\] we assume\[ - 3\]. So, the final
condition\[\left( 1 \right)\]becomes,
\[\left( 1 \right) \to \dfrac{{2x + 5}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0\]
Where, \[x = - 3\]
\[\dfrac{{2\left( { - 3} \right) + 5}}{{\left( { - 3 - 2} \right)\left( { - 3 + 1} \right)}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{{ - 6 + 5}}{{\left( { - 5} \right)\left( { - 2} \right)}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{{ - 1}}{{10}} \prec 0\]
The above equation satisfies the condition.
In the interval\[\left( {\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}, - 1} \right)\], we assume \[x = - 2\]
\[\left( 1 \right) \to \dfrac{{2x + 5}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{{2\left( { - 2} \right) + 5}}{{\left( { - 2 - 2} \right)\left( { - 2 + 1} \right)}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{{ - 4 + 5}}{{ - 1 \times - 4}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{1}{4} \prec 0\]
The above equation doesn’t satisfy the condition.
In the interval\[\left( { - 1,2} \right)\], we assume\[x = 0\]
\[\left( 1 \right) \to \dfrac{{2x + 5}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{{2\left( 0 \right) + 5}}{{\left( {0 - 2} \right)\left( {0 + 1} \right)}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2} \prec 0\]
The above equation satisfies the condition.
In the interval\[\left( {2,\infty } \right)\], we assume\[x = 3\]
\[\left( 1 \right) \to \dfrac{{2x + 5}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{{2\left( 3 \right) + 5}}{{\left( {3 - 2} \right)\left( {3 + 1} \right)}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{{6 + 5}}{{4 \times 1}} \prec 0\]
\[\dfrac{{11}}{4} \prec 0\]
The above equation doesn’t satisfy the condition.
So, the final answer is\[x \in \left( { - \infty ,\left( {\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}} \right)} \right) \cup \left( { - 1,2} \right)\]
Note: The total limit of the number line is\[\left( { - \infty , + \infty } \right)\]. In this type of question we should use the arithmetic operation of addition/ subtraction/ multiplication/ division/ cross multiplication. Take care when assuming the value of\[x\]in the number line. If the\[x\]value is a fraction number, convert it into a decimal number for easy calculation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




