
Solve the inequality: $\sin \left( {3x} \right) < \sin x$.
Answer
521.1k+ views
Hint: In the given question, we have to solve the trigonometric inequality given to us in the problem itself. So, we have made use of the algebraic and trigonometric formulae and rules in order to simplify the inequality and find a solution set to the given trigonometric inequality. One must know that we can multiply a positive number without changing the sign of inequality.
Complete step by step solution:
In the given question, we are provided with a trigonometric inequality $\sin \left( {3x} \right) < \sin x$.
Now, we know the trigonometric formula for the triple angle of sine as $\sin \left( {3x} \right) = 3\sin x - 4{\sin ^3}x$. So, substituting the value of $\sin \left( {3x} \right)$ in the given trigonometric inequality, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 3\sin x - 4{\sin ^3}x < \sin x$
Taking all the terms to the right side of the inequality, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 0 < \sin x + 4{\sin ^3}x - 3\sin x$
Simplifying the expression further, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 4{\sin ^3}x - 2\sin x > 0$
Taking common terms outside of the bracket, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 2\sin x\left( {2{{\sin }^2}x - 1} \right) > 0$
Taking $2$ common from the bracket and simplifying the expression, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 4\sin x\left( {{{\sin }^2}x - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) > 0$
Using the algebraic identity ${a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a - b} \right)\left( {a + b} \right)$, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 4\sin x\left( {\sin x - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)\left( {\sin x + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right) > 0$
Now, replacing $\sin x$ as t in the inequality, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 4t\left( {t - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)\left( {t + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right) > 0$
Now, we can solve the above inequality using the wavy curve method in which we draw a rough sketch of the function given on the left side of the inequality and see the regions where it is positive.
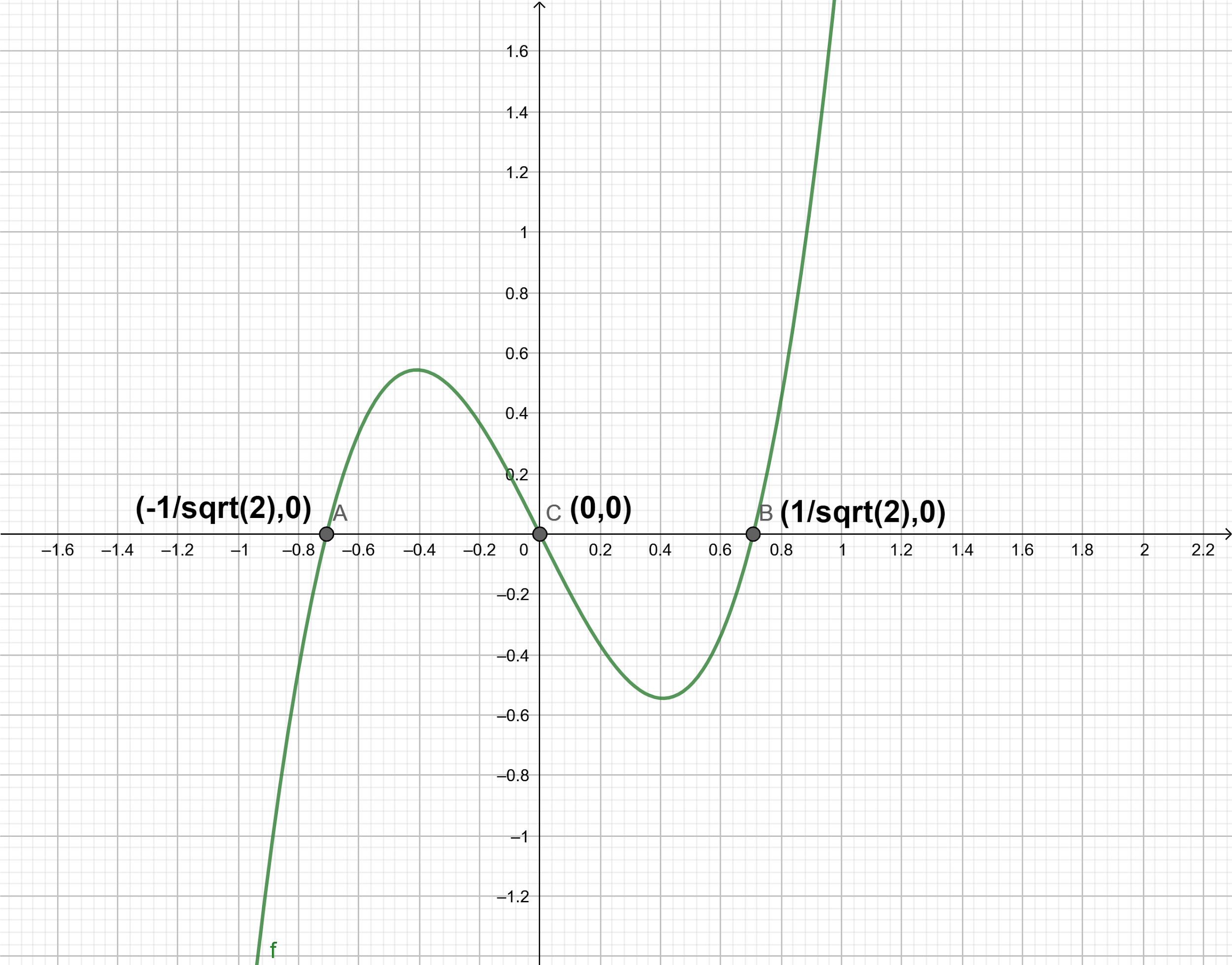
So, we get that the expression $4t\left( {t - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)\left( {t + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)$ is positive for $ - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} < t < 0$ and $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} < t$. So, substituting back $\sin x$ as t, we get, $ - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} < \sin x < 0$ and $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} < \sin x$.
