
Solve the given inequalities graphically:
$3x + 2y \leqslant 12,x \geqslant 1,y \geqslant 2$
Answer
500.7k+ views
Hint: First, we will solve the inequality given in the question and from the solution of inequality, we will plot those points on a graph. After plotting the point, we will connect those points by a straight line. For each line, we will check whether it’s inequality at origin and accordingly shade that portion on the graph.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given inequalities are $3x + 2y \leqslant 12,x \geqslant 1,y \geqslant 2$.
The solution for $3x + 2y \leqslant 12$ is
Let’s, x = 0, then
$2y = 12$
$\Rightarrow y=6$
Now, let’s y=0, then
$3x=12$
$\Rightarrow x=4$
i.e., $(0,6)$ and $(4,0)$.
Plotting all these points on a graph,
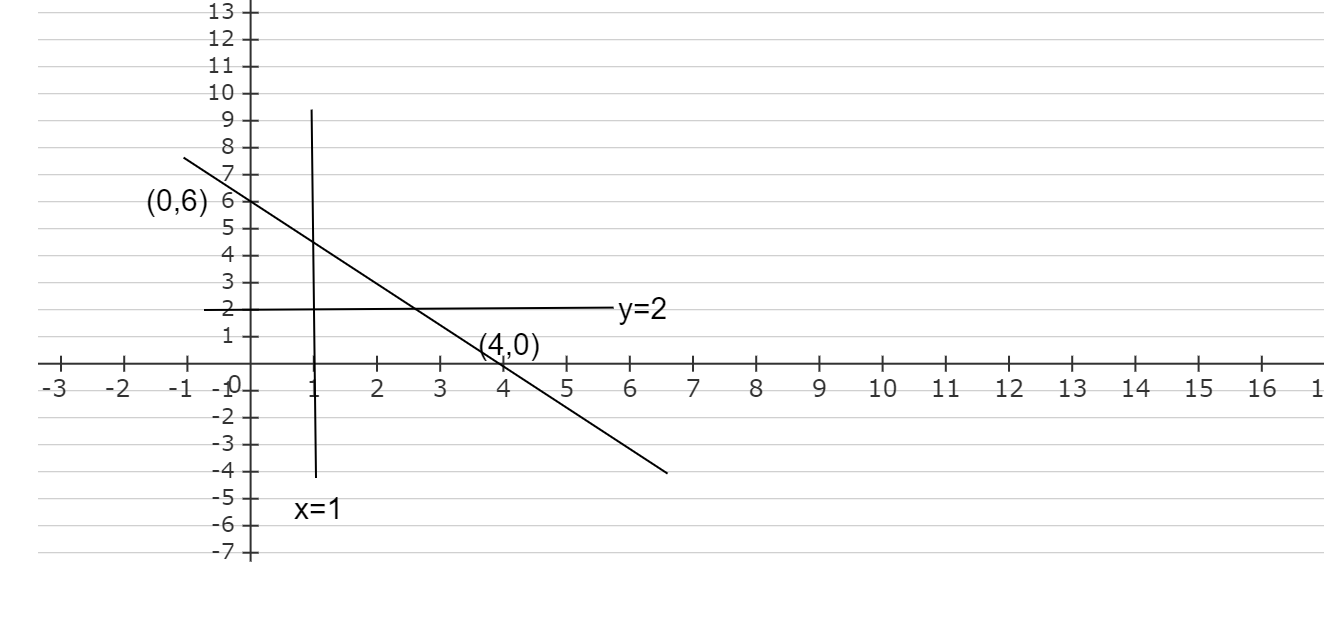
Now we will check the position of origin with respect to the inequalities,
For $3x + 2y \leqslant 12$ at $(0,0)$ , $3(0) + 2(0) \leqslant 12 < 0$. Hence $(0,0)$ lies in the inequality $3x + 2y \leqslant 12$.
For $x \geqslant 1$ at $(0,0)$ , $0 - 1 < 0$. Hence $(0,0)$ lies does not lie in the inequality $x \geqslant 1$.
For $y \geqslant 2$ at $(0,0)$ , $0 - 2 < 0$. Hence $(0,0)$ lies does not lie in the inequality $y \geqslant 2$.
The inequality $3x + 2y \leqslant 12$is towards the origin and $x \geqslant 1$ and $y \geqslant 2$ are away from the origin.
