
Solve the following inequality:
$\left| {\dfrac{{2x - 1}}{{x - 1}}} \right| > 2$
Answer
501k+ views
Hint: First we will split the modulus function over the inequality. That is we will take once the positive value of the modulus function, then the negative value for the modulus function over the inequality. Then on solving the two inequalities we will get two answers. Then, by comparing the two answers we will get the more appropriate and valid answer for our given question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, the given inequality is,
$\left| {\dfrac{{2x - 1}}{{x - 1}}} \right| > 2$
Now, we will take the positive value for the modulus function and once negative value.
Therefore, first taking the positive value, we get,
$\left( {\dfrac{{2x - 1}}{{x - 1}}} \right) > 2$
Subtracting $2$ from both sides of the inequality, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2x - 1}}{{x - 1}} - 2 > 0$
Now, taking LCM on left hand side, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2x - 1 - 2\left( {x - 1} \right)}}{{x - 1}} > 0$
Now, opening the brackets and simplifying, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2x - 1 - 2x + 2}}{{x - 1}} > 0$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{x - 1}} > 0$
Therefore, here for $\dfrac{1}{{x - 1}}$ to be greater than $0$, $x - 1$ must be greater than $0$.
That is, $x - 1 > 0$
$ \Rightarrow x > 1$
We can write it as, $x \in \left( {1,\infty } \right) - - - \left( 1 \right)$
Now, taking the negative value of the modulus function, we get,
$ - \left( {\dfrac{{2x - 1}}{{x - 1}}} \right) > 2$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{ - 2x + 1}}{{x - 1}}} \right) > 2$
Subtracting $2$ from both sides of the inequality, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{ - 2x + 1}}{{x - 1}}} \right) - 2 > 0$
Now, taking LCM on left hand side, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - 2x + 1 - 2\left( {x - 1} \right)}}{{x - 1}} > 0$
Now, opening the brackets and simplifying, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - 2x + 1 - 2x + 2}}{{x - 1}} > 0$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - 4x + 3}}{{x - 1}} > 0$
Taking $ - 1$ common from the numerator, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - (4x - 3)}}{{x - 1}} > 0$
Now, multiplying both sides with $ - 1$, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{4x - 3}}{{x - 1}} < 0$
[Since, multiplying $ - 1$ over the inequality changes the direction of the inequality]
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{x - \dfrac{3}{4}}}{{x - 1}} < 0$
Since, here $x - 1 \ne 0$.
So, we can multiply both sides of the inequality by $x - 1$.
Therefore, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \left( {x - \dfrac{3}{4}} \right)\left( {x - 1} \right) < 0$
Now, using the method of interval over the real line, we get,
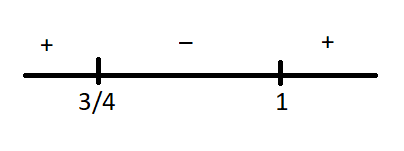
Since, the inequality is less than $0$, so we will take the negative region in the real line.
Therefore, $\dfrac{3}{4} < x < 1$.
We can also write it as, $x \in \left( {\dfrac{3}{4},1} \right) - - - \left( 2 \right)$
Therefore, from $\left( 1 \right)$ and $\left( 2 \right)$, we can say that the most appropriate region where it satisfies the inequality is,
$(\dfrac{3}{4}, 1)$ or $ {1,\infty } \right)$
Note: Here to solve the problem, we have taken the value of modulus function once positive and one negative. But we can also do the same by converting the inequality directly, but taking the positive value and negative value of the number on the right hand side, that is,
$\left( {\dfrac{{2x - 1}}{{x - 1}}} \right) > 2$ and $\left( {\dfrac{{2x - 1}}{{x - 1}}} \right) < - 2$, and then solve accordingly. This will make the calculations much easier.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, the given inequality is,
$\left| {\dfrac{{2x - 1}}{{x - 1}}} \right| > 2$
Now, we will take the positive value for the modulus function and once negative value.
Therefore, first taking the positive value, we get,
$\left( {\dfrac{{2x - 1}}{{x - 1}}} \right) > 2$
Subtracting $2$ from both sides of the inequality, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2x - 1}}{{x - 1}} - 2 > 0$
Now, taking LCM on left hand side, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2x - 1 - 2\left( {x - 1} \right)}}{{x - 1}} > 0$
Now, opening the brackets and simplifying, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2x - 1 - 2x + 2}}{{x - 1}} > 0$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{x - 1}} > 0$
Therefore, here for $\dfrac{1}{{x - 1}}$ to be greater than $0$, $x - 1$ must be greater than $0$.
That is, $x - 1 > 0$
$ \Rightarrow x > 1$
We can write it as, $x \in \left( {1,\infty } \right) - - - \left( 1 \right)$
Now, taking the negative value of the modulus function, we get,
$ - \left( {\dfrac{{2x - 1}}{{x - 1}}} \right) > 2$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{ - 2x + 1}}{{x - 1}}} \right) > 2$
Subtracting $2$ from both sides of the inequality, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{ - 2x + 1}}{{x - 1}}} \right) - 2 > 0$
Now, taking LCM on left hand side, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - 2x + 1 - 2\left( {x - 1} \right)}}{{x - 1}} > 0$
Now, opening the brackets and simplifying, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - 2x + 1 - 2x + 2}}{{x - 1}} > 0$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - 4x + 3}}{{x - 1}} > 0$
Taking $ - 1$ common from the numerator, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - (4x - 3)}}{{x - 1}} > 0$
Now, multiplying both sides with $ - 1$, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{4x - 3}}{{x - 1}} < 0$
[Since, multiplying $ - 1$ over the inequality changes the direction of the inequality]
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{x - \dfrac{3}{4}}}{{x - 1}} < 0$
Since, here $x - 1 \ne 0$.
So, we can multiply both sides of the inequality by $x - 1$.
Therefore, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \left( {x - \dfrac{3}{4}} \right)\left( {x - 1} \right) < 0$
Now, using the method of interval over the real line, we get,

Since, the inequality is less than $0$, so we will take the negative region in the real line.
Therefore, $\dfrac{3}{4} < x < 1$.
We can also write it as, $x \in \left( {\dfrac{3}{4},1} \right) - - - \left( 2 \right)$
Therefore, from $\left( 1 \right)$ and $\left( 2 \right)$, we can say that the most appropriate region where it satisfies the inequality is,
$(\dfrac{3}{4}, 1)$ or $ {1,\infty } \right)$
Note: Here to solve the problem, we have taken the value of modulus function once positive and one negative. But we can also do the same by converting the inequality directly, but taking the positive value and negative value of the number on the right hand side, that is,
$\left( {\dfrac{{2x - 1}}{{x - 1}}} \right) > 2$ and $\left( {\dfrac{{2x - 1}}{{x - 1}}} \right) < - 2$, and then solve accordingly. This will make the calculations much easier.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