We also know that the value of $\sin x$ lies from $ - 1$ to $1$. Hence, the solution of the inequality $\sin \left( {3x} \right) < \sin x$ are the values of x for which $ - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} < \sin x < 0$ and $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} < \sin x < 1$.
Therefore, taking the union of solutions sets of the inequality $\sin \left( {3x} \right) < \sin x$, we get the solution set as $\sin x \in ( - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }},0) \cup (\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }},1]$.
Now, taking into consideration the interval of $\left[ {0,2\pi } \right]$, we find the solution set for the given trigonometric inequality. So, $\sin x \in ( - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }},0) \cup (\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }},1]$.
We know that sine function is positive in first and second quadrats and is negative in third and fourth quadrants. We also know that the value of $\sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right) = \sin \left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right) = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$ and $\sin \left( {\dfrac{{5\pi }}{4}} \right) = \sin \left( {\dfrac{{7\pi }}{4}} \right) = - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$.
Hence, for $\sin x \in ( - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }},0) \cup (\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }},1]$, x belongs to \[\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4},\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right) \cup \left( {\pi ,\dfrac{{5\pi }}{4}} \right) \cup \left( {\dfrac{{7\pi }}{4},2\pi } \right)\].
So, the solution set of the inequality $\sin \left( {3x} \right) < \sin x$ in the interval $\left[ {0,2\pi } \right]$ is \[\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4},\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right) \cup \left( {\pi ,\dfrac{{5\pi }}{4}} \right) \cup \left( {\dfrac{{7\pi }}{4},2\pi } \right)\]
Note:
One must know that when multiplying both sides of the inequality by a positive integer does not change the sign of inequality but when we multiply both sides of the inequality by a negative number, the signs of inequality change. One must know basic trigonometric formulae and identities in order to solve such questions involving trigonometric inequality. One should take care of the calculations and should recheck them to verify the final answer.
Complete step by step solution:
In the given question, we are provided with a trigonometric inequality $\sin \left( {3x} \right) < \sin x$.
Now, we know the trigonometric formula for the triple angle of sine as $\sin \left( {3x} \right) = 3\sin x - 4{\sin ^3}x$. So, substituting the value of $\sin \left( {3x} \right)$ in the given trigonometric inequality, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 3\sin x - 4{\sin ^3}x < \sin x$
Taking all the terms to the right side of the inequality, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 0 < \sin x + 4{\sin ^3}x - 3\sin x$
Simplifying the expression further, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 4{\sin ^3}x - 2\sin x > 0$
Taking common terms outside of the bracket, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 2\sin x\left( {2{{\sin }^2}x - 1} \right) > 0$
Taking $2$ common from the bracket and simplifying the expression, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 4\sin x\left( {{{\sin }^2}x - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) > 0$
Using the algebraic identity ${a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a - b} \right)\left( {a + b} \right)$, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 4\sin x\left( {\sin x - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)\left( {\sin x + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right) > 0$
Now, replacing $\sin x$ as t in the inequality, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 4t\left( {t - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)\left( {t + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right) > 0$
Now, we can solve the above inequality using the wavy curve method in which we draw a rough sketch of the function given on the left side of the inequality and see the regions where it is positive.

So, we get that the expression $4t\left( {t - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)\left( {t + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)$ is positive for $ - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} < t < 0$ and $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} < t$. So, substituting back $\sin x$ as t, we get, $ - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} < \sin x < 0$ and $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} < \sin x$.
We also know that the value of $\sin x$ lies from $ - 1$ to $1$. Hence, the solution of the inequality $\sin \left( {3x} \right) < \sin x$ are the values of x for which $ - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} < \sin x < 0$ and $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} < \sin x < 1$.
Therefore, taking the union of solutions sets of the inequality $\sin \left( {3x} \right) < \sin x$, we get the solution set as $\sin x \in ( - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }},0) \cup (\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }},1]$.
Now, taking into consideration the interval of $\left[ {0,2\pi } \right]$, we find the solution set for the given trigonometric inequality. So, $\sin x \in ( - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }},0) \cup (\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }},1]$.
We know that sine function is positive in first and second quadrats and is negative in third and fourth quadrants. We also know that the value of $\sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right) = \sin \left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right) = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$ and $\sin \left( {\dfrac{{5\pi }}{4}} \right) = \sin \left( {\dfrac{{7\pi }}{4}} \right) = - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$.
Hence, for $\sin x \in ( - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }},0) \cup (\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }},1]$, x belongs to \[\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4},\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right) \cup \left( {\pi ,\dfrac{{5\pi }}{4}} \right) \cup \left( {\dfrac{{7\pi }}{4},2\pi } \right)\].
So, the solution set of the inequality $\sin \left( {3x} \right) < \sin x$ in the interval $\left[ {0,2\pi } \right]$ is \[\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4},\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right) \cup \left( {\pi ,\dfrac{{5\pi }}{4}} \right) \cup \left( {\dfrac{{7\pi }}{4},2\pi } \right)\]
Note:
One must know that when multiplying both sides of the inequality by a positive integer does not change the sign of inequality but when we multiply both sides of the inequality by a negative number, the signs of inequality change. One must know basic trigonometric formulae and identities in order to solve such questions involving trigonometric inequality. One should take care of the calculations and should recheck them to verify the final answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 11 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