After shading the inequality part in the graph, we get the graph as,
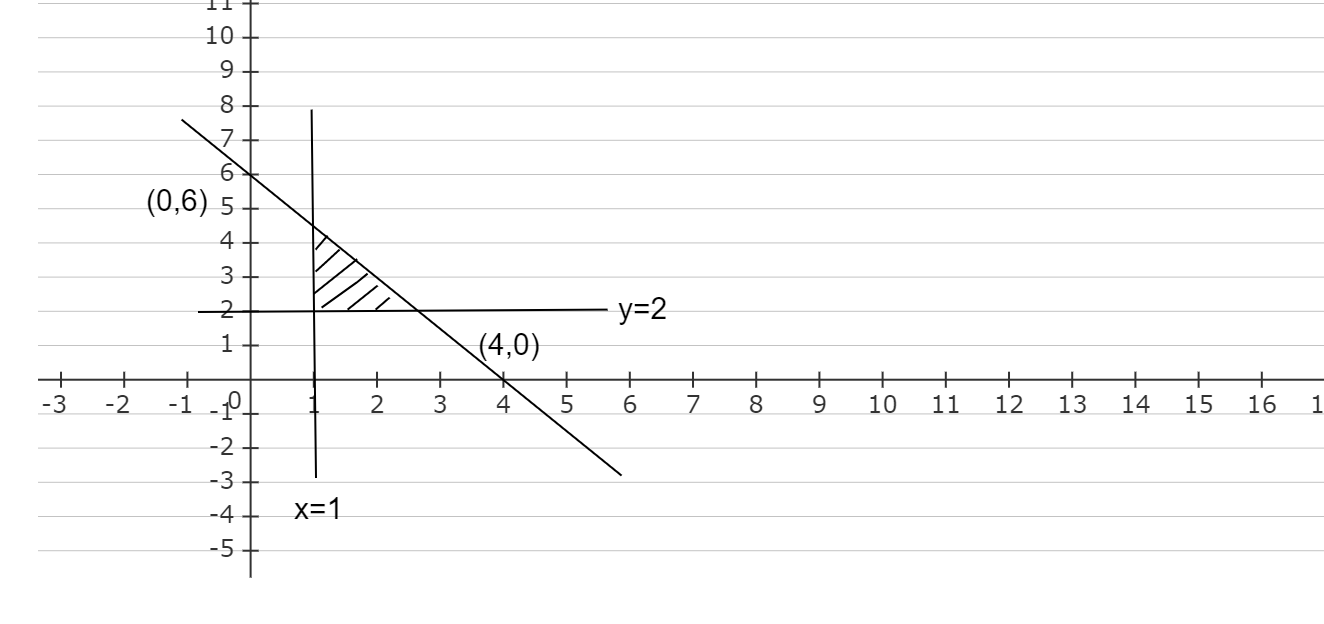
The shaded part in the above graph represents the solution of the given inequalities.
Note: Any solution to an inequality is the fee of that variable which makes inequality a true statement. For example, assume we've an inequality of $x < 5$ . In one of these cases, all the values of x which are much less than $5$ make this inequality a true inequality. While fixing inequalities we want to preserve a few policies in thought, identical numbers may be added or subtracted from both aspects of the inequality. Both facets of inequality may be extended (or divided) by the identical wonderful quantity. However, when both aspects are increased or divided by means of a bad quantity, then the sign of inequality is reversed. These operations do not affect inequality and may be used to simplify inequality for us.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given inequalities are $3x + 2y \leqslant 12,x \geqslant 1,y \geqslant 2$.
The solution for $3x + 2y \leqslant 12$ is
Let’s, x = 0, then
$2y = 12$
$\Rightarrow y=6$
Now, let’s y=0, then
$3x=12$
$\Rightarrow x=4$
| $x$ | $0$ | $4$ |
| $y$ | $6$ | $0$ |
i.e., $(0,6)$ and $(4,0)$.
Plotting all these points on a graph,

Now we will check the position of origin with respect to the inequalities,
For $3x + 2y \leqslant 12$ at $(0,0)$ , $3(0) + 2(0) \leqslant 12 < 0$. Hence $(0,0)$ lies in the inequality $3x + 2y \leqslant 12$.
For $x \geqslant 1$ at $(0,0)$ , $0 - 1 < 0$. Hence $(0,0)$ lies does not lie in the inequality $x \geqslant 1$.
For $y \geqslant 2$ at $(0,0)$ , $0 - 2 < 0$. Hence $(0,0)$ lies does not lie in the inequality $y \geqslant 2$.
The inequality $3x + 2y \leqslant 12$is towards the origin and $x \geqslant 1$ and $y \geqslant 2$ are away from the origin.
After shading the inequality part in the graph, we get the graph as,

The shaded part in the above graph represents the solution of the given inequalities.
Note: Any solution to an inequality is the fee of that variable which makes inequality a true statement. For example, assume we've an inequality of $x < 5$ . In one of these cases, all the values of x which are much less than $5$ make this inequality a true inequality. While fixing inequalities we want to preserve a few policies in thought, identical numbers may be added or subtracted from both aspects of the inequality. Both facets of inequality may be extended (or divided) by the identical wonderful quantity. However, when both aspects are increased or divided by means of a bad quantity, then the sign of inequality is reversed. These operations do not affect inequality and may be used to simplify inequality for us.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




