
How do you solve the following linear system equations: – 3x + 2y = 12 and 5x + 2y = – 4.
Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint: We are asked to solve the linear equations – 3x + 2y = 12 and 5x + 2y = – 4. To find the solution, we will first see which are the possible ways to solve such problems and then after that we will use one method to solve. We will find the value of x and y one by one. We will use the graphical method to understand the different ways to solve our problem.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We are given the linear equations as – 3x + 2y = 12 and 5x + 2y = – 4. We can see that our equations are linear and it has two variables x and y. So it is a linear equation in two variables. We have to find the solution of these two equations. We know that to find the solution of a linear equation in two variables, there are various methods like Elimination method, Substitution Method, Cross – Multiplication Method, Graphical method. To find the solution, we can use any of the following and by each method, we will always have the answer as the same.
We will use the elimination method in this. We will eliminate any one of the variables and then solve for the remaining variables. To eliminate any variable, we will make their coefficient equal by multiplying the equation with the appropriate constant and then we will add or subtract as required to eliminate. Once the variable is eliminated, then we will solve for the other variable. Now, we have,
\[\begin{align}
& -3x+2y=12.....\left( i \right) \\
& 5x+2y=-4......\left( ii \right) \\
\end{align}\]
We can see that the coefficient of y in both the equation is the same. So, we will eliminate y here as it will lessen our calculation. Now, we will subtract equation (i) from equation (ii). So, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& 5x+2y=-4 \\
& -3x+2y=12 \\
& \underline{+\text{ }-\text{ }-} \\
& 8x=-16 \\
\end{align}\]
So, we get y in eliminated and we are left with 8x = – 16. Now, dividing both the sides by 8, we get,
\[\Rightarrow x=-2\]
So, we get the value of x as 2.
We put x = – 2 in any of the two equations and solve for y. Putting x = – 2 in equation (i), we get,
\[\Rightarrow -3\left( -2 \right)+2y=12\]
\[\Rightarrow 6+2y=12\]
Solving further, we get,
\[\Rightarrow 2y=6\]
Dividing both the sides by 2, we get,
\[\Rightarrow y=3\]
So, we get, y = 3.
So, the solution for – 3x + 2y = 12 and 5x + 2y = – 4 is x = – 2 and y = 3.
Note: Another way we can use to solve is the graphical method in which we will sketch the graph of – 3x + 2y = 12 and 5x + 2y = – 4 in the same axis and the point where these two will intersect is referred to as the solution of our problem. Now we will sketch – 3x + 2y = 12 and 5x + 2y = – 4 on graph and we get,
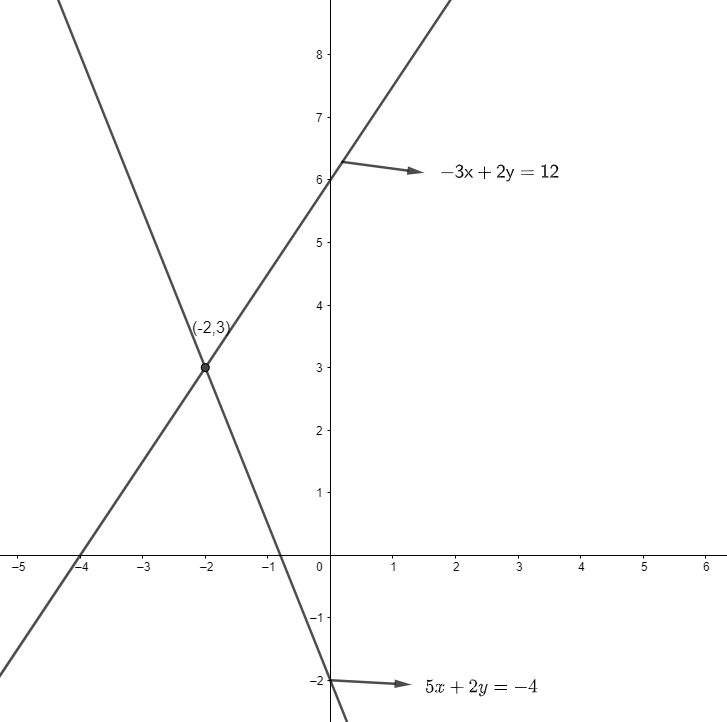
So, the point of intersection is (– 2, 3), so the solution is x = – 2 and y = 3.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We are given the linear equations as – 3x + 2y = 12 and 5x + 2y = – 4. We can see that our equations are linear and it has two variables x and y. So it is a linear equation in two variables. We have to find the solution of these two equations. We know that to find the solution of a linear equation in two variables, there are various methods like Elimination method, Substitution Method, Cross – Multiplication Method, Graphical method. To find the solution, we can use any of the following and by each method, we will always have the answer as the same.
We will use the elimination method in this. We will eliminate any one of the variables and then solve for the remaining variables. To eliminate any variable, we will make their coefficient equal by multiplying the equation with the appropriate constant and then we will add or subtract as required to eliminate. Once the variable is eliminated, then we will solve for the other variable. Now, we have,
\[\begin{align}
& -3x+2y=12.....\left( i \right) \\
& 5x+2y=-4......\left( ii \right) \\
\end{align}\]
We can see that the coefficient of y in both the equation is the same. So, we will eliminate y here as it will lessen our calculation. Now, we will subtract equation (i) from equation (ii). So, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& 5x+2y=-4 \\
& -3x+2y=12 \\
& \underline{+\text{ }-\text{ }-} \\
& 8x=-16 \\
\end{align}\]
So, we get y in eliminated and we are left with 8x = – 16. Now, dividing both the sides by 8, we get,
\[\Rightarrow x=-2\]
So, we get the value of x as 2.
We put x = – 2 in any of the two equations and solve for y. Putting x = – 2 in equation (i), we get,
\[\Rightarrow -3\left( -2 \right)+2y=12\]
\[\Rightarrow 6+2y=12\]
Solving further, we get,
\[\Rightarrow 2y=6\]
Dividing both the sides by 2, we get,
\[\Rightarrow y=3\]
So, we get, y = 3.
So, the solution for – 3x + 2y = 12 and 5x + 2y = – 4 is x = – 2 and y = 3.
Note: Another way we can use to solve is the graphical method in which we will sketch the graph of – 3x + 2y = 12 and 5x + 2y = – 4 in the same axis and the point where these two will intersect is referred to as the solution of our problem. Now we will sketch – 3x + 2y = 12 and 5x + 2y = – 4 on graph and we get,

So, the point of intersection is (– 2, 3), so the solution is x = – 2 and y = 3.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




