
Solve the following inequation and represent the solution set on a number line.
\[-8\dfrac{1}{2}<-\dfrac{1}{2}-4x\le 7\dfrac{1}{2},x\in R\]
Answer
602.1k+ views
Hint: At first, break the given inequality into two inequalities and then do basic operations keeping the rules of the inequality to find the ranges of x and finally find the intersection of the range.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we are given an inequation and we have to find the solution set of x and represent it on a number line. The inequation given in the question is,
\[-8\dfrac{1}{2}<-\dfrac{1}{2}-4x\le 7\dfrac{1}{2},\text{ where }x\in R\]
So, at first, let’s break the inequation into two in equations as,
\[-8\dfrac{1}{2}<-\dfrac{1}{2}-4x\text{ and }\dfrac{-1}{2}-4x\le 7\dfrac{1}{2}\]
We will solve the inequality one by one. So, the first inequality is,
\[-8\dfrac{1}{2}<-\dfrac{1}{2}-4x\]
We will add (4x + 9) to both sides of the inequality, the sides of the inequality will not change. So, we get,
\[4x+9-8\dfrac{1}{2}<-\dfrac{1}{2}-4x+4x+9\]
\[\Rightarrow 4x+\dfrac{1}{2}<8\dfrac{1}{2}\]
Now, we will subtract \[\dfrac{1}{2}\] from both the sides of the inequality, the sides of the inequality will not change, so we get,
\[4x+\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}<8\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow 4x<8\]
Now, we will divide by 4 to the sides, so we get,
\[x<\dfrac{8}{4}\]
\[\Rightarrow x<2\]
Now, we will go for the second inequality,
\[\text{ }\dfrac{-1}{2}-4x\le 7\dfrac{1}{2}\]
So, we will first add \[\dfrac{1}{2}\] to both the sides, so we get,
\[\dfrac{-1}{2}-4x+\dfrac{1}{2}\le 7\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow -4x\le 8\]
Now, we will divide by – 4 to both sides, here the side of the inequality changes. So, we get,
\[x\ge -2\]
In the earlier inequality, we got x < 2 and in the latter one, we get \[x\ge -2\] which can be written as, \[-2\le x<2.\] So, in the number line it will be,
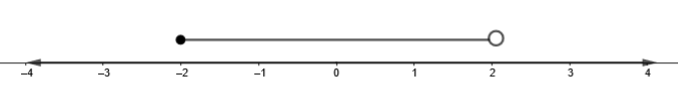
Note: The sides of the inequality only change in two cases. The first one is when the inequality is multiplied by a negative number and the second one is when divided by a negative number.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we are given an inequation and we have to find the solution set of x and represent it on a number line. The inequation given in the question is,
\[-8\dfrac{1}{2}<-\dfrac{1}{2}-4x\le 7\dfrac{1}{2},\text{ where }x\in R\]
So, at first, let’s break the inequation into two in equations as,
\[-8\dfrac{1}{2}<-\dfrac{1}{2}-4x\text{ and }\dfrac{-1}{2}-4x\le 7\dfrac{1}{2}\]
We will solve the inequality one by one. So, the first inequality is,
\[-8\dfrac{1}{2}<-\dfrac{1}{2}-4x\]
We will add (4x + 9) to both sides of the inequality, the sides of the inequality will not change. So, we get,
\[4x+9-8\dfrac{1}{2}<-\dfrac{1}{2}-4x+4x+9\]
\[\Rightarrow 4x+\dfrac{1}{2}<8\dfrac{1}{2}\]
Now, we will subtract \[\dfrac{1}{2}\] from both the sides of the inequality, the sides of the inequality will not change, so we get,
\[4x+\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}<8\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow 4x<8\]
Now, we will divide by 4 to the sides, so we get,
\[x<\dfrac{8}{4}\]
\[\Rightarrow x<2\]
Now, we will go for the second inequality,
\[\text{ }\dfrac{-1}{2}-4x\le 7\dfrac{1}{2}\]
So, we will first add \[\dfrac{1}{2}\] to both the sides, so we get,
\[\dfrac{-1}{2}-4x+\dfrac{1}{2}\le 7\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow -4x\le 8\]
Now, we will divide by – 4 to both sides, here the side of the inequality changes. So, we get,
\[x\ge -2\]
In the earlier inequality, we got x < 2 and in the latter one, we get \[x\ge -2\] which can be written as, \[-2\le x<2.\] So, in the number line it will be,

Note: The sides of the inequality only change in two cases. The first one is when the inequality is multiplied by a negative number and the second one is when divided by a negative number.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




